DPKG
DPKG, short for Debian Package Manager, is similar to RPM on Red Hat-based systems. It is used to install, remove, upgrade, list, and verify packages with the .deb extension. However, note that DPKG does not automatically resolve or manage dependencies. This can lead to installation issues if required dependencies are missing. You can perform common package management tasks with DPKG using the following commands:Using DPKG directly is useful for managing individual
.deb files, but dependency issues might require additional manual resolution.APT
APT (Advanced Package Tool) is a user-friendly front-end for DPKG that automatically handles dependency resolution. When you install a package using APT, it ensures that all required dependencies are installed alongside the requested package. This feature makes it a preferred choice for many users over directly using DPKG. For example, to install GIMP while automatically handling dependencies, use the following command: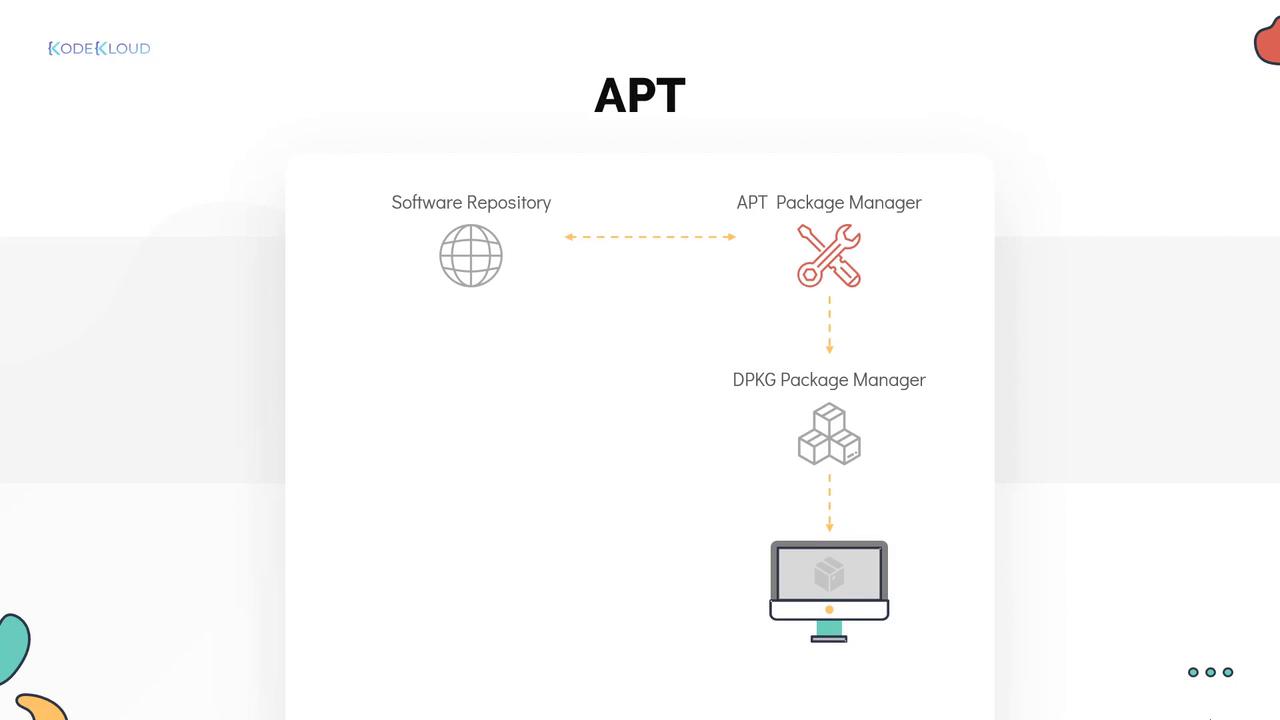
Common APT Commands
Below is a table summarizing key APT commands along with their use cases:| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Update repositories | Refresh the package repository information | [~]$ apt update |
| Upgrade packages | Upgrade installed packages to the latest version in the repository | [~]$ apt upgrade |
| Install a package | Install a package (e.g., Telnet) and resolve dependencies automatically | [~]$ apt install telnet |
| Remove a package | Remove an installed package | [~]$ apt remove telnet |
| Search for a package | Search for a package within the repository | [~]$ apt search telnet |
apt edit-sources or by directly editing the /etc/apt/sources.list file with your preferred text editor such as Vim or Nano.
APT simplifies package management by automatically managing dependencies and providing an intuitive command-line interface. It is an essential tool for maintaining system packages on Debian-based distributions.
Summary
This article introduced the basics of DPKG and APT for package management in Debian-based distributions. While DPKG is ideal for managing individual.deb files, APT provides enhanced functionality by resolving dependencies and managing repositories. Mastering these tools is crucial for ensuring a smooth software installation and management experience.
For further reading, consider reviewing the Kubernetes Documentation and exploring additional package management best practices.