podTemplate. We’ll compare a Declarative Pipeline on a static agent versus a Scripted Pipeline on a dynamic K8s agent, then walk through defining pod templates and share a full example.
- Jenkins server with the Kubernetes Plugin installed
- Access to a Kubernetes cluster and a configured Kubernetes cloud in Jenkins
- Credentials for any external services (e.g., MongoDB, Gitea) stored in Jenkins
Declarative Pipeline Example
Here’s a standard Declarative Pipeline bound to a static Jenkins agent:agent block:
Scripted Pipeline with podTemplate
For Scripted Pipelines, thepodTemplate step defines how Jenkins spins up Pods. You have two main options:
- Define Pod Templates in the Jenkins UI
- Generate with the Snippet Generator
1. Defining Pod Templates in the Jenkins UI
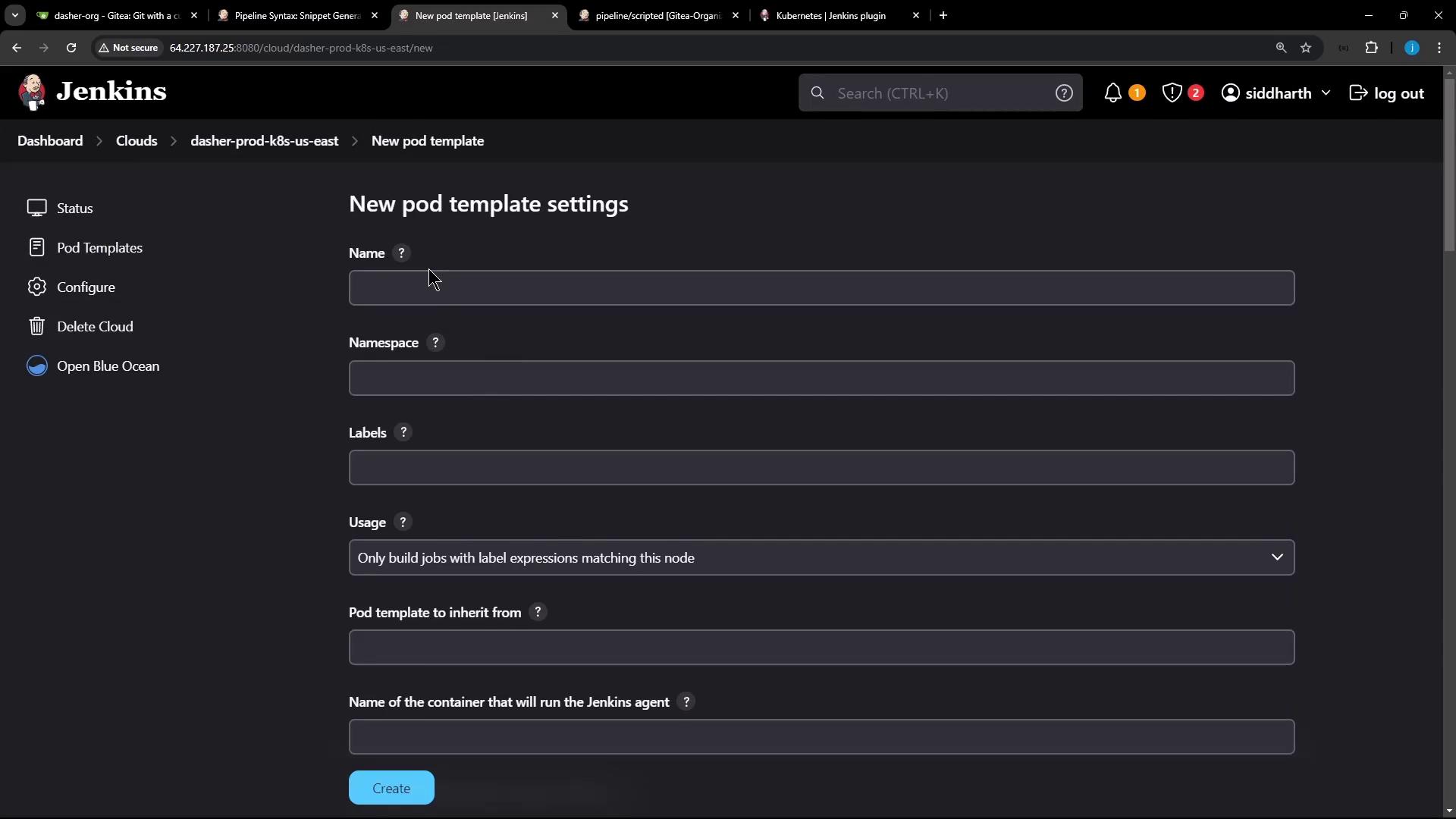
Navigate to Manage Jenkins → Configure Clouds → dasher-prod-k8s-us-east and click Add Pod Template. Configure Name, Namespace, Labels, Usage, then add container templates:
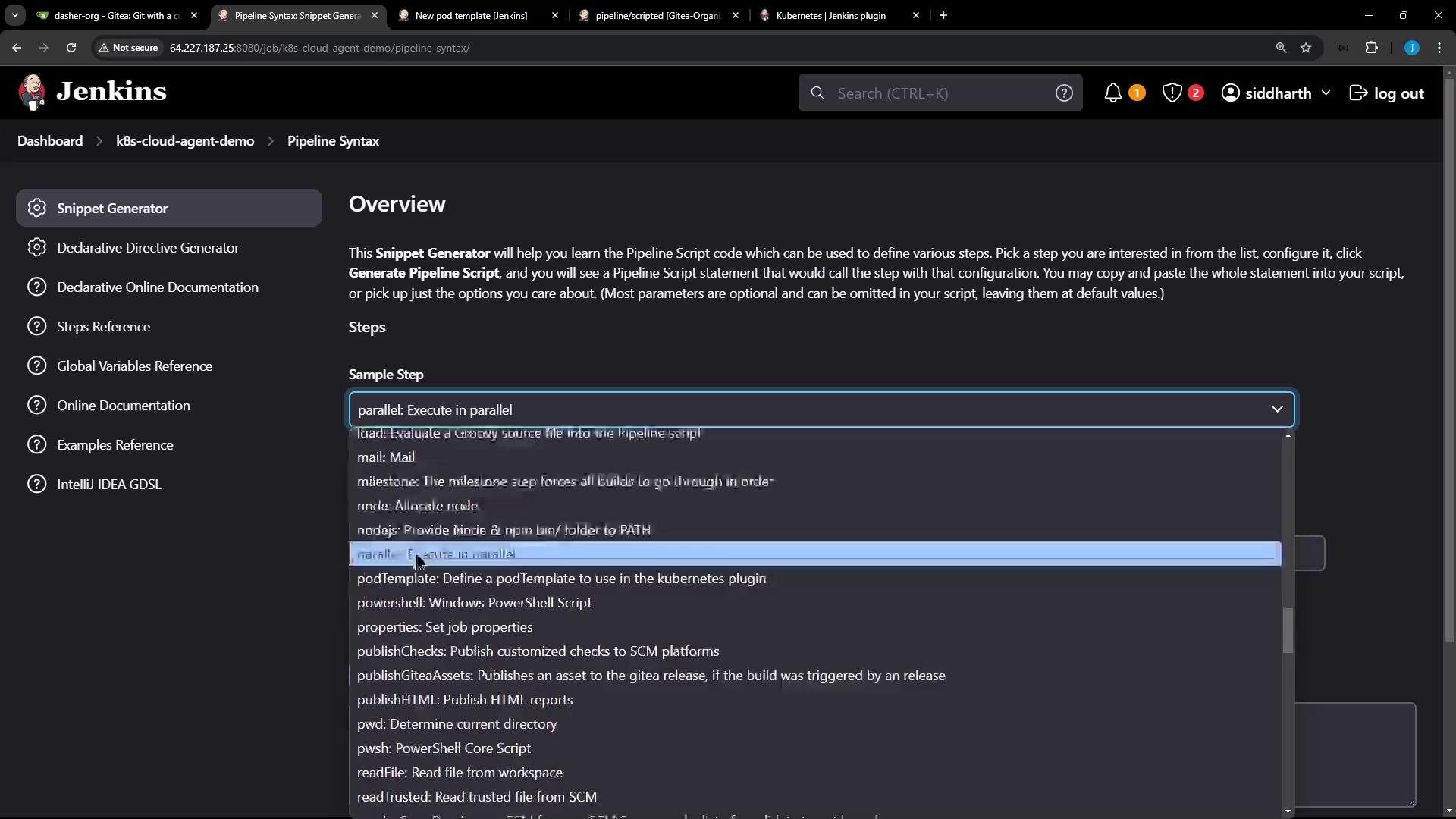
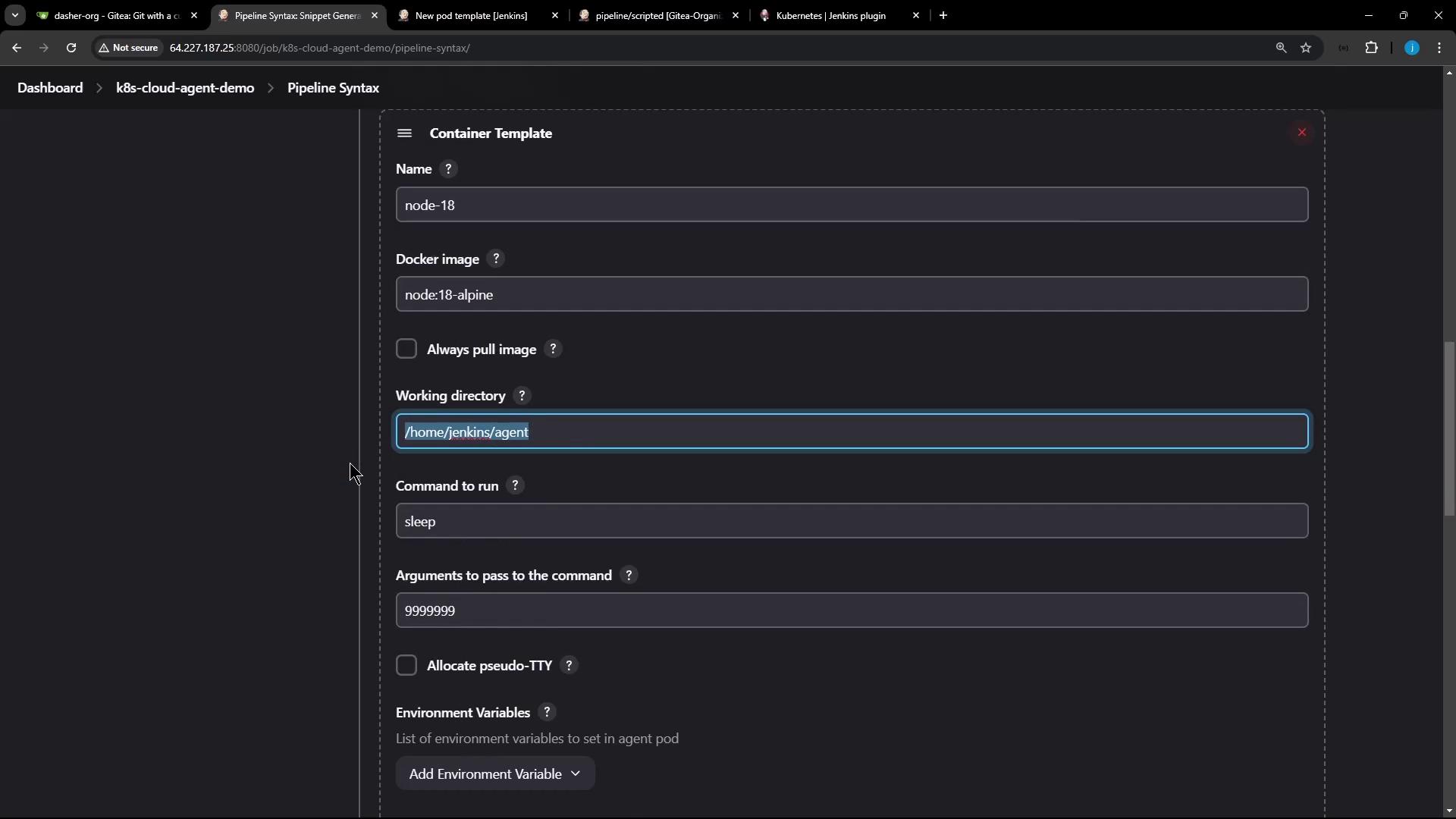
2. Using the Snippet Generator
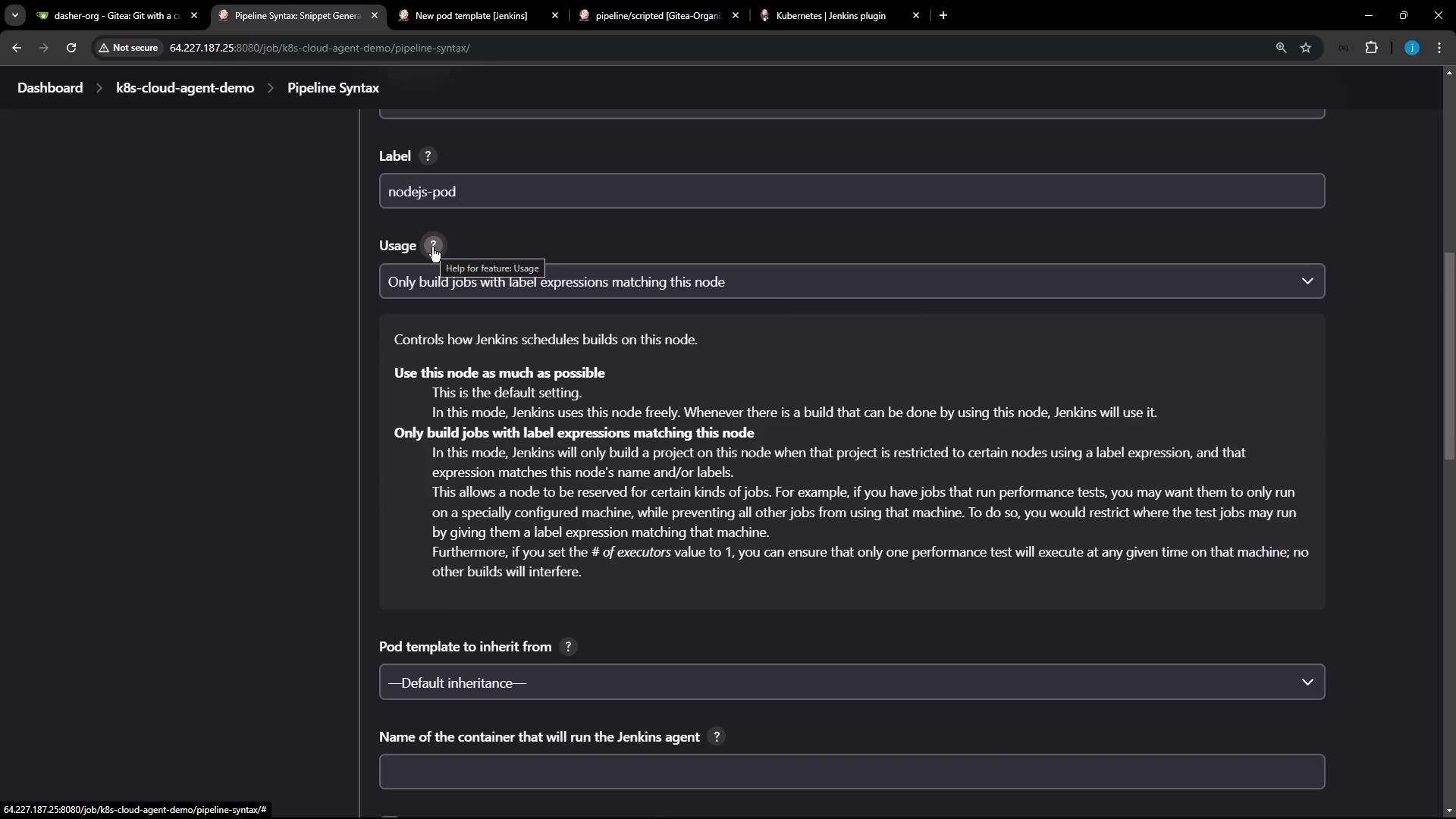
Open Pipeline Syntax → Snippet Generator, choose podTemplate, then select your cloud and a unique label (e.g.,nodejs-pod). Click Add Container Template:
Full Scripted Jenkinsfile Example
Below is a consolidated Scripted Pipeline that uses:- A static node for checkout and dependency install
- A Kubernetes pod for isolated unit testing
- stash/unstash for sharing artifacts
node-18 container:
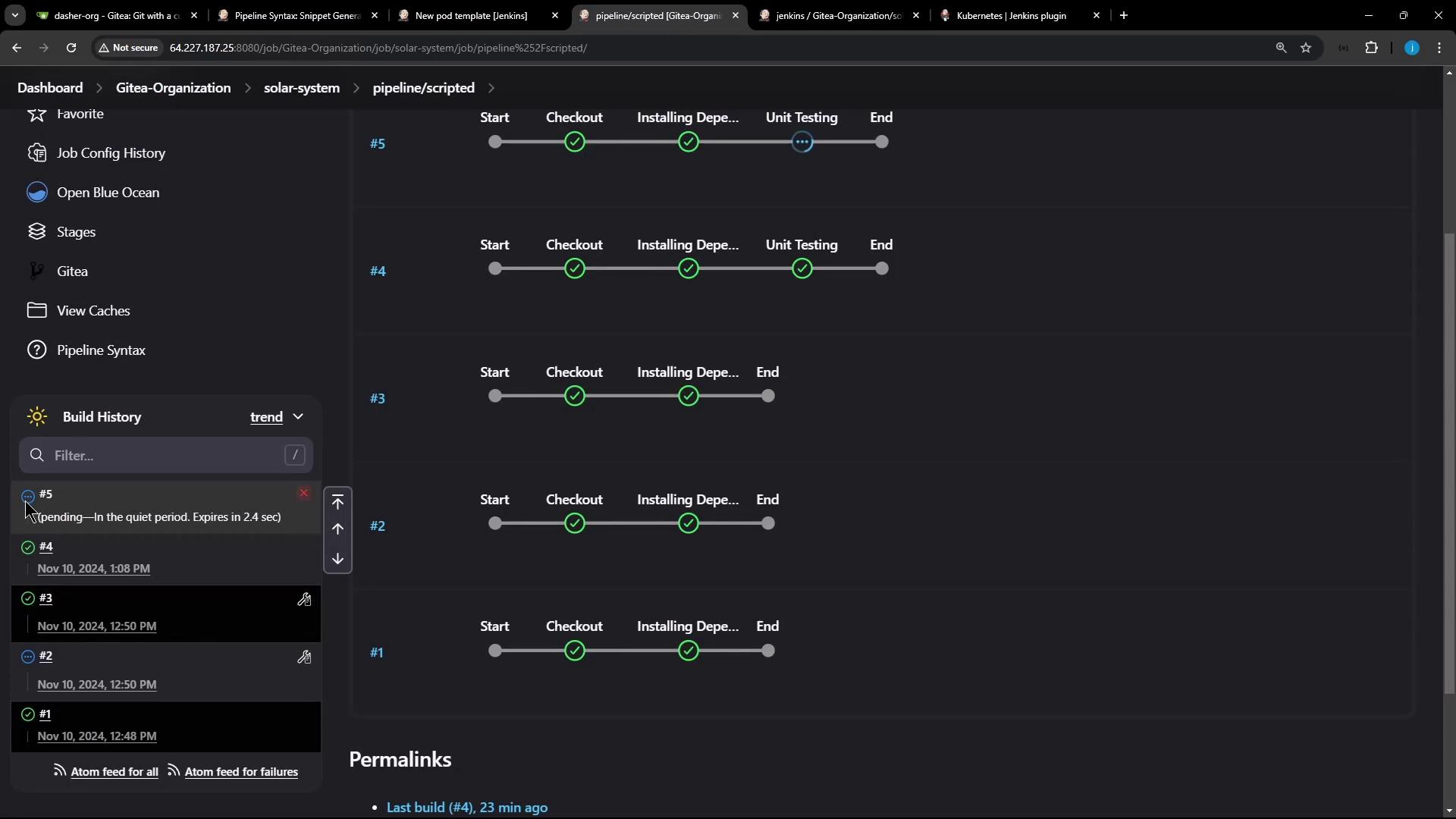
Pipeline Stage Summary
| Stage | Agent | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Checkout | ubuntu-docker-jdk17-node20 | SCM checkout |
| Installing Dependencies | ubuntu-docker-jdk17-node20 | npm install, stash node_modules |
| Unit Testing | nodejs-pod (container node-18) | Unstash modules, run tests with credentials |
podTemplate, node, container, and stash/unstash to coordinate across stages.