
Tip: Use the following command to view the status of your rollout:
Deployment Strategies
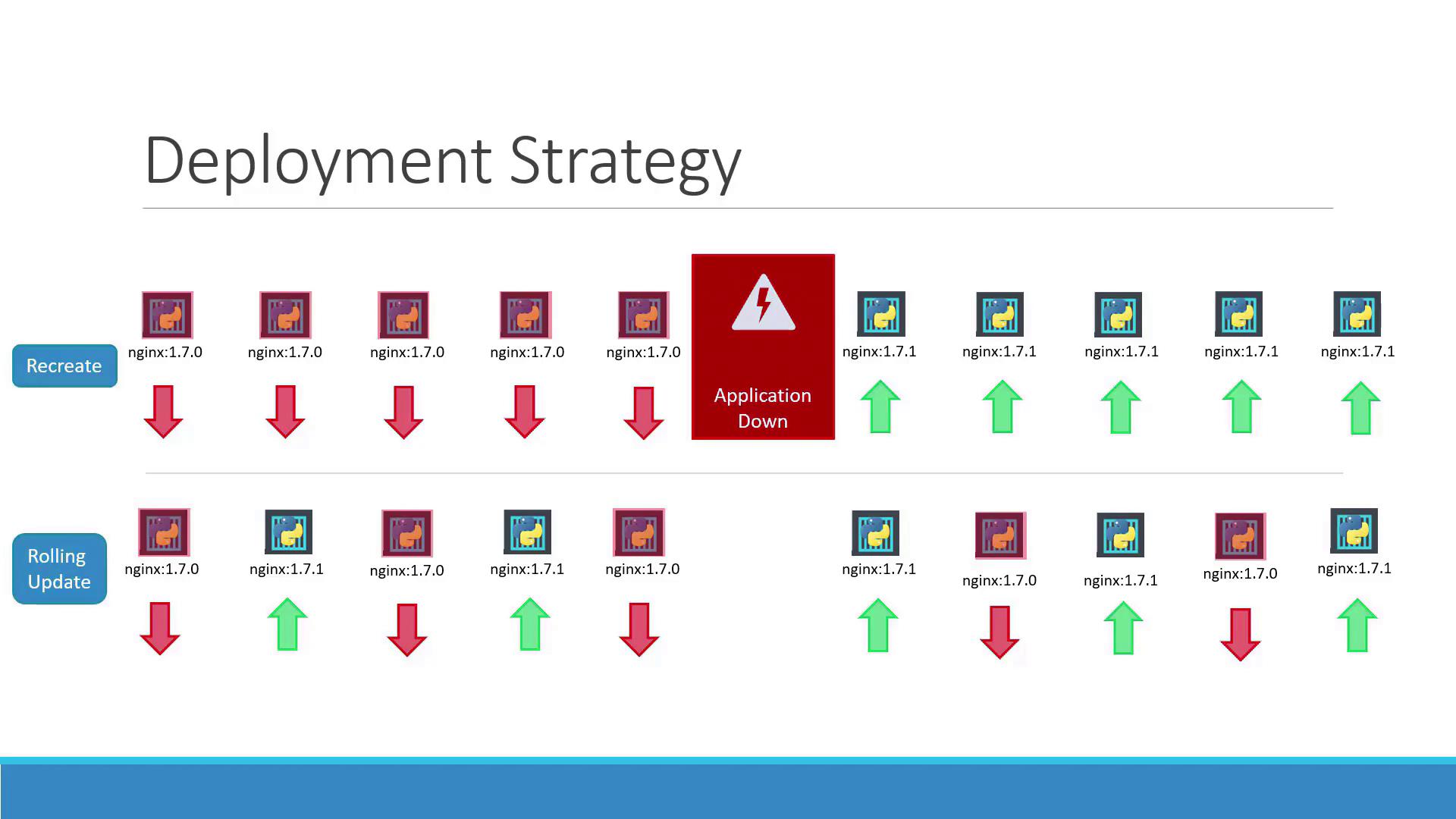
Kubernetes supports two primary deployment strategies:- Recreate Strategy With the recreate strategy, if you have, for example, five replicas, all replicas are terminated and then replaced with new ones running the updated version. The main drawback is potential downtime, as the application is temporarily unavailable.
- Rolling Update Strategy The rolling update strategy gradually replaces the old version with the new one by updating replicas one at a time. This ensures continuous application availability during the upgrade. Note that Kubernetes uses the rolling update strategy by default when no specific strategy is configured.
Updating a Deployment
There are multiple methods to update your deployment. You can update the container image version, modify labels, or adjust the number of replicas. If you are using a deployment definition file, simply modify the file and apply the update:
Caution: Updating with kubectl set image modifies the running configuration, which may differ from the file-based configuration. Remember to update your deployment definition file accordingly.
Below is an example deployment definition file after updating the container image version:
Examining Deployment Details
Describing your deployment provides insights into the underlying processes and differences between deployment strategies. When using the recreate strategy, the old ReplicaSet scales down to zero before the new one scales up. Run:Understanding the Underlying Process
When you create a deployment (for example, with five replicas), Kubernetes automatically creates a ReplicaSet that manages the corresponding pods. During an upgrade, a new ReplicaSet is created for the updated configuration while the old ReplicaSet gradually terminates its pods. You can monitor these changes by running:Quick Reference Summary
Below is a summary of the key commands used to create, update, monitor, and roll back your deployments:| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl create -f deployment-definition.yml | Create a new deployment |
kubectl get deployments | List current deployments |
kubectl apply -f deployment-definition.yml | Apply changes from the deployment definition file |
kubectl set image deployment/myapp-deployment nginx=nginx:1.9.1 | Update a deployment’s container image |
kubectl rollout status deployment/myapp-deployment | Check the status of the deployment rollout |
kubectl rollout undo deployment/myapp-deployment | Roll back to the previous deployment revision |
