In this guide, you’ll learn how to integrate SonarQube static analysis into a Jenkins pipeline for a Spring Boot application. We’ll cover:
Starting SonarQube in Docker
Creating and configuring a SonarQube project
Running analysis locally with Maven
Embedding SonarQube in your Jenkinsfile
Enforcing custom quality gates
Prerequisites
Docker installed and running
Jenkins server with Docker and Pipeline plugins
Maven project for your Spring Boot application
Ensure your SonarQube Docker container always listens on port 9000 after VM restarts.
1. Start and Verify SonarQube Container Run SonarQube in Docker:
docker run -d --name sonarqube -p 9000:9000 sonarqube:latest
Confirm the container is up:
docker ps -a | grep -i sonar # Expected: # 5b47910fdc73 sonarqube:latest "bin/run.sh bin/sona…" Up 13 minutes 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp sonarqube
2. Log In and Create a New Project Open your browser at http://<VM_IP>:9000. Log in with the default admin credentials:
Username: adminPassword: admin
Change the default password immediately to secure your SonarQube instance.
Once logged in, click Create new project :
Fill in the Project key and Display name (e.g., numeric-application), then generate a token (e.g., Jenkins Pipeline):
3. Run Local Analysis with Maven Select Maven as your build tool. Copy and customize the displayed command:
mvn sonar:sonar \ -Dsonar.projectKey=numeric-application \ -Dsonar.host.url=http://devsecops-demo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com:9000 \ -Dsonar.login=YOUR_SONAR_TOKEN
You can run this locally to verify successful analysis before Jenkins integration.
4. Integrate SonarQube into Jenkins Pipeline Add a SonarQube stage in your Jenkinsfile after unit and mutation test stages.
Stage Purpose Unit Tests Execute JUnit tests and collect coverage Mutation Tests Run PIT mutation testing SonarQube – SAST Perform static code analysis with SonarQube Docker Build and Push Build Docker image and push to registry
pipeline { agent any environment { SONAR_TOKEN = credentials( 'sonar-token' ) } stages { stage( 'Unit Tests - JUnit and JaCoCo' ) { steps { sh 'mvn test' } post { always { junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml' jacoco execPattern : 'target/jacoco.exec' } } } stage( 'Mutation Tests - PIT' ) { steps { sh 'mvn org.pitest:pitest-maven:mutationCoverage' } post { always { pitmutation mutationStatsFile : '**/target/pit-reports/**/mutations.xml' } } } stage( 'SonarQube - SAST' ) { steps { sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true' archiveArtifacts artifacts : 'target/*.jar' , fingerprint : true sh """ mvn sonar:sonar \ -Dsonar.projectKey=numeric-application \ -Dsonar.host.url=http://devsecops-demo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com:9000 \ -Dsonar.login= ${ SONAR_TOKEN } """ } } stage( 'Docker Build and Push' ) { steps { withDockerRegistry([ credentialsId : 'docker-hub' , url : '' ]) { sh 'docker build -t siddharth67/numeric-app:${GIT_COMMIT} .' sh 'docker push siddharth67/numeric-app:${GIT_COMMIT}' } } } // Add deployment stages below } }
Commit and push your Jenkinsfile. Jenkins will trigger a build and execute the new SonarQube stage:
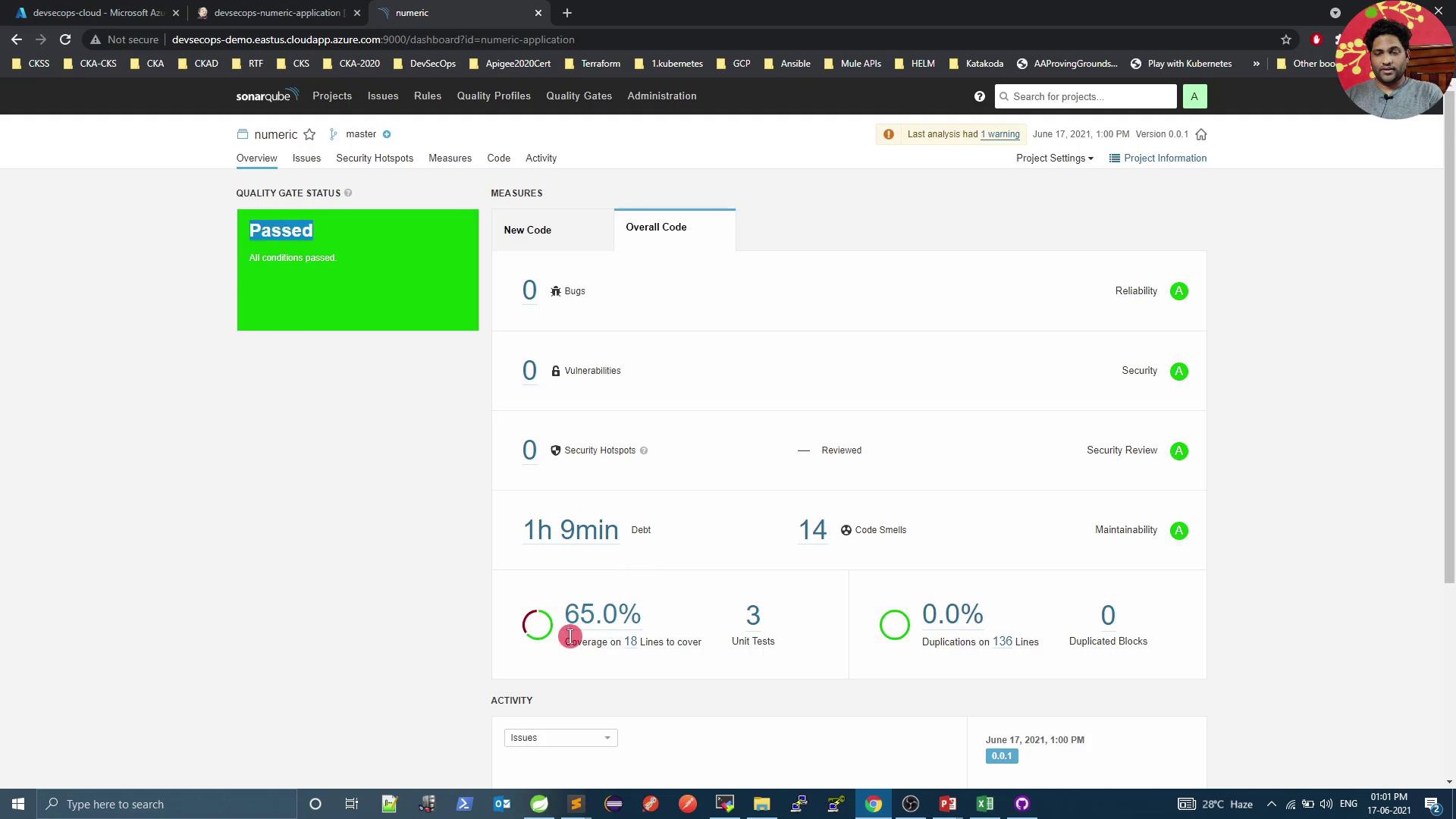
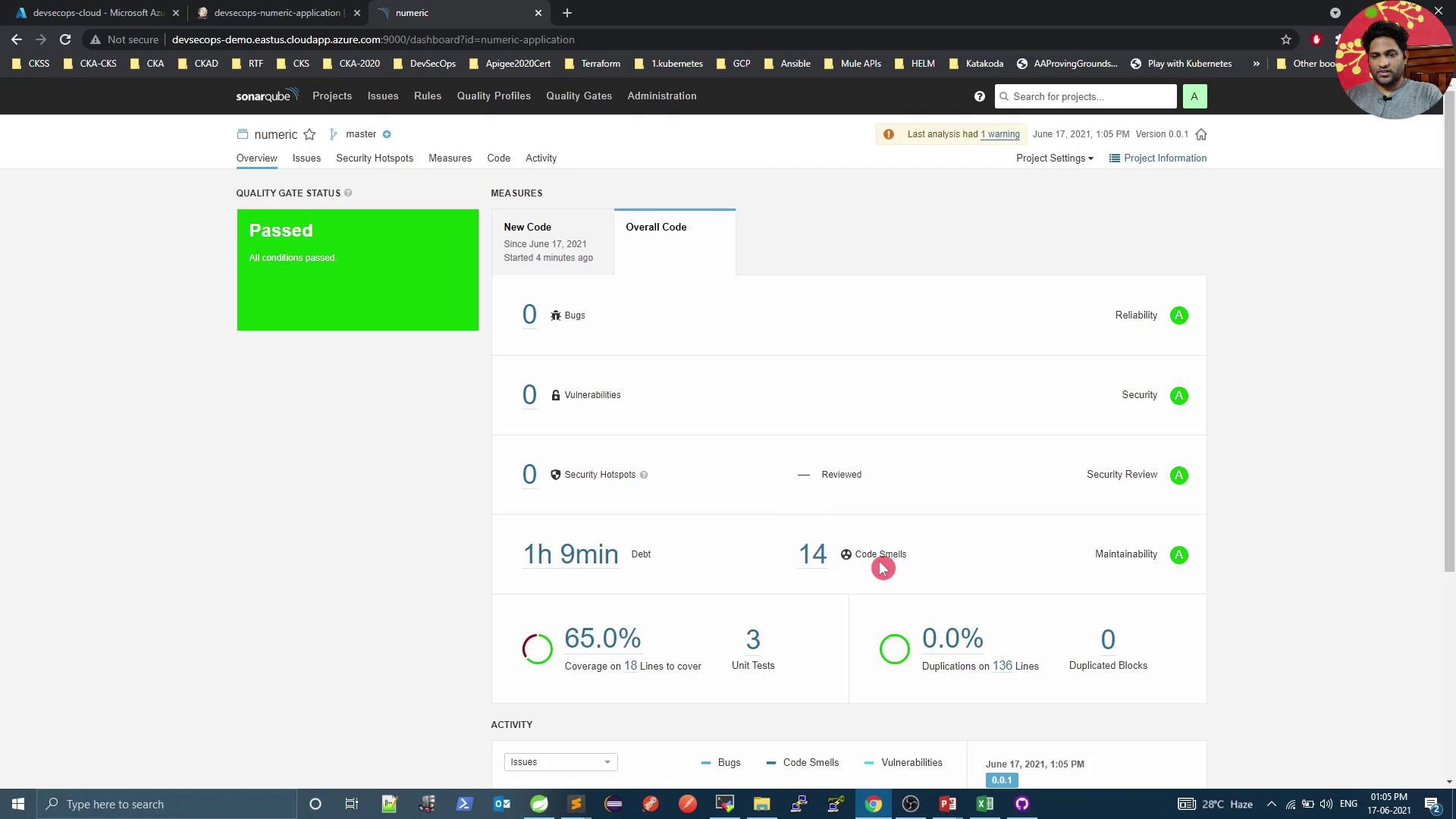
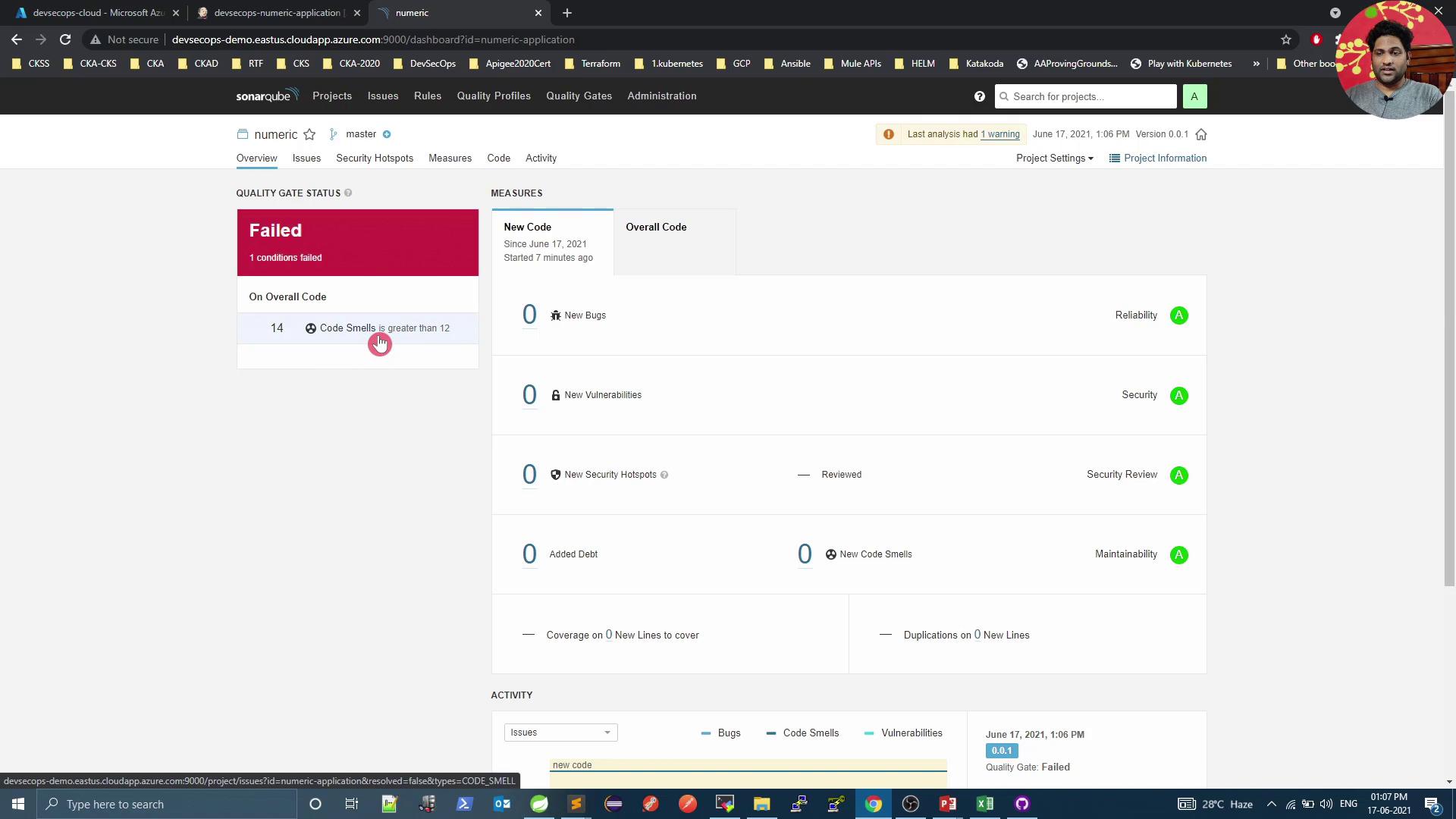
5. Review Analysis Results in SonarQube After pipeline completion, go back to SonarQube to inspect metrics and quality gate status:
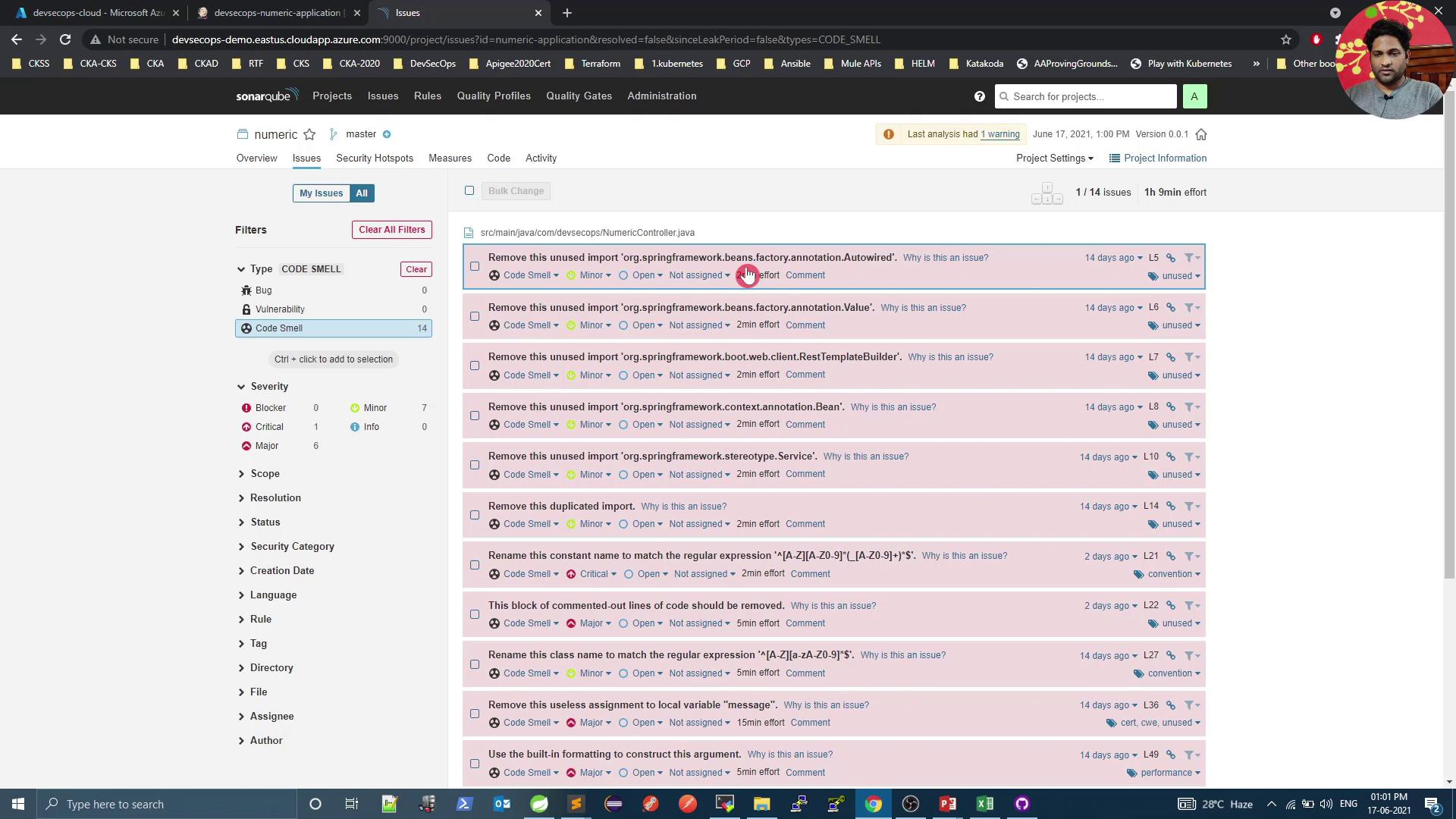
Click Code Smells to explore issues such as unused imports:
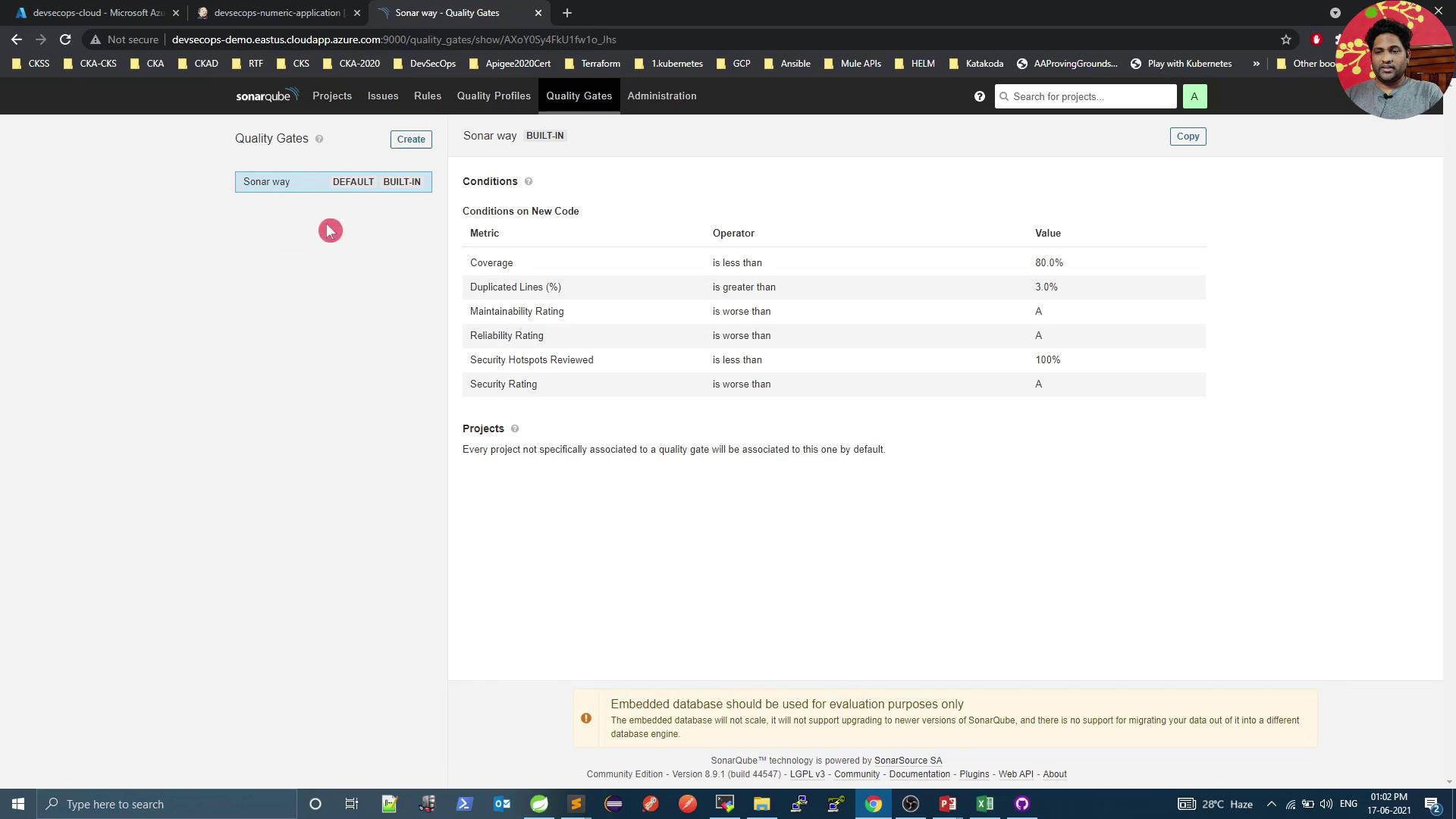
6. Enforce Custom Quality Gates Navigate to Quality Gates to define or modify pass/fail criteria:
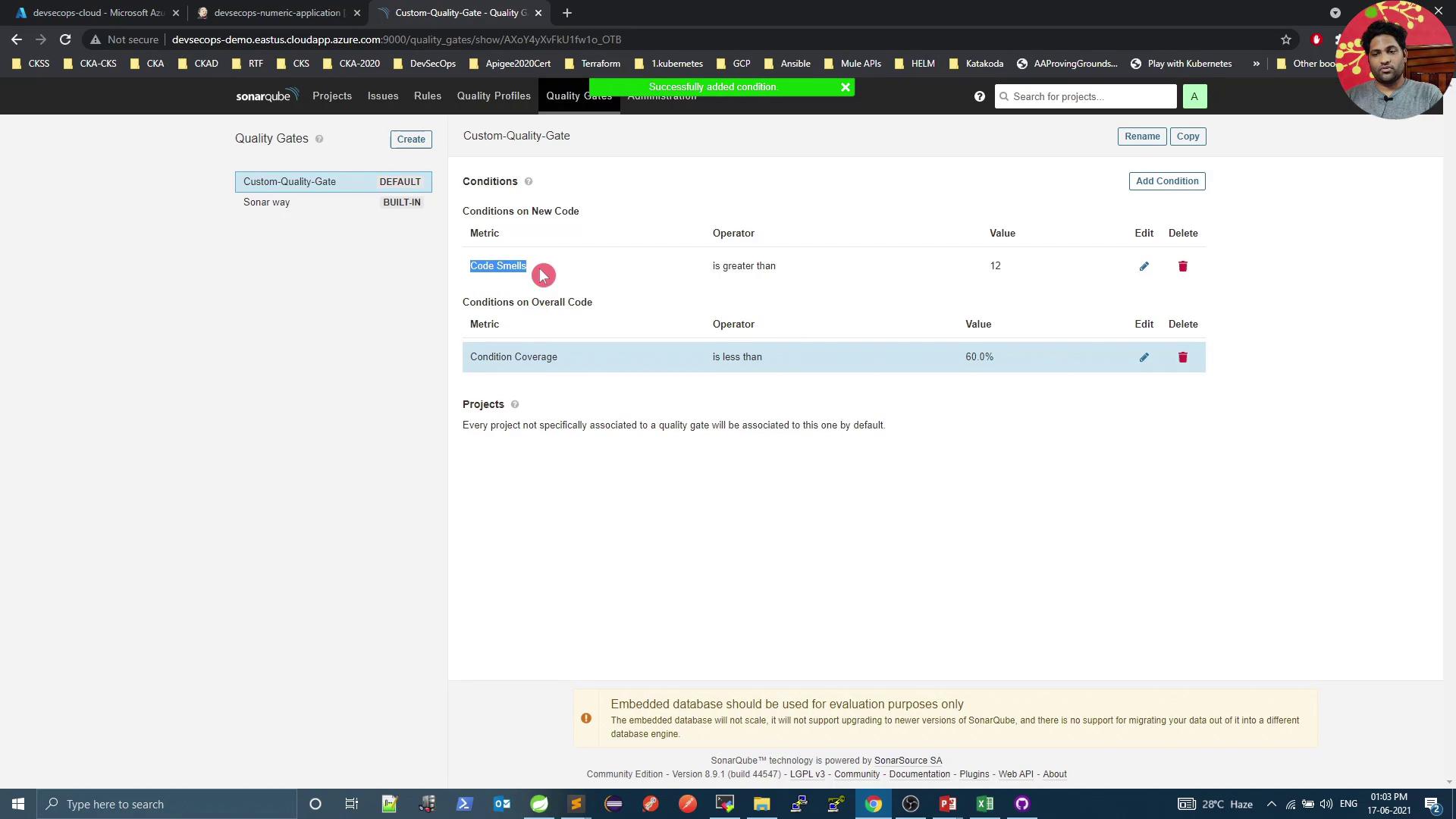
Create a new gate (e.g., Custom Quality Gate ), set it as default, and add conditions:
Overall code smells ≤ 12Overall coverage ≥ 60%
Rerun the pipeline. Initially, you may still see Passed —the first condition applies to new code only:
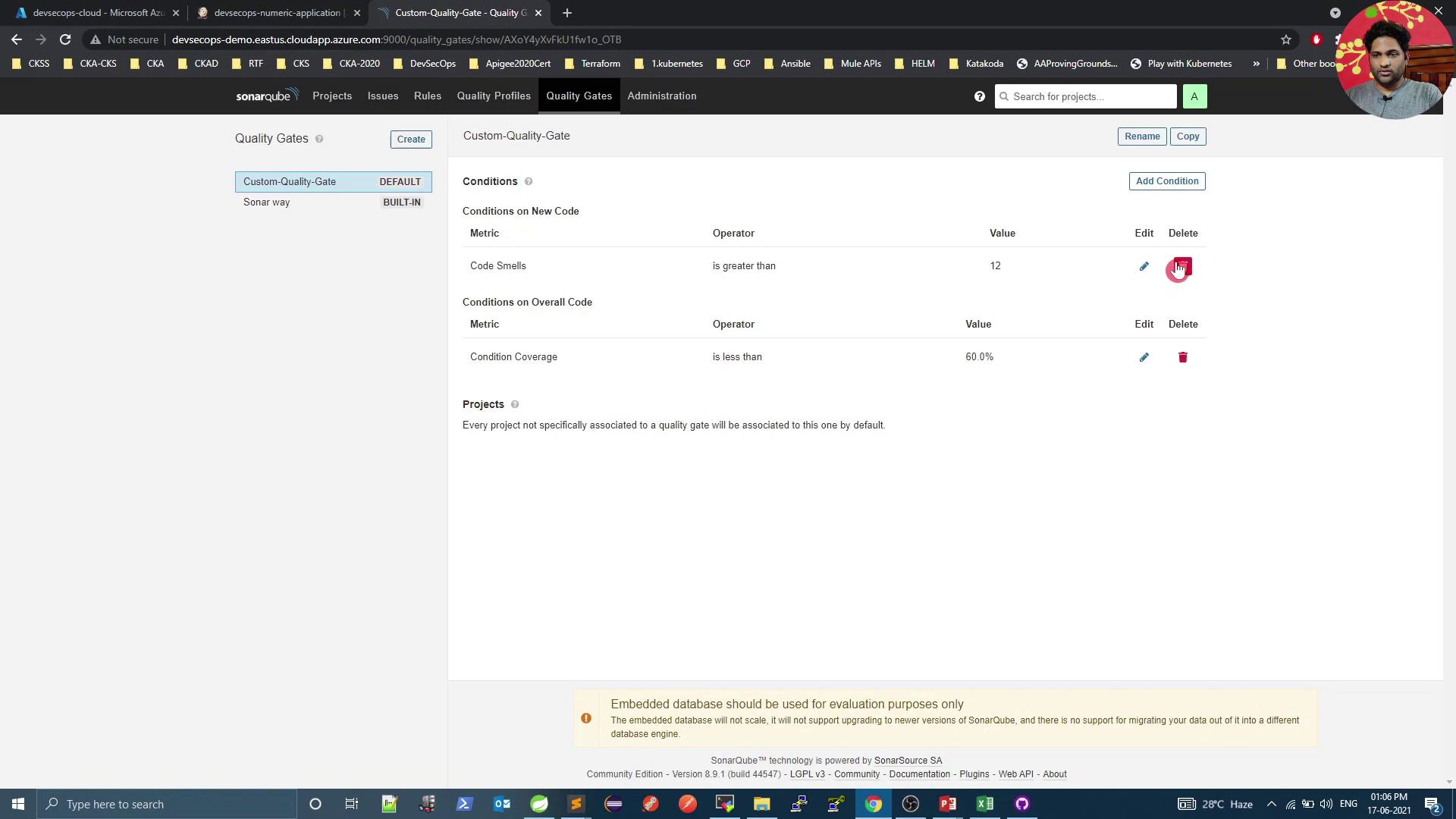
Adjust the code-smells condition to Overall code smells > 12 :
Run the pipeline again. Once SonarQube processes the report, the gate will Fail due to excessive code smells:
References