What is GitLab CI/CD?
GitLab CI/CD is a built-in continuous integration and delivery system that runs pipeline jobs automatically on repository events. You define workflows in a single YAML file, and GitLab handles everything from spinning up environments to reporting results.
How CI/CD Jobs Are Executed
Every job in a pipeline runs on a Runner, a lightweight agent that executes tasks in an isolated environment. GitLab offers two Runner categories:- SaaS Runners (hosted by GitLab.com)
- Self-Managed Runners (run on your own infrastructure)
This article covers SaaS Runners. Self-managed Runners will be detailed in a separate guide.

SaaS Runners
SaaS Runners are enabled by default for all GitLab.com projects—no additional setup required. Depending on your build requirements, choose from:| Runner Type | Platform | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Runners | Ubuntu, Alpine | Broad language & tooling support |
| Windows Runners (Beta) | Windows Server | Windows-specific builds (PowerShell, .NET, etc.) |
| macOS Runners (Beta) | macOS | Apple ecosystem builds (Xcode, Swift, CocoaPods) |
| GPU-enabled Runners | Linux + GPUs | High-performance workloads (ML training, inference) |
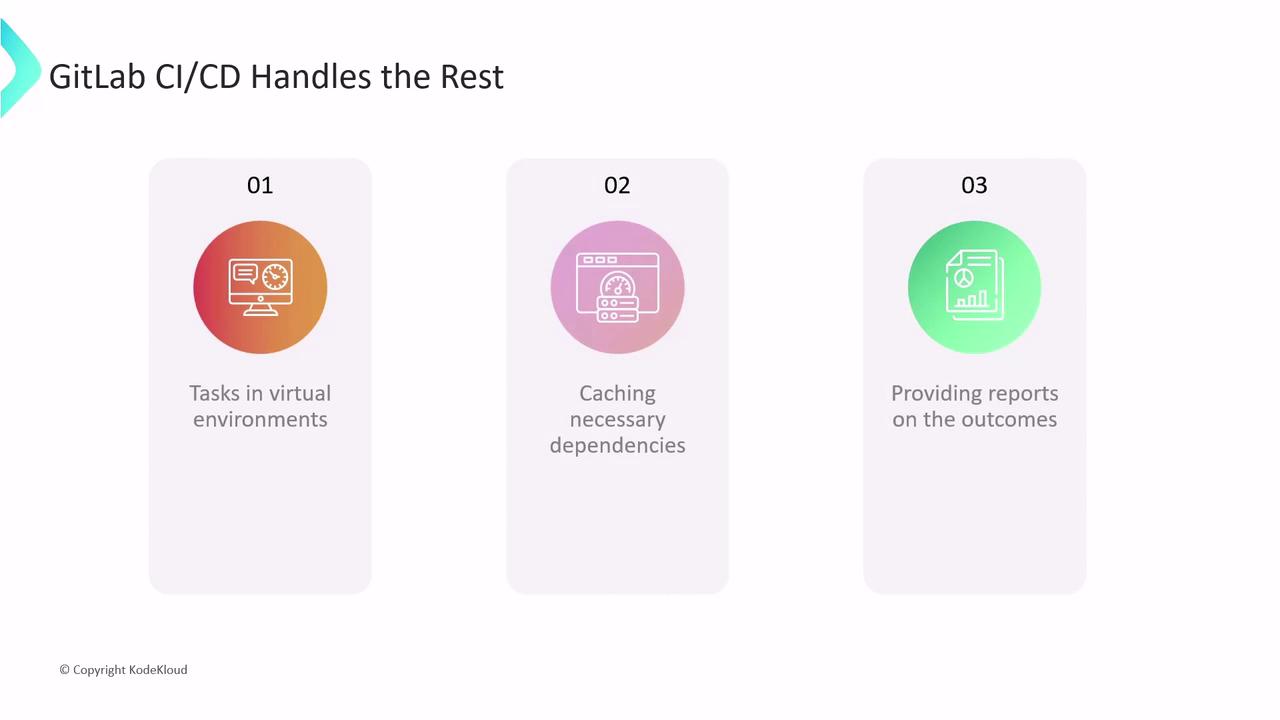
- Provisioning a fresh VM or container for each job
- Caching dependencies to accelerate subsequent builds
- Reporting detailed job status and logs
- Streamlined releases—deliver features and fixes faster
- Fewer manual errors—consistent, repeatable deployments
- Improved quality—catch issues earlier in the pipeline

Defining a Pipeline
A pipeline is a sequence of one or more jobs triggered by repository events (e.g., commits, merge requests). To define yours, create a file named.gitlab-ci.yml at your project root:
- The pipeline runs only on the
mainbranch unit_test_jobexecutes in parallel on Linux, Windows, and macOS Runners- Each job uses the
node:17-alpine3.14Docker image and runsnpm installfollowed bynpm test
Viewing Logs and Artifacts
Inspect job logs or download generated artifacts via the GitLab UI or REST API:- Go to CI/CD > Pipelines
- Select a pipeline to view stages and jobs
- Click a job to see console output and download artifacts (e.g., test reports, binaries)
Next Steps
You’ve now learned how to:- Configure CI/CD pipelines in GitLab
- Choose and use SaaS Runners
- Define jobs, parallel execution, and view logs
Links and References
Continue exploring DevOps best practices and unlock the full power of GitLab CI/CD for your projects.