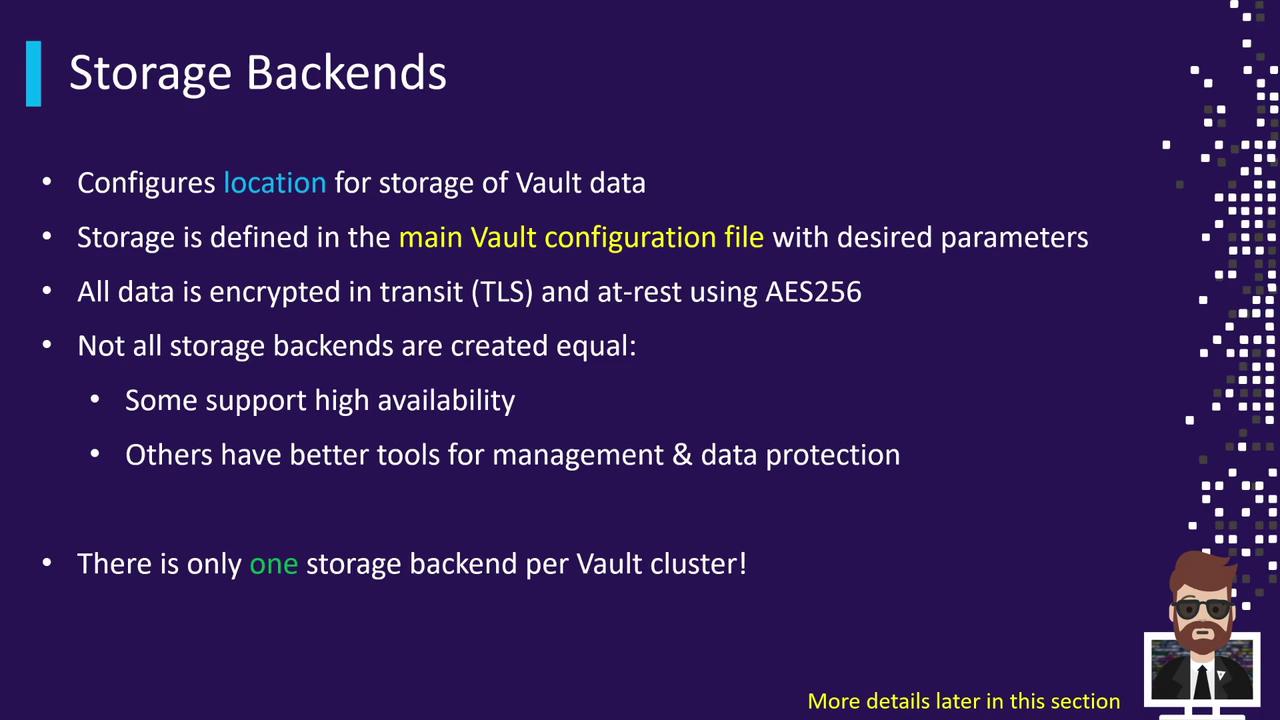
Storage Backends
Vault stores all its data—keys, secrets, configuration—in a single, pluggable Storage Backend. This includes:- Encryption in Transit: TLS secures data as it moves.
- Encryption at Rest: AES-256 encrypts data on disk.
A Vault cluster can be configured with exactly one storage backend. For high availability or geo-replication, run multiple clusters with distinct backends.
| Backend | High Availability | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Consul | Yes | Native snapshots, leader election |
| DynamoDB | Yes | Point-in-time recovery, horizontal scale |
| File / S3 | Depends | Simple setup, manual backup required |
vault.hcl under the storage stanza. Each backend type has its own set of configuration parameters.
Secrets Engines
Secrets Engines are responsible for managing or generating secrets. You mount them at specific paths and interact via API, CLI, or integrations.| Engine Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| KV (Key/Value) | Store and retrieve static secrets |
| Database | Generate dynamic database credentials |
| AWS / GCP | Provision cloud IAM credentials dynamically |
| Transit | Perform cryptographic operations (encrypt/decrypt) |
Secrets Engines are isolated by mount path. You can enable multiple instances of the same engine under different paths for segmentation.

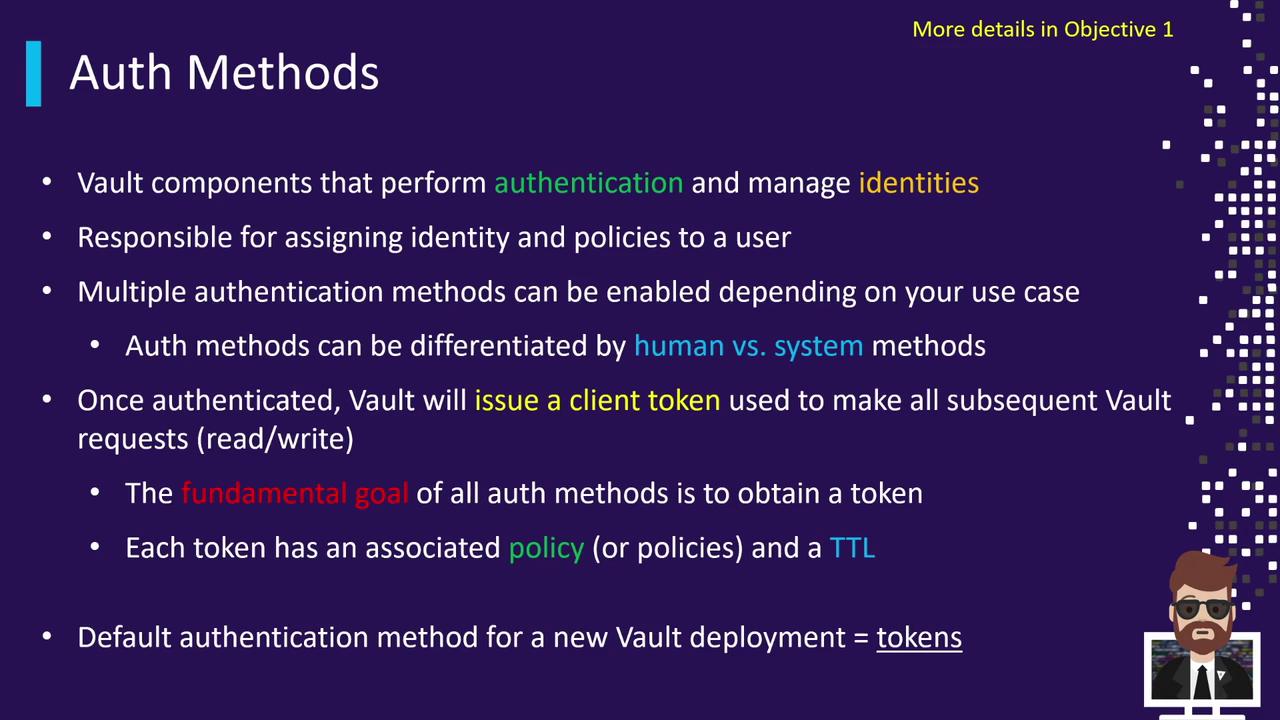
Auth Methods
Auth Methods connect external identity systems to Vault, authenticate clients, and issue tokens scoped by policies.| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Human-centric | LDAP, OIDC, Username/Password |
| Machine-centric | AppRole, Kubernetes, TLS Certs |
The root token from initialization should be used sparingly. Rotate or revoke it after enabling safer auth methods.
Audit Devices
Audit Devices capture every Vault request and response in JSON format. They ensure full accountability and tamper-proof logging by hashing sensitive fields.- Mandatory Logging: Requests only succeed once written to at least one audit device.
- Multiple Devices: Enable file, syslog, socket, or other endpoints simultaneously.
- JSON Output: Simplifies integration with SIEM and log analysis tools.
If an audit device becomes unavailable (disk full, network failure), Vault will block operations to maintain audit integrity.
