Table of Contents
- Core Message Types
- Message Workflow
- Statefulness and LLMs
- Implementing in LangChain
- Links and References
Core Message Types
When working with a chat model, all communication is framed as a sequence of three distinct message objects:| Message Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| System | Establishes persona or global settings | “Act like a physics teacher.” |
| Human | Captures user input or inquiries | “Explain Newton’s laws.” |
| AI | Contains the model’s generated response | “Newton’s first law states…” |
System and human messages together form the prompt sent to the model. AI messages are the model’s replies based on that prompt sequence.
Message Workflow
Below is a high-level flowchart illustrating how your application composes and processes these messages before, during, and after calling the chat model API: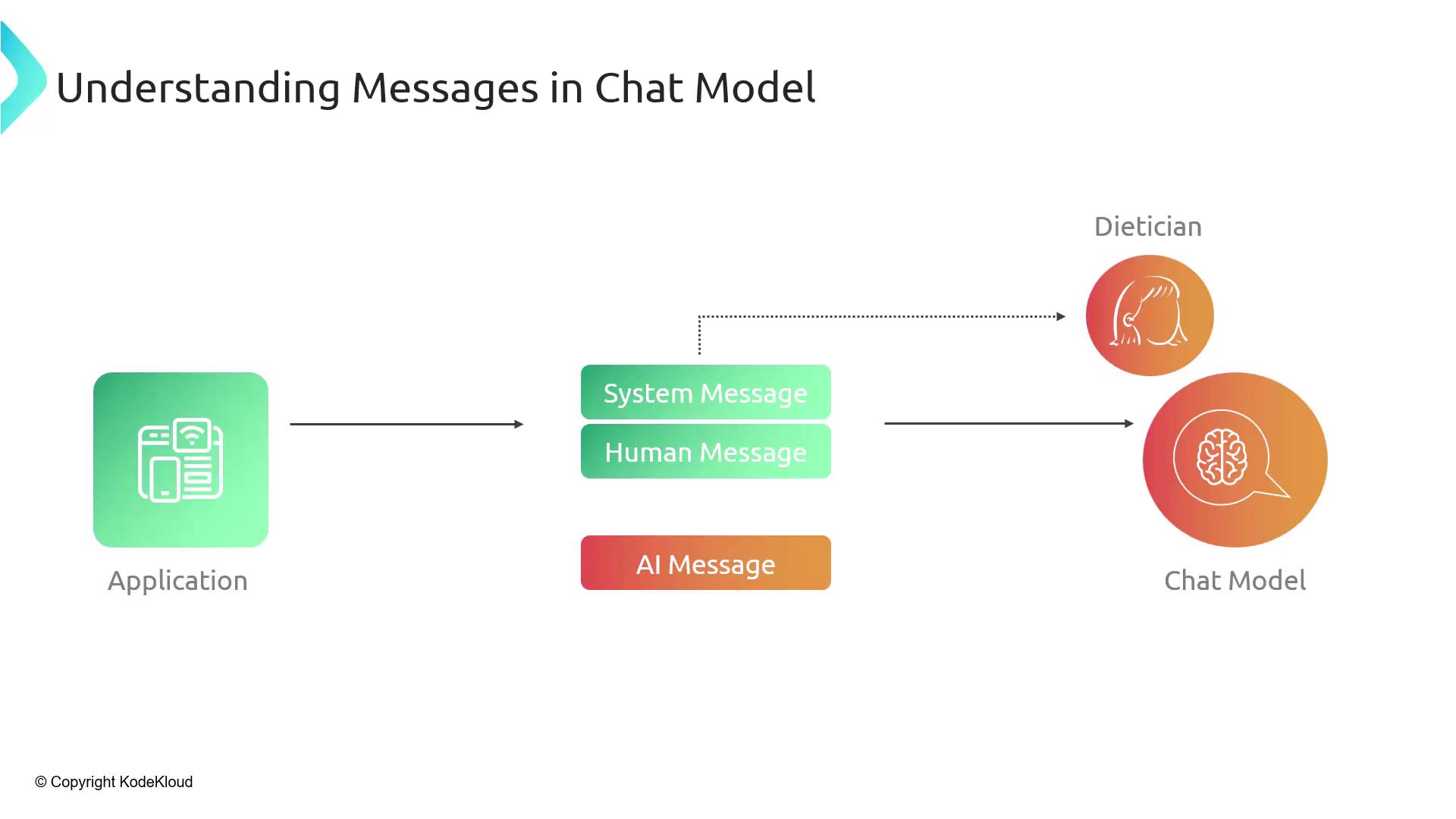
- Initialize System Message
- Accept Human Message
- Invoke Chat Model
- Receive AI Message
- Render Response to User
Statefulness and LLMs
Large language models (LLMs) do not maintain memory across separate sessions. This means every new conversation must include its system message to preserve context.If you omit the system message at the start of a session, the model will have no persona or configuration, leading to unpredictable or generic responses.