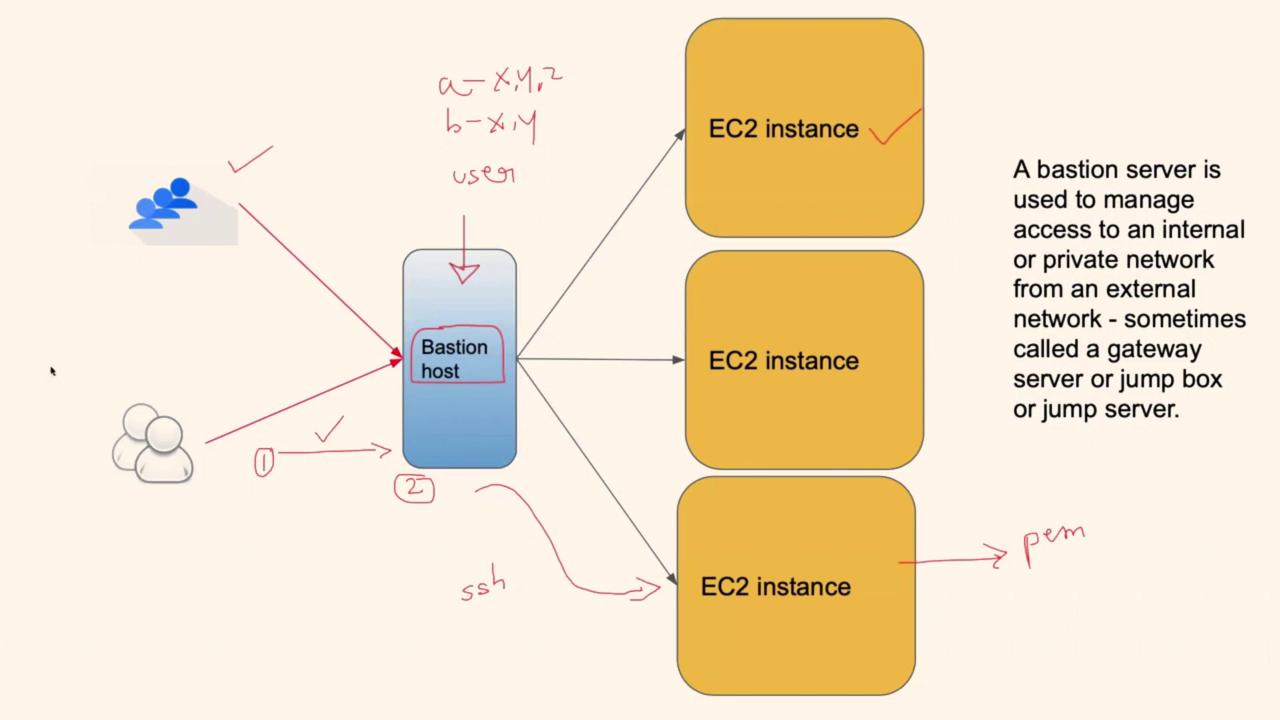
Understanding the Bastion Host Concept
When managing multiple EC2 instances or servers behind a private Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), you face the challenge of providing secure, controlled access for users. Rather than granting each user direct access, which can risk security by exposing sensitive credentials or internal configurations, the Bastion host provides a safe access point. Imagine a scenario:- Instead of each user connecting directly to the private servers, they first log into the Bastion host.
- From this secure gateway, the user can then access only the specific servers they are authorized to manage.
A Bastion host is not intended to perform heavy computing tasks; its primary role is to serve as a controlled gateway, enforcing strict user access rules.
- Limiting direct exposure of your private infrastructure.
- Allowing centralized monitoring and logging of all access activities.
- Enabling administrators to enforce granular permissions (e.g., User A can access Servers X, Y, and Z whereas User B may only access Servers X and Y).
How the Bastion Host Works
The operational flow of a Bastion host setup is straightforward:-
User Authentication:
A user initiates an SSH connection to the Bastion host, where authentication validates their identity. -
Access Control:
After successful authentication, the user may SSH from the Bastion host to the internal servers for which they have permission. -
Permission Enforcement:
If the user attempts to access a server without the necessary permissions, the connection is automatically denied.
Critical Advantage of Using a Bastion Host
Decommissioning the Bastion host during maintenance or in response to a security concern is an effective way to mitigate risk and protect the integrity of your internal network.
Summary
In summary, a Bastion host (also known as a gateway server, jump box, or jump server) is a dedicated server designed to manage external access to a private network. It provides:- Secure management and monitoring of user access.
- A controlled gateway that prevents unauthorized direct access to internal servers.
- Immediate isolation of external access when decommissioned, thereby enhancing network security.
For further reading and a deeper dive into secure network architectures, consider exploring the following resources: