In this tutorial, you’ll use Packer to bake a custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI) with Vault 1.7.1 pre-installed. We’ll walk through cloning the repo, configuring the Packer template, downloading Vault, building the AMI, and launching an EC2 instance.
This repository (github.com/bryankrausen/hashicorp) contains all my HashiCorp training content—Terraform, Vault, Packer, and more—plus discount links and coupons.
Repository Structure Navigate to the vault/packer directory. You’ll find:
‐ vault.pkr.hcl : Packer HCL2 templatefiles/ : Vault configuration examples
Inside files/:
Filename Description vault.hclVault server configuration vault.servicesystemd unit file for Vault vault_int_storage.hclExample using integrated storage
1. Download Vault 1.7.1 Head to the official release page and grab the Linux ZIP:
https://releases.hashicorp.com/vault/1.7.1/vault_1.7.1_linux_amd64.zip
Example listing on the download page:
vault_1.7.1_SHA256SUMS vault_1.7.1_linux_amd64.zip vault_1.7.1_darwin_amd64.zip …
Make sure to verify the SHA256 checksum to ensure file integrity.
Open vault.pkr.hcl and define:
Variables (AWS region, VPC/Subnet IDs, path to Vault ZIP)Data source for Amazon Linux 2 AMIamazon-ebsProvisioners to upload and install Vault
variable "aws_region" { type = string default = env ( "AWS_REGION" ) } variable "vault_zip" { type = string default = "/path/to/vault_1.7.1_linux_amd64.zip" } variable "vpc_id" { type = string default = "vpc-xxxx" } variable "subnet_id" { type = string default = "subnet-xxxx" } data "aws_ami" "amazon_linux_2" { most_recent = true owners = [ "amazon" ] filter { name = "name" values = [ "amzn2-ami-hvm-*-x86_64-gp2" ] } } source "amazon-ebs" "vault-amzn2" { region = var . aws_region ami_name = "vault-amazonlinux2-{{timestamp}}" instance_type = "t2.micro" source_ami = data . aws_ami . amazon_linux_2 . id ssh_username = "ec2-user" associate_public_ip_address = true subnet_id = var . subnet_id vpc_id = var . vpc_id tags = { Name = "HashiCorp Vault" OS = "Amazon Linux 2" } } build { sources = [ "source.amazon-ebs.vault-amzn2" ] provisioner "file" { source = var . vault_zip destination = "/tmp/vault.zip" } provisioner "file" { source = "files/" destination = "/tmp" } provisioner "shell" { inline = [ "unzip /tmp/vault.zip -d /usr/local/bin" , "chmod +x /usr/local/bin/vault" , "mkdir -p /etc/vault.d" , "mv /tmp/vault.hcl /etc/vault.d/" , "mv /tmp/vault_int_storage.hcl /etc/vault.d/" , "mv /tmp/vault.service /etc/systemd/system/" , "systemctl daemon-reload" , "systemctl enable vault" ] } }
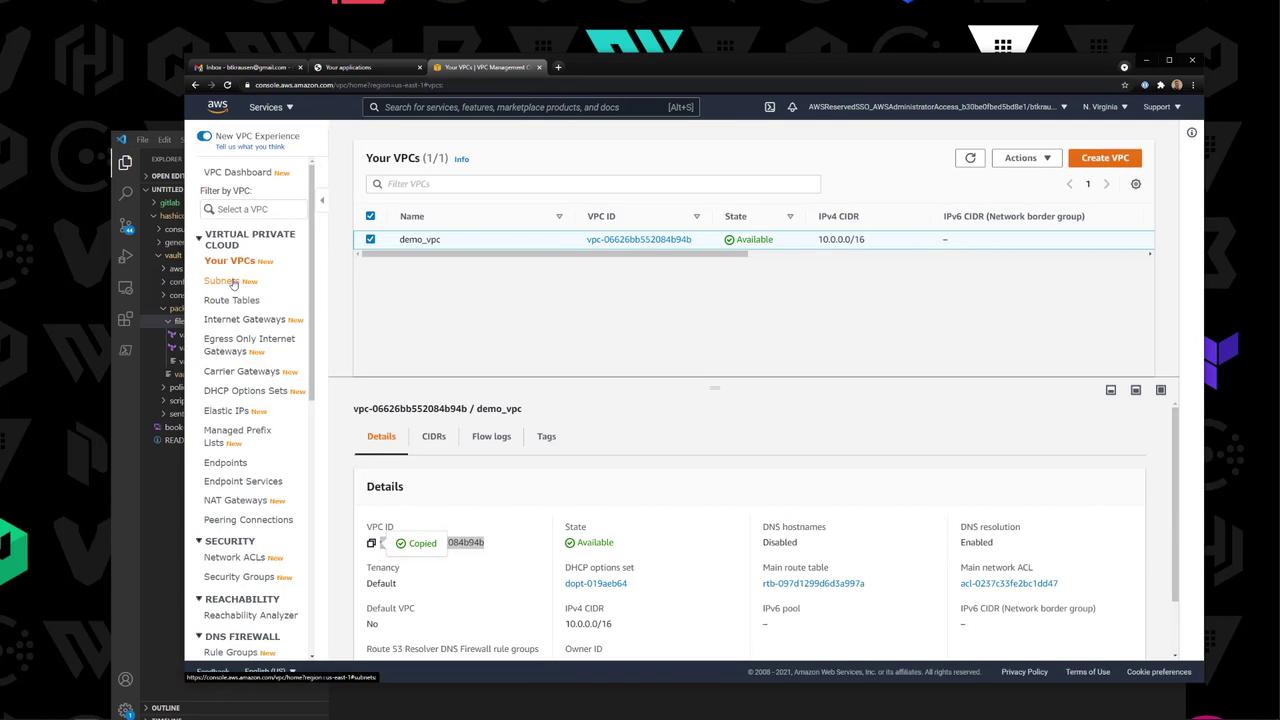
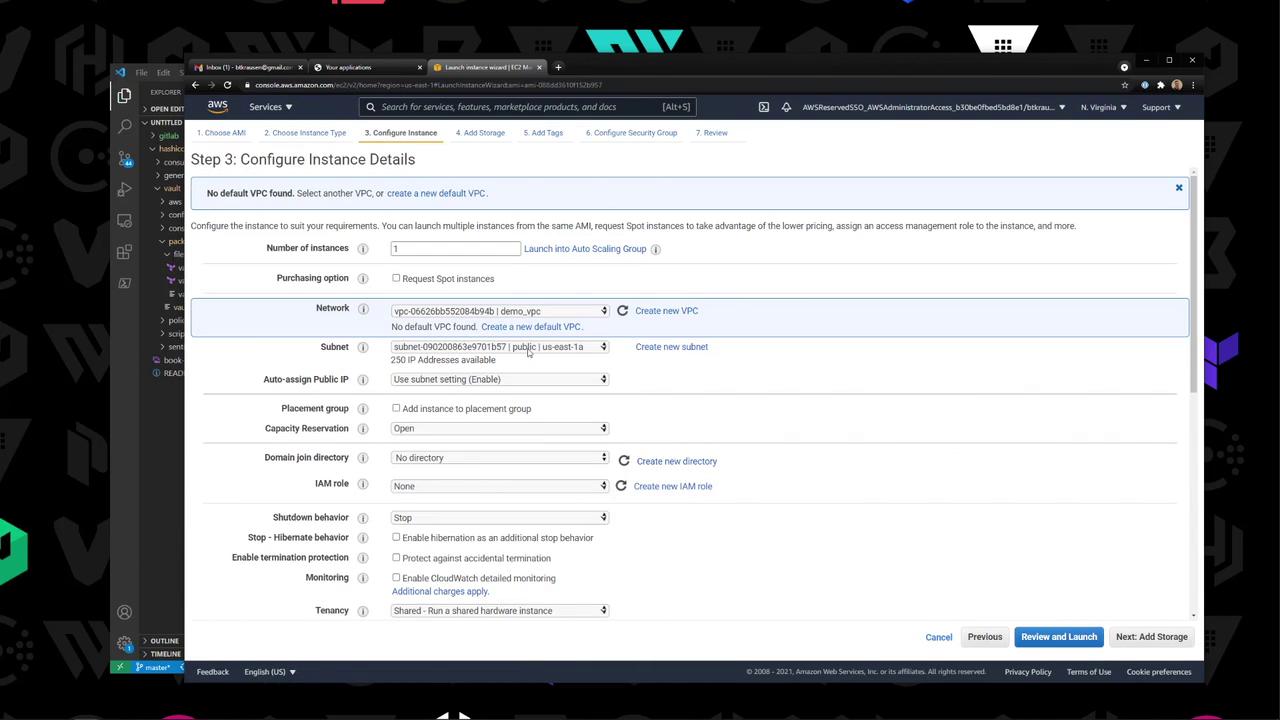
3. Set AWS Variables Retrieve your VPC and Subnet IDs from the AWS VPC console:
You can either update the default values in vault.pkr.hcl or pass them at build time:
packer build \ -var aws_region=us-east-1 \ -var vpc_id=vpc-123456 \ -var subnet_id=subnet-abcdef \ vault.pkr.hcl
4. Validate & Build the AMI packer validate vault.pkr.hcl packer build vault.pkr.hcl
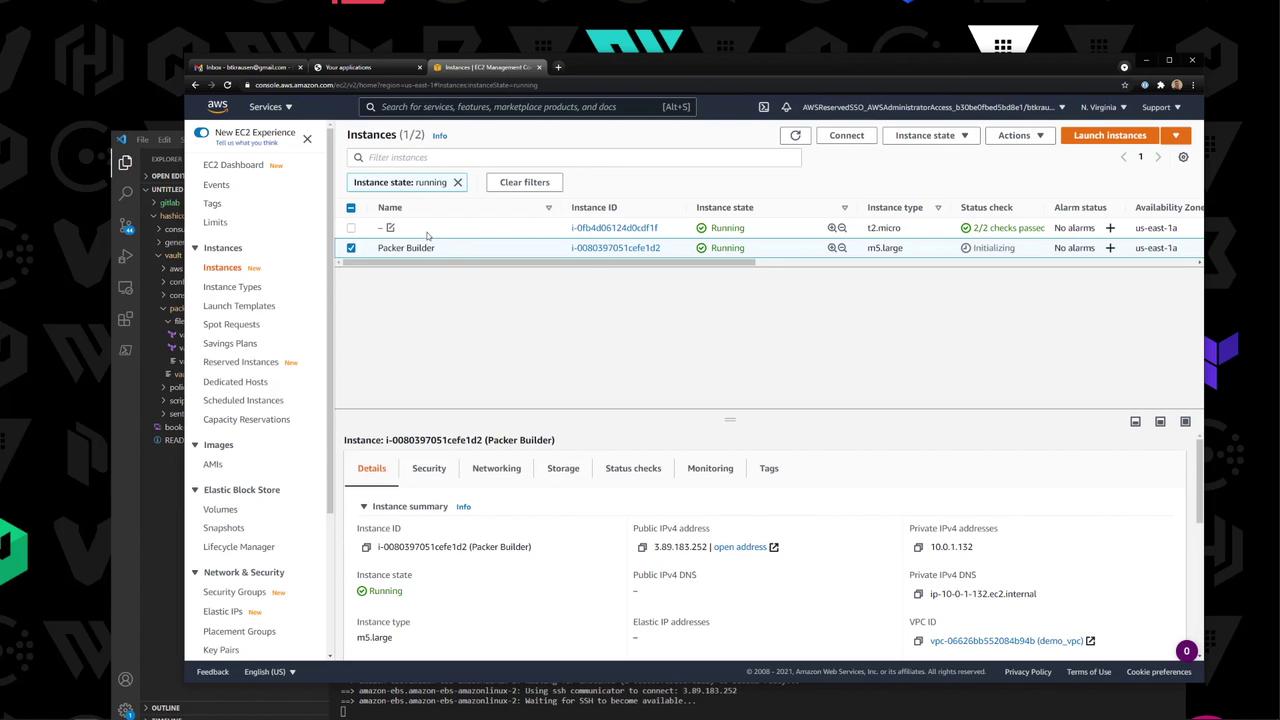
Packer will launch a builder EC2 instance, upload your files, install Vault, and register a new AMI.
amazon-ebs.vault-amzn2: Creating AMI: vault-amazonlinux2- < timestam p > from instance i-0b8... ... amazon-ebs.vault-amzn2: Builds finished. The artifacts of successful builds are:
5. Verify the Builder Instance In the EC2 console, watch the temporary Packer builder instance spin up and terminate:
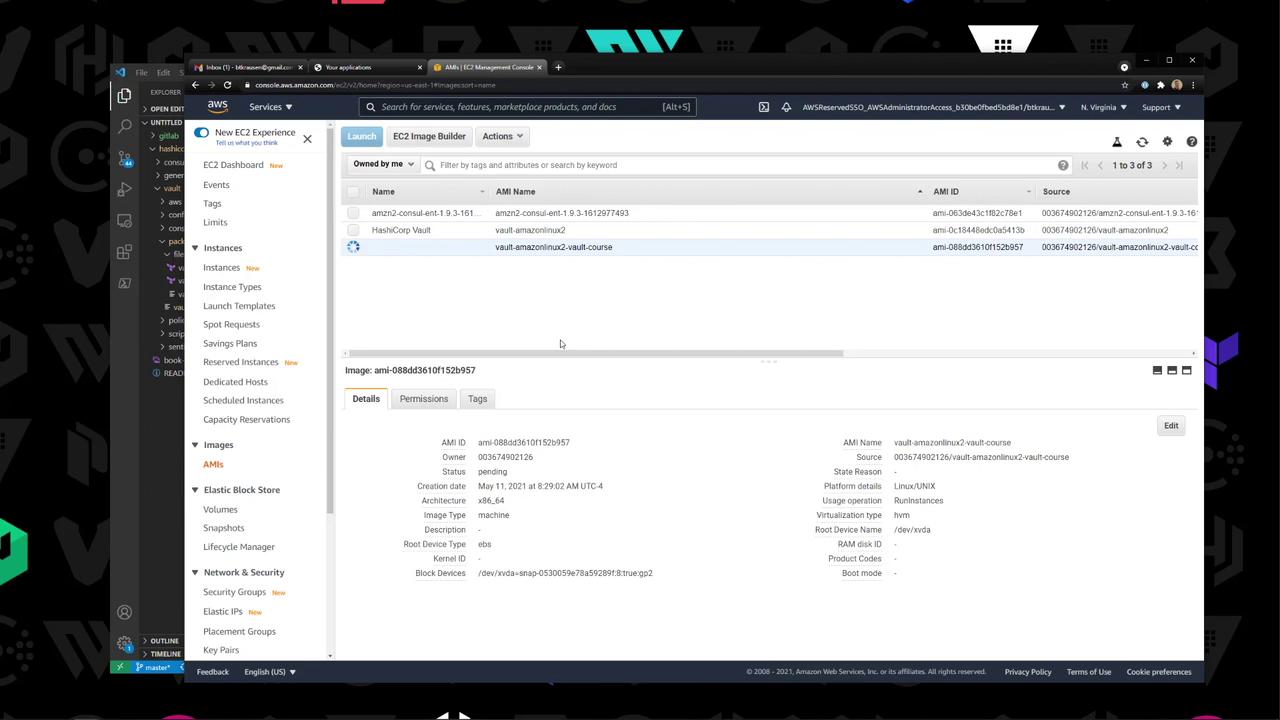
6. Check the New AMI Under EC2 → AMIs , confirm your vault-amazonlinux2-* AMI is available:
7. Launch & Validate an Instance
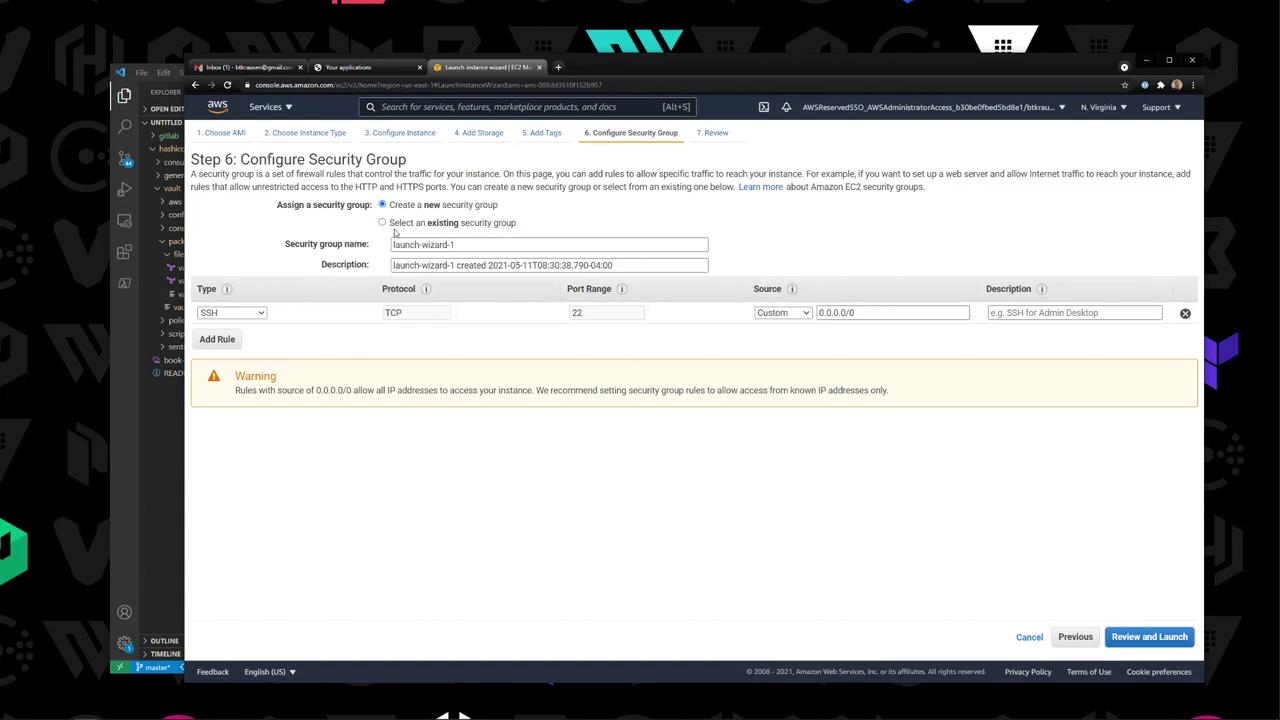
Launch : Select the custom AMI, choose T2 Micro, enable public IP.Security Group : Open SSH (port 22) from your IP.
SSH into the new instance and verify Vault:
ssh -i key.pem ec2-user@ < public-i p > sudo systemctl status vault vault version # Vault v1.7.1 (971142289796a60d0d96d0d06a0590e44e)
Congratulations—you now have a reusable AMI with Vault 1.7.1 installed!
Links & References