When planning for enterprise storage deployments, always evaluate the specific requirements of your infrastructure, including scalability, performance, and availability.
1. Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
Direct-Attached Storage (DAS) connects storage devices directly to a host system. The operating system recognizes these devices as block devices, allowing for excellent performance with minimal latency because there is no network or firewall overhead.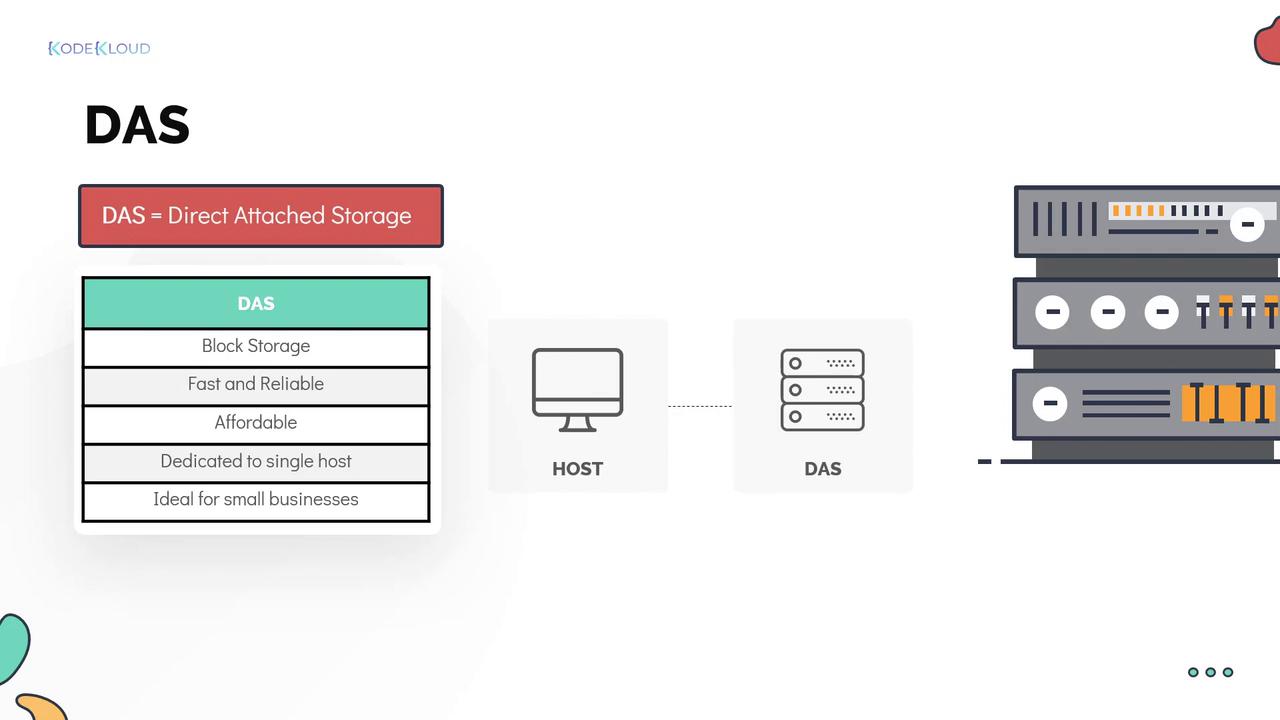
2. Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
Network-Attached Storage (NAS) is ideal for mid-to-large businesses that require shared file storage accessible over a network. NAS devices are physically separate from the computing hosts, and data is transferred via a network connection. Even if the physical distance is minimal—such as devices within the same rack in a data center—the data still travels through network infrastructure. NAS typically functions as an NFS server, exporting storage as directories or shares that can be accessed simultaneously by multiple hosts. Its design supports centralized shared storage with high availability and good performance, particularly with high-speed Ethernet connectivity. NAS is well-suited for web servers, application servers, and non-production database environments. It is important to note that installing an operating system directly on a NAS device is generally not recommended.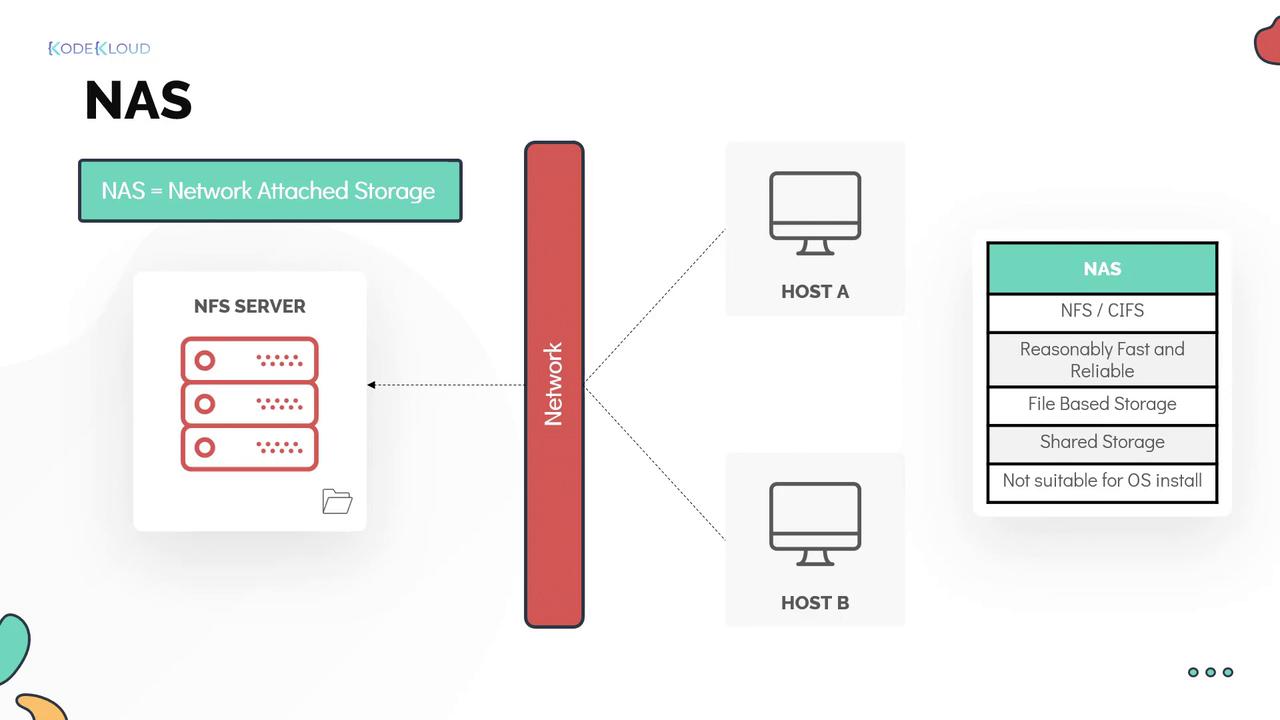
3. Storage Area Network (SAN)
Storage Area Network (SAN) provides block storage designed for enterprises running mission-critical applications that demand high throughput and low latency. In a SAN system, storage is allocated to hosts as Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs), which represent sections of a shared storage pool presented as logical disks to the server.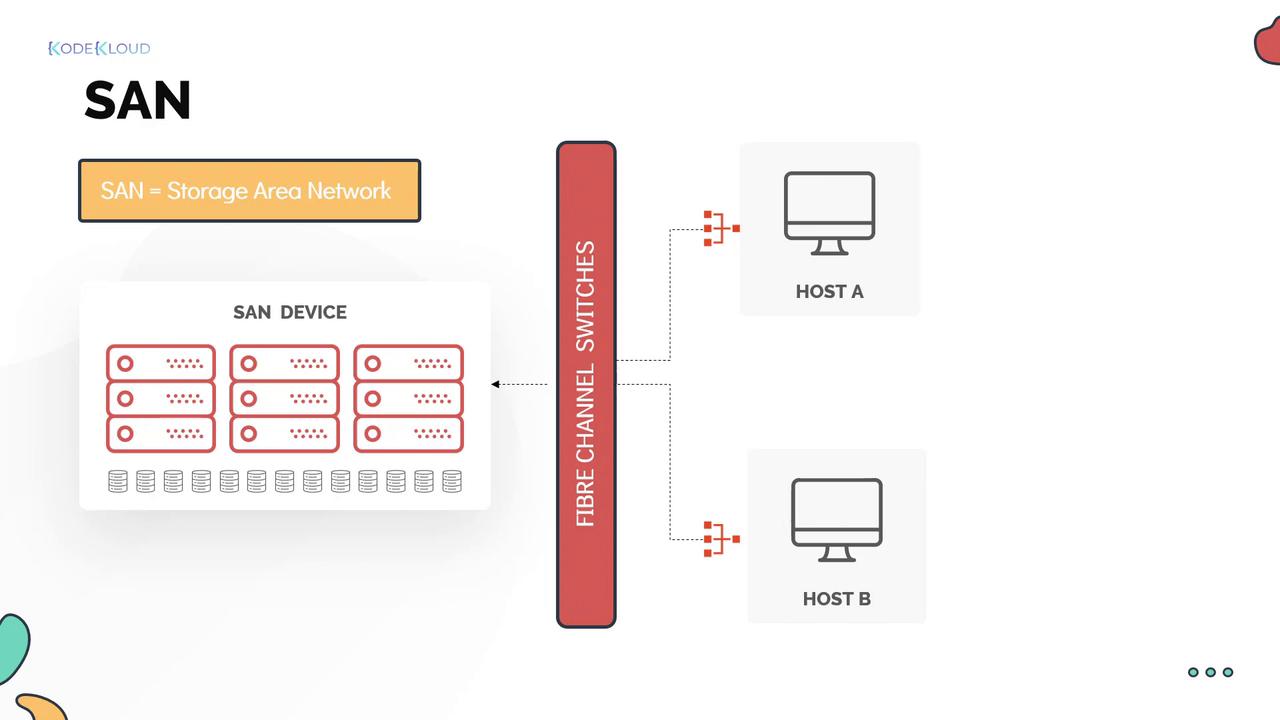
SAN is best for handling mission-critical applications and databases—such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and virtualized environments using platforms like VMware, KVM, or Microsoft Hyper-V—due to its high performance and reliability.
By understanding the differences among DAS, NAS, and SAN, IT professionals can better choose the appropriate storage solution tailored to their performance requirements, scalability needs, and overall infrastructure design. For further reading on storage technologies and enterprise IT solutions, explore the following resources: