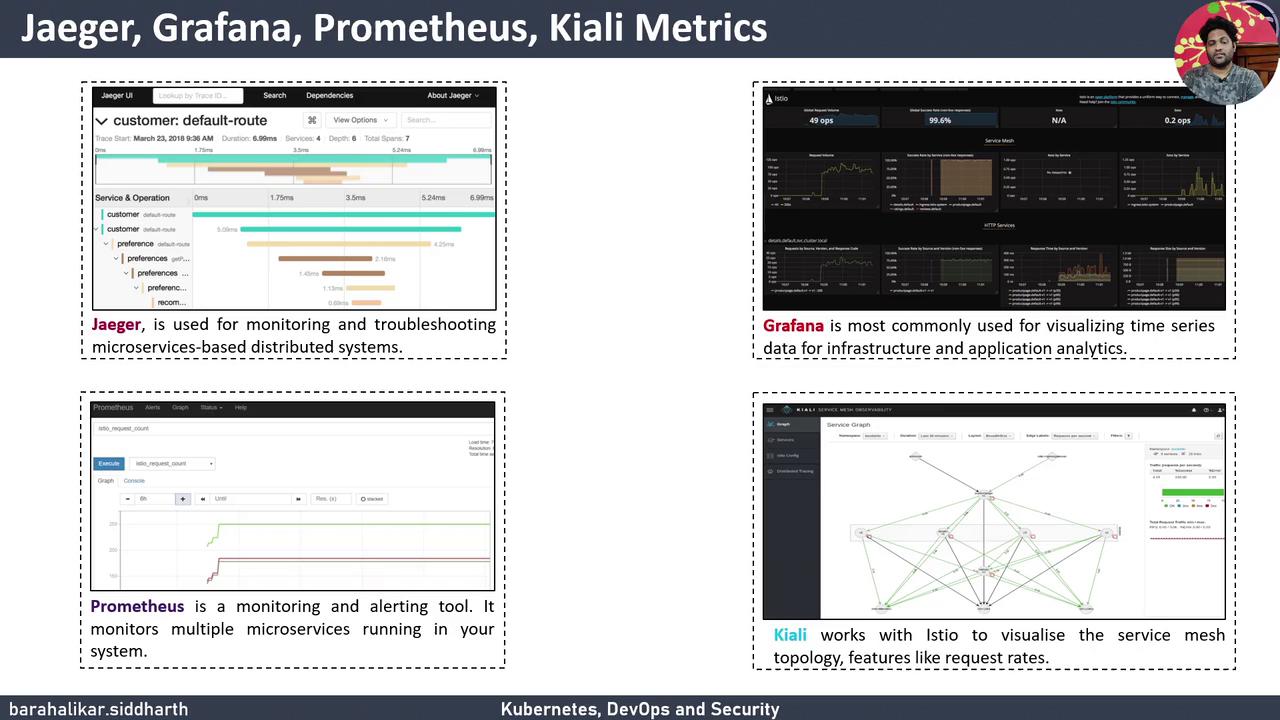
Learn how to download, install, and verify Istio 1.9.0 on a Kubernetes cluster using the demo profile. You’ll also explore built-in add-ons like Kiali, Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger for full observability.
Prerequisites
A running Kubernetes cluster (version compatible with Istio 1.9.0)
kubectl configured to interact with your cluster
Step 1: Download and Install Istio 1.1 Download Istio 1.9.0 Fetch the installer script and extract the release:
curl -Ls https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION = 1.9.0 sh - cd istio-1.9.0 export PATH = $PWD / bin : $PATH
1.2 Install the Demo Profile
The demo profile is preconfigured with observability add-ons for testing and learning. It is not recommended for production environments.
Install Istio’s control plane and sample add-ons:
istioctl install --set profile=demo -y kubectl apply -f samples/addons
1.3 Verify Installation Output After installation, you should see messages similar to:
namespace "istio-system" created configmap "istio-sidecar-injector" created customresourcedefinition "virtualservices.networking.istio.io" configured customresourcedefinition "destinationrules.networking.istio.io" configured deployment "grafana" created deployment "kiali" created service "grafana" created service "kiali" created
Step 2: Istio Components Overview Once installed, Istio deploys core control-plane components and add-ons. Here’s what you get:
Component Purpose Namespace istio-system Isolates the service mesh control plane ConfigMap istio-sidecar-injector Automates Envoy sidecar injection CRDs (VirtualService, DestinationRule) Define traffic management policies Control Plane (istiod, gateways) Manages configuration and proxies Jaeger Distributed tracing Prometheus Metrics collection and alerting Grafana Visualize time-series data Kiali Service mesh observability and topology maps
Step 3: Verify the Control Plane and Add-ons 3.1 List All Istio Resources Run:
kubectl -n istio-system get all
Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/istiod-xxxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m pod/istio-ingressgateway-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m pod/istio-egressgateway-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m pod/prometheus-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/2 Running 0 1m pod/grafana-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m pod/jaeger-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m pod/kiali-xxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 1m NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) service/istiod ClusterIP 10.0.0.123 <none> 15012/TCP,443/TCP service/istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.0.0.124 <pending> 80:31500/TCP,443:31501/TCP service/prometheus ClusterIP 10.0.0.125 <none> 9090/TCP service/grafana ClusterIP 10.0.0.126 <none> 3000/TCP service/jaeger-collector ClusterIP 10.0.0.127 <none> 14250/TCP,14268/TCP service/kiali ClusterIP 10.0.0.128 <none> 20001/TCP
Step 4: Enable Automatic Sidecar Injection Label your application namespace to inject Envoy sidecars automatically:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
Enabling sidecar injection will add an Envoy proxy to every pod in the default namespace. Ensure your workloads are compatible.
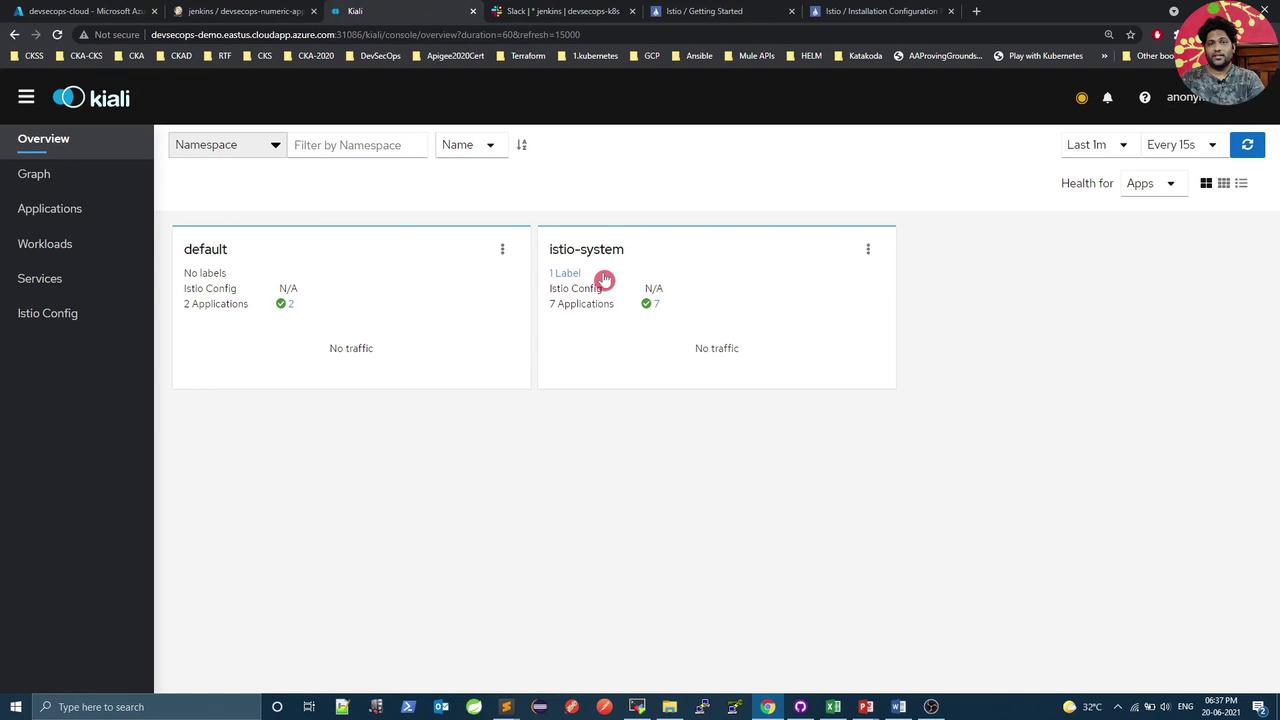
Step 5: Access the Kiali Dashboard By default, Kiali’s service is ClusterIP. To expose it on a NodePort:
5.1 Change Service Type kubectl edit service kiali -n istio-system
In the editor, update:
Save and exit.
5.2 Retrieve and Use the NodePort kubectl get service kiali -n istio-system
Sample output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kiali NodePort 10.0.0.128 <none> 20001:32001/TCP,9090:32002/TCP 2m
Point your browser to:
to open the Kiali UI.
Links and References