Why Mask Variables?
Hardcoding credentials in.gitlab-ci.yml can lead to leaks if your repo is public or if someone gains read access. Masked variables let you:
- Store secrets outside the codebase
- Prevent values from appearing in pipeline output
- Manage credentials centrally
Project-level variables are available to all jobs by default. Use Environment scope and Protected flags to limit where and by whom they can be used.
Example: Hardcoded Password in .gitlab-ci.yml
PASSWORD directly in the YAML exposes it in your repository and logs—a significant security risk.
Storing a Masked Variable in Project Settings
Follow these steps to add a masked variable in GitLab:- Go to Settings > CI/CD in your project.
- Expand the Variables section.
- Click Add variable.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Key | DOCKER_PASSWORD |
| Value | s3cUrePaSsW0rd |
| Masked | Hides the value from job logs |
| Protected | Only available on protected branches (optional) |
| Environment scope | Use * to allow in all environments |
Anyone with Developer or Maintainer permissions can reveal or edit the variable value in project settings.

Referencing the Variable in .gitlab-ci.yml
You no longer need to define PASSWORD at the job level. Simply call the masked variable:
$DOCKER_PASSWORD is automatically injected into the job environment.
Simplifying the Pipeline for Demos
To run only specific jobs (e.g.,docker_push and deploy_ec2), hide others by prefixing their names with a dot (.). Hidden jobs appear in the editor but are skipped at runtime:
.build_file, .test_file, etc.) will not execute, ensuring only docker_push and deploy_ec2 run in your demo.
Example Pipeline Run
After pushing your changes, the pipeline triggers with just the visible jobs: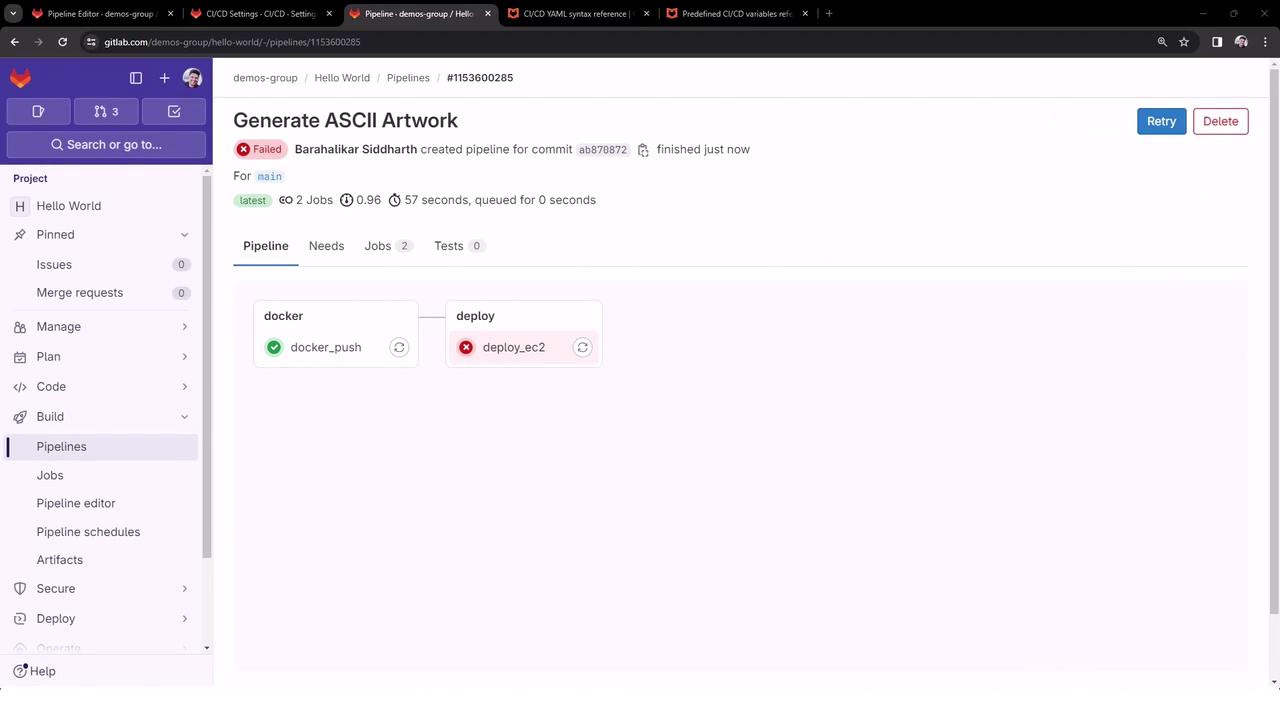
docker_push Logs
deploy_ec2 Logs
$DOCKER_PASSWORD would be available—and masked—here as well.
Summary
By storing sensitive values in GitLab’s CI/CD settings and enabling the Masked flag, you can:- Eliminate secrets from your code repository
- Prevent credentials from appearing in job logs
- Reference variables globally using
$VARIABLE_NAME