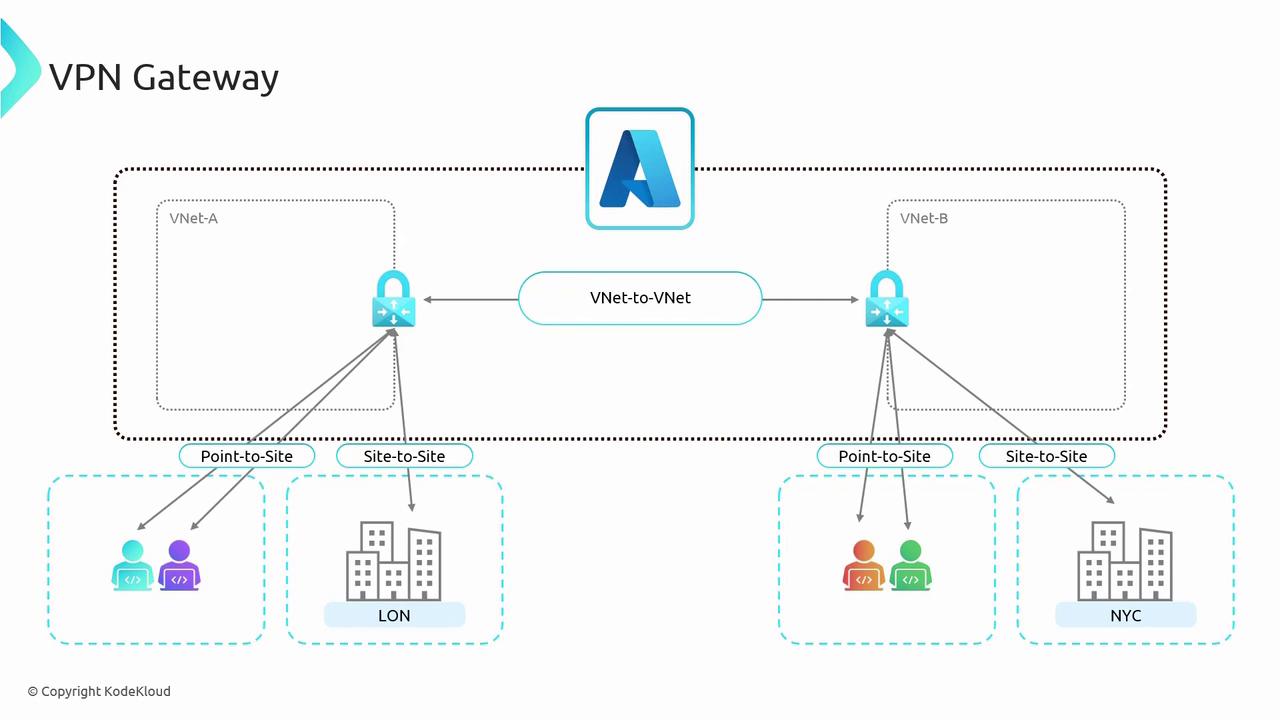
Understanding VPN Gateway concepts is crucial, as they serve as the foundation for Gateway Transit—a concept that is particularly relevant for exam scenarios.
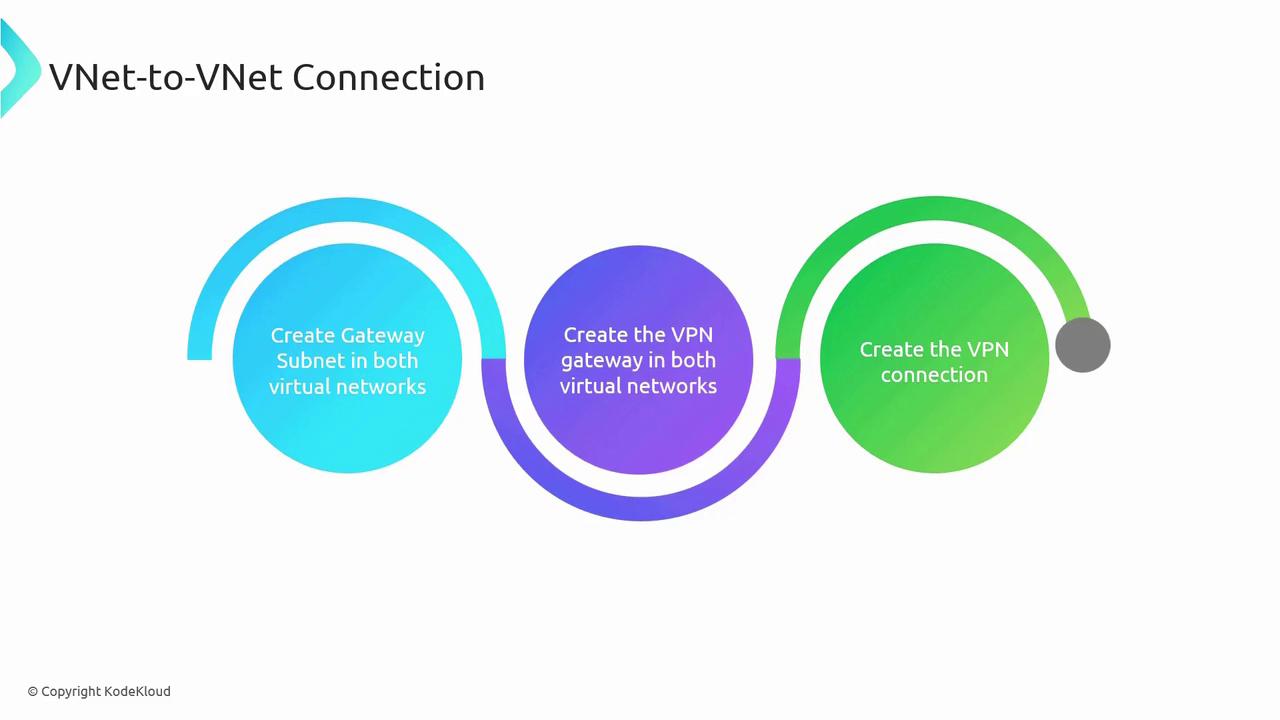
- Create a gateway subnet in each VNet.
- Deploy a VPN Gateway in each virtual network.
- Establish the VNet-to-VNet connection between the two gateways.
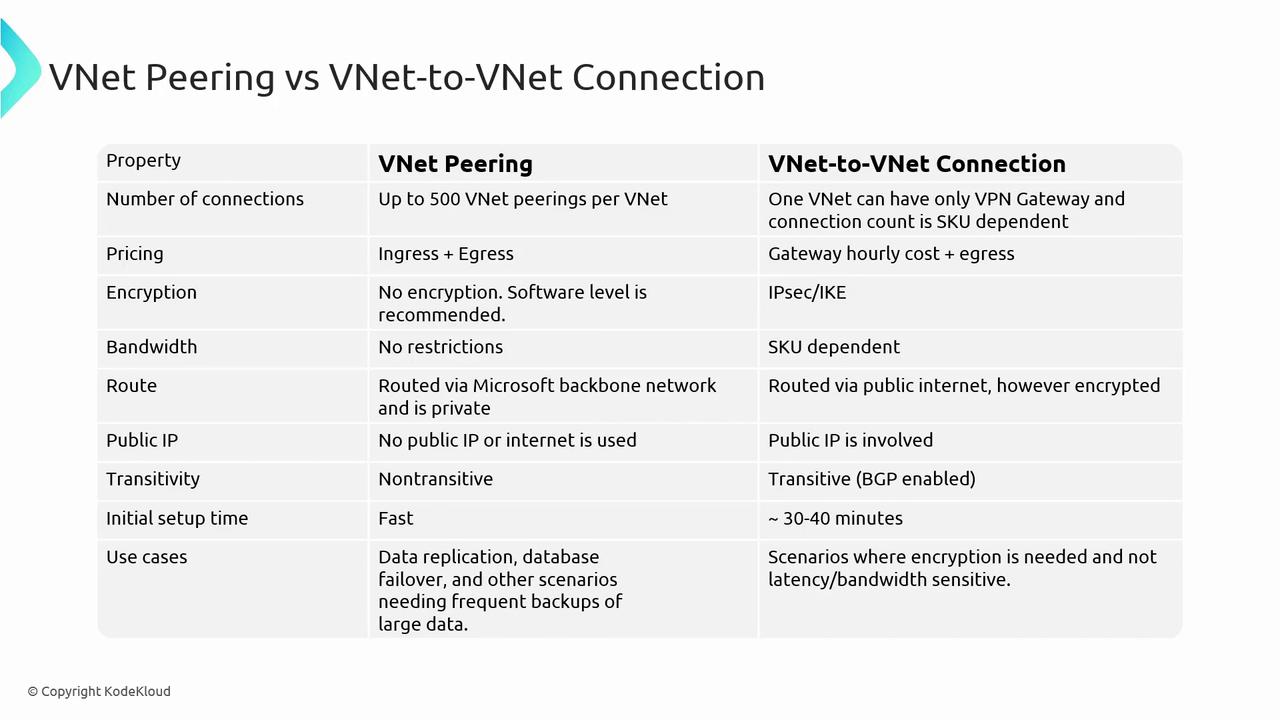
Comparison Between VNet Peering and VNet-to-VNet Connections
| Feature | VNet Peering | VNet-to-VNet Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Connections | Supports up to 500 peerings per VNet. For example, VNet A can peer with VNets B, C, D, etc. | Supports a single VPN Gateway per VNet, but a gateway can handle multiple connections as determined by the SKU (up to 300 in some cases). |
| Pricing | Only data ingress and egress charges apply; you pay solely for data transfers. | In addition to data egress charges, there is an hourly cost for the gateway, regardless of active usage. |
| Encryption | Lacks built-in encryption; however, software-level encryption can be implemented. | Offers built-in encryption using IPsec or Internet Key Exchange (IKE), making it ideal for scenarios where encryption is mandatory. |
| Bandwidth | Utilizes Microsoft’s backbone network without bandwidth restrictions; suitable for high data transfers with low latency. | Bandwidth is determined by the chosen SKU, with higher-end SKUs offering up to 10 Gbps. |
| Routing | Traffic is routed through Microsoft’s backbone network, ensuring fast and private connectivity. | Uses the public internet via an encrypted VPN tunnel, which may affect performance depending on the SKU and network conditions. |
| Public IP Requirement | Does not require public IP addresses as traffic remains within the Microsoft backbone. | Requires a public IP for the deployment of the virtual network gateway. |
| Transitivity | Non-transitive; for example, if VNet A peers with VNet B and VNet B peers with VNet C, connectivity between VNet A and VNet C is not automatic. | Can be configured as transitive with Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) enabled, allowing routes from other networks to be published and used for communication. |
| Initial Setup Time | Can be configured rapidly. | Takes between 30 to 40 minutes per VPN gateway. With two gateways, expect an overall deployment time of around 45 to 50 minutes. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for data replication, failover, and large-scale backups due to its high-speed, low-latency connectivity. | Preferred in environments where encryption is critical, despite reliance on the public internet and SKU-dependent performance. |