Architecture Overview
This end-to-end architecture demonstrates how Fluent Bit integrates within a Kubernetes ecosystem to collect and forward logs:- Kubernetes Cluster: Forms the backbone of the system.
- Elasticsearch & Kibana: Operate within the Kubernetes environment or on Elastic Cloud to process and visualize logs.
- Dedicated Namespace for Front-End Application: Fluent Bit runs here, meticulously collecting all logs generated by the pods in this namespace.
- Additional Namespaces: Contain a database and a payment backend, managed independently—illustrating a microservices architecture where different teams oversee their respective services.
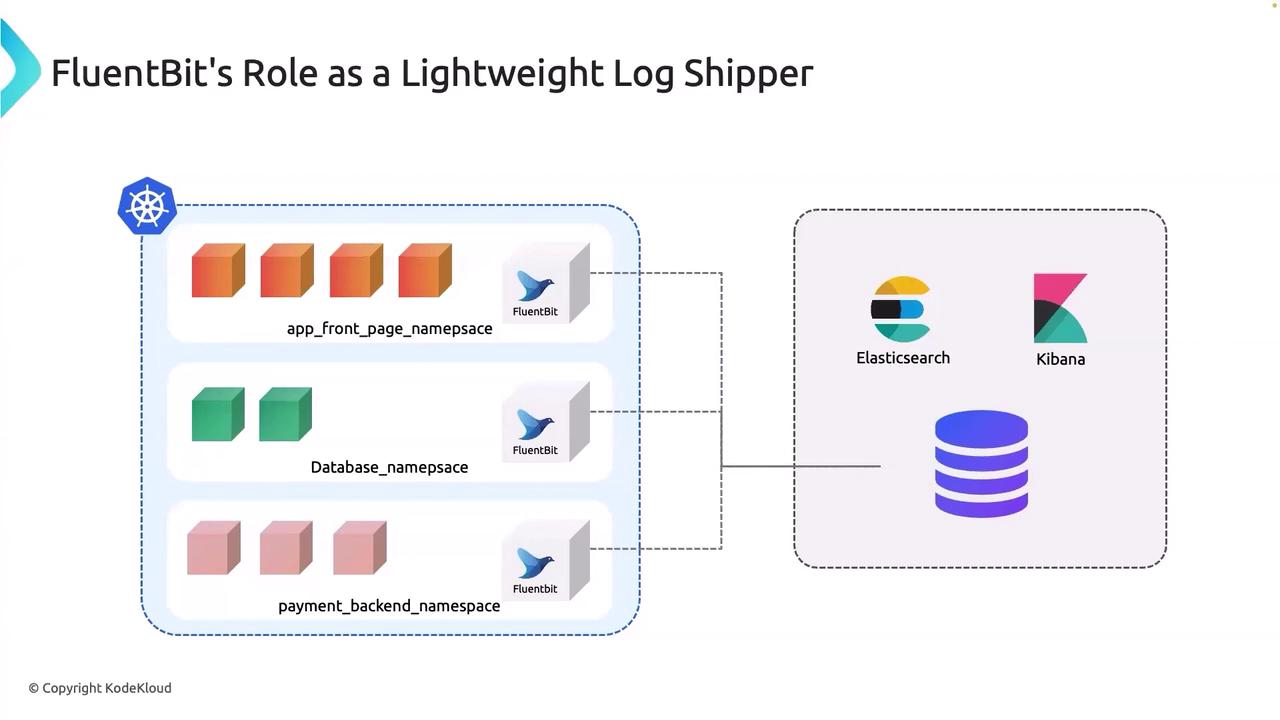
While alternatives like Fluentd or Logstash are available, Fluent Bit is often preferred for its lightweight footprint, efficient performance, and lower resource consumption. It offers comparable functionalities for log collection, filtering, and forwarding.
Key Functions of Fluent Bit
Fluent Bit’s functionality is centered around three core processes:- Collecting Logs: Capturing logs from various sources within the Kubernetes environment.
- Filtering Logs: Processing and refining log data to ensure consistency and relevance.
- Forwarding Logs: Transmitting the processed logs to Elasticsearch (output function) for storage and analysis.
Ensure that Fluent Bit is properly configured for your specific environment. Incorrect configurations may lead to incomplete log collection or performance issues in production.