Autoscaling with the Terminal Command
To quickly autoscale a deployment from the terminal, use theoc autoscale command. This command requires you to specify the deployment name along with the minimum and maximum number of replicas.
For instance, to autoscale the “image-registry” deployment, execute:
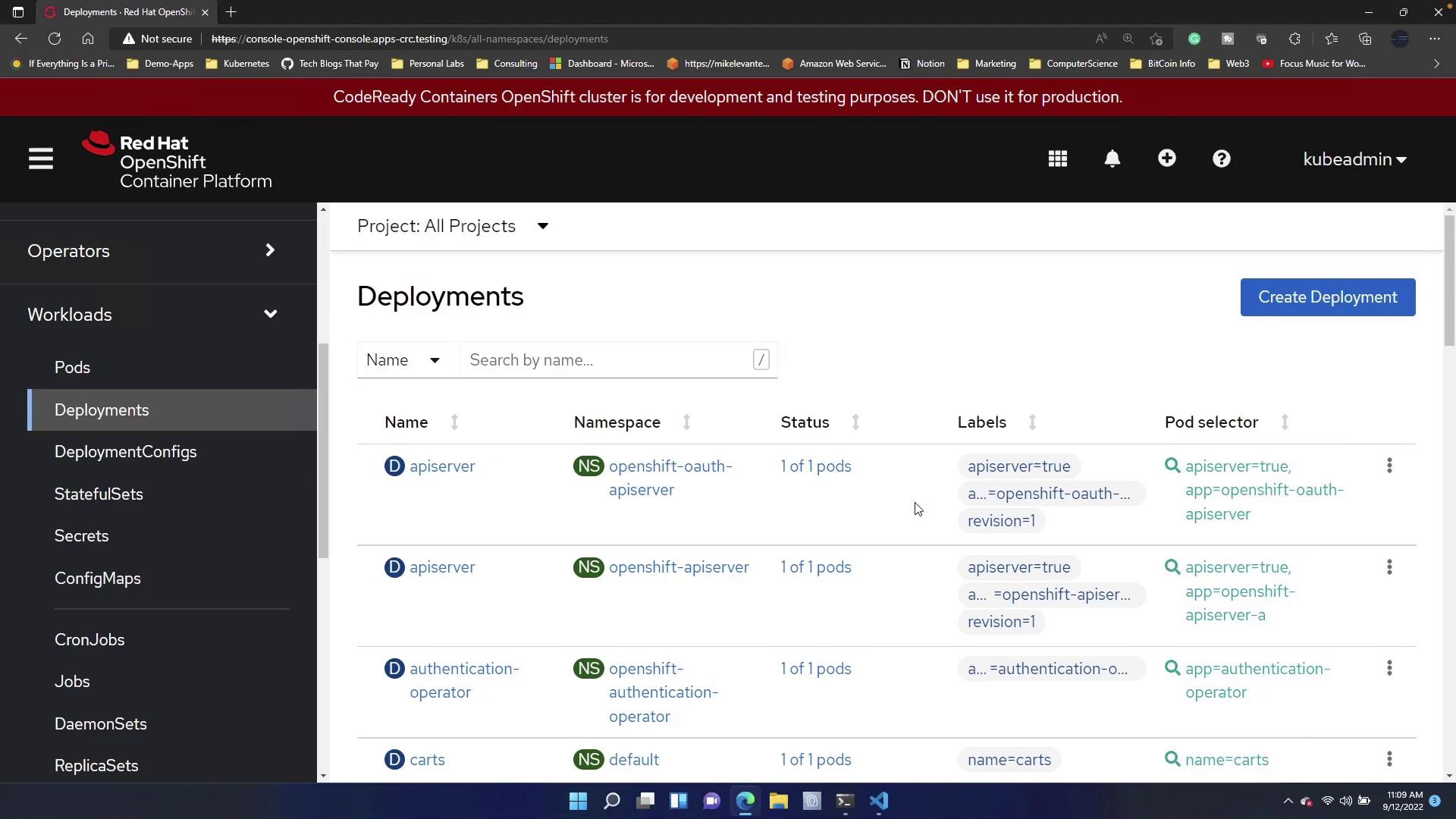
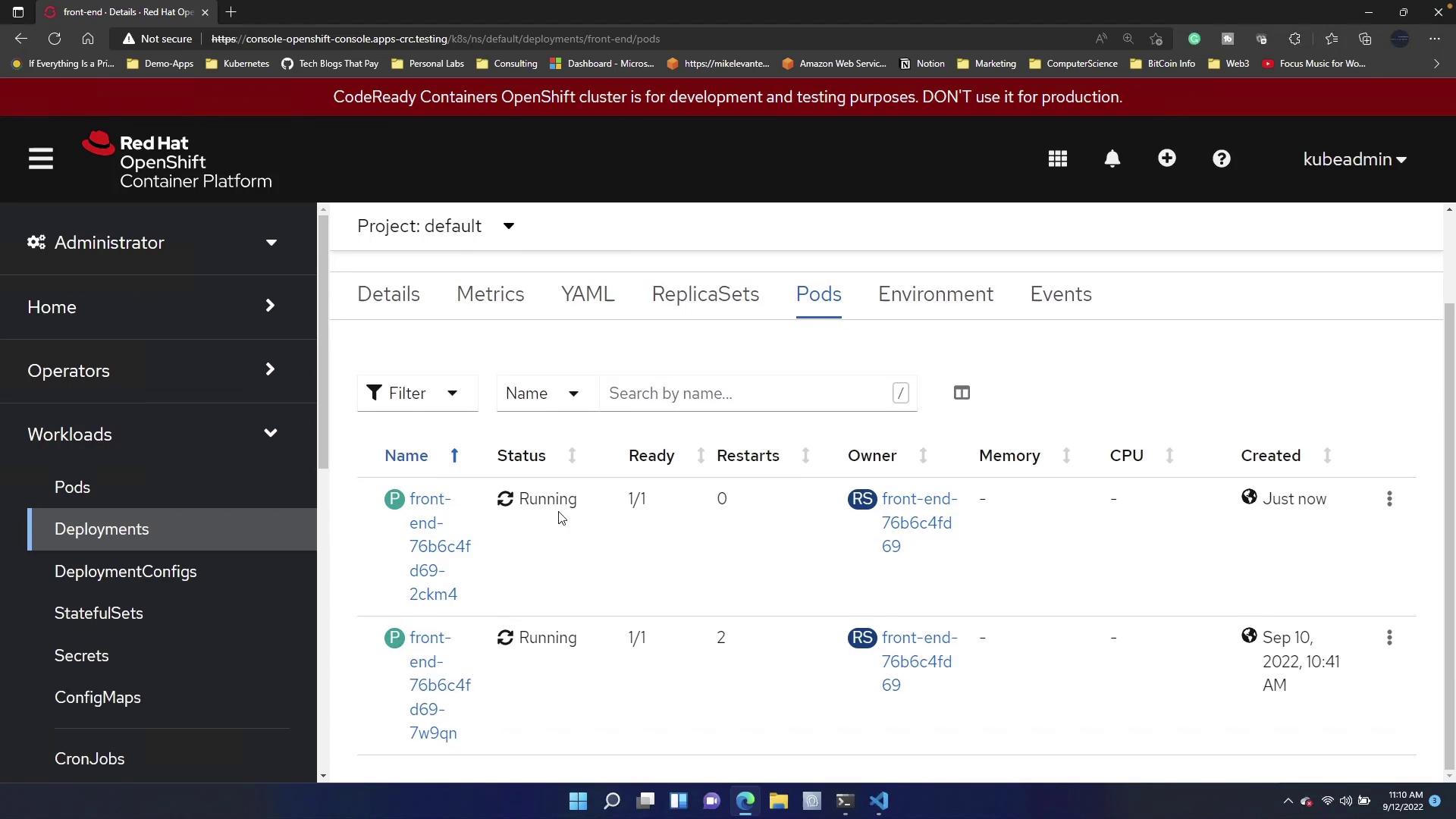
Autoscaling via the terminal command offers a quick and effective way to adjust resources in response to varying traffic loads.
Configuring a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler with a YAML Manifest
Defining autoscaling via a YAML manifest provides a declarative approach to managing deployment resources. Start by navigating to the Deployments section in the OpenShift console, click on Create New Deployment, and clear the pre-filled template. Then, insert the following manifest for the “image-registry” deployment:Manifest Breakdown
- apiVersion and kind: Define the resource as a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
- metadata: Specifies the HPA name (“front-end”) and the namespace (“default”).
- spec: Configures the autoscaling behavior:
minReplicas: 3andmaxReplicas: 7determine the scaling boundaries.scaleTargetRefidentifies the target deployment.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 75sets the CPU usage threshold for scaling.
- status: Reflects the current state managed by the system (e.g.,
currentReplicas: 5).
If an HPA is already configured for the deployment, attempting to create a new one may fail. Remove the existing autoscaler before applying the new manifest.
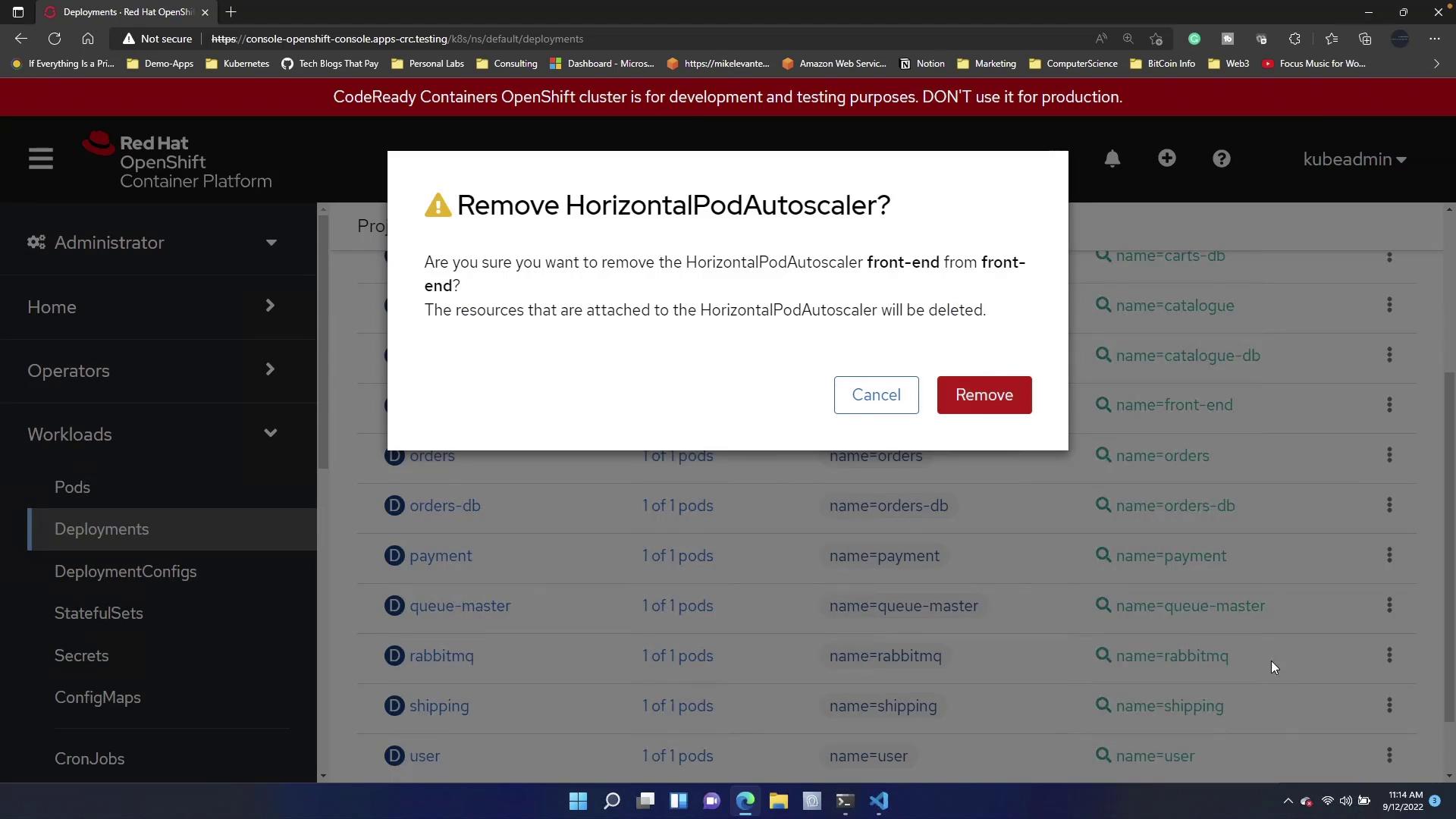
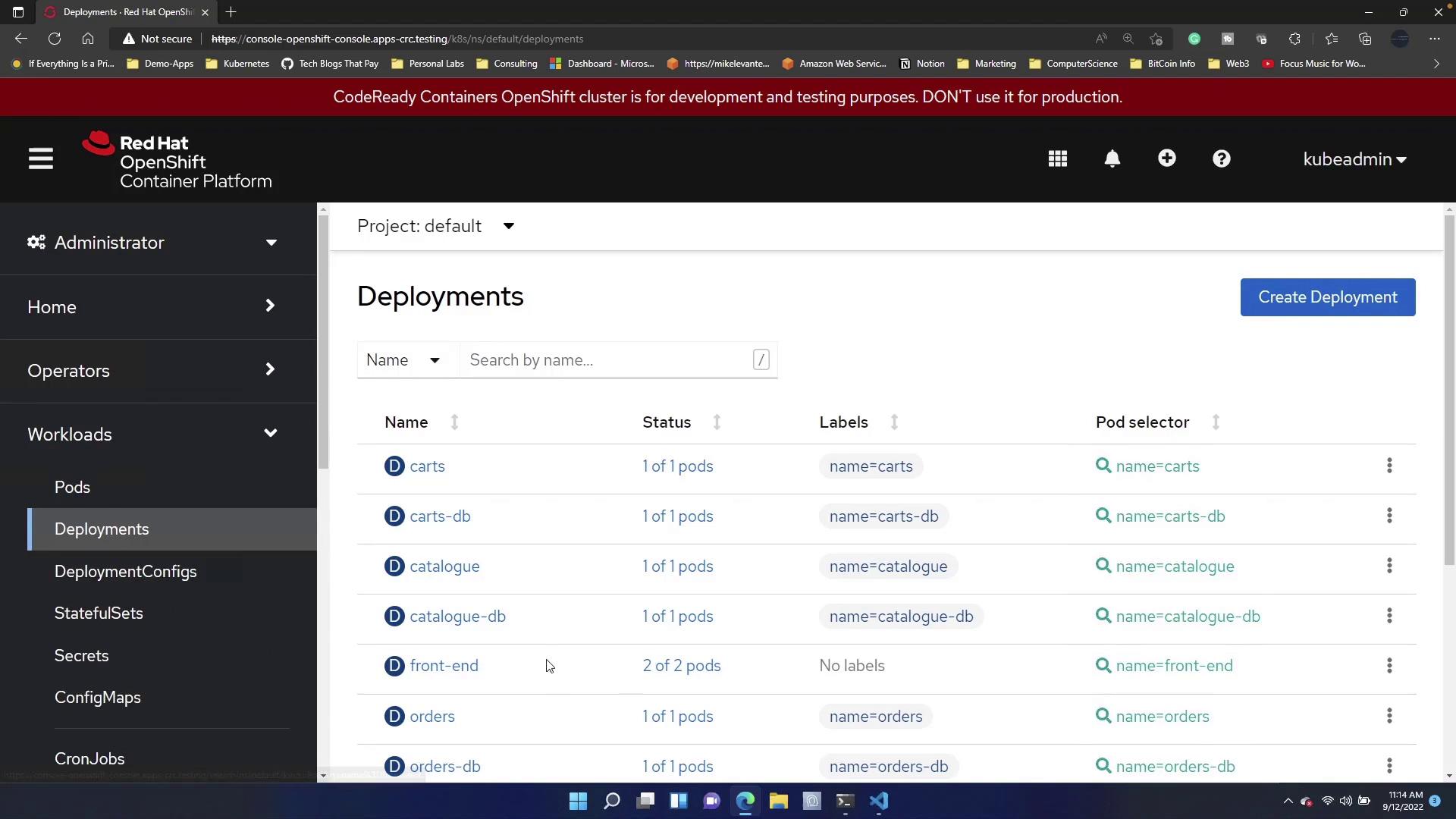
This guide demonstrated how to implement autoscaling in OpenShift using both terminal commands and a YAML-based Horizontal Pod Autoscaler. By employing these techniques, your deployments can automatically adjust to changing workloads, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization. For further information, consider visiting the OpenShift Documentation and expanding your knowledge on container orchestration and autoscaling best practices.