/var/log or other directories defined by your application’s configuration. Whether you stop and then start the container or simply restart it, the logs remain intact. Note, however, that the application might begin writing to a new log file upon restart.
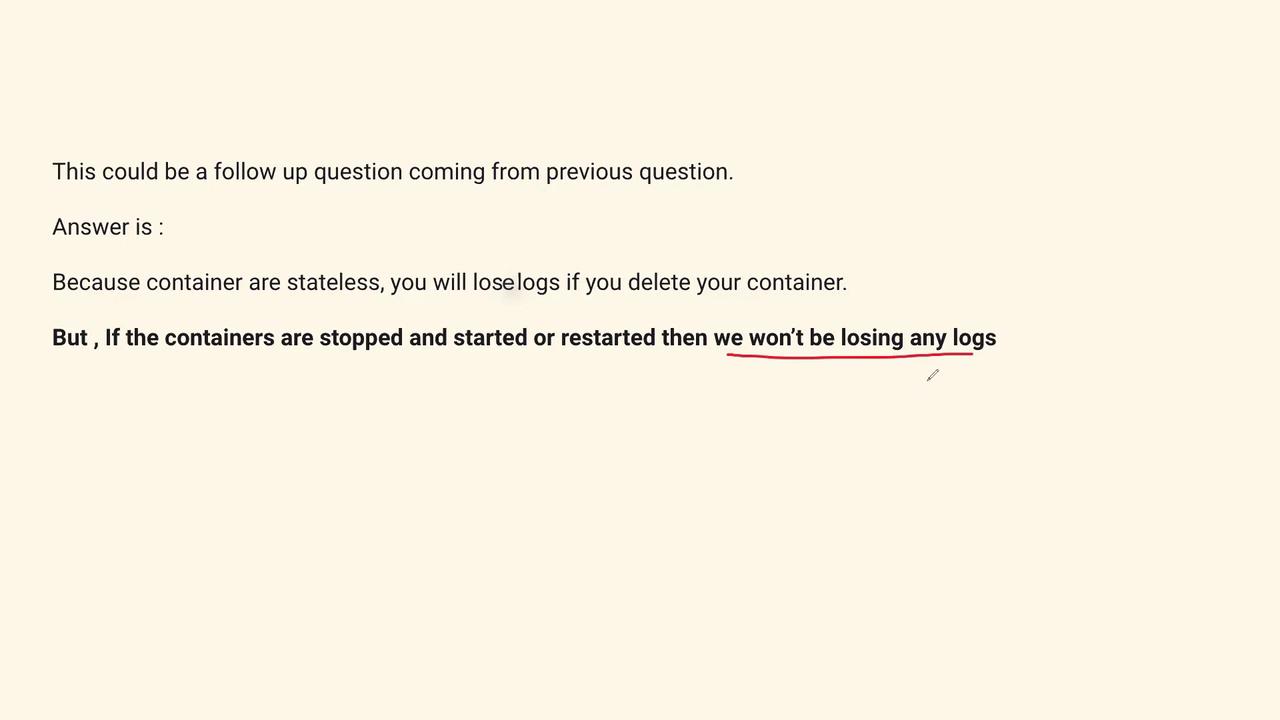
Although container logs persist across restarts, if a container is deleted, its logs are also removed. To avoid losing log data, it is recommended to use external persistent storage or integrate centralized logging solutions such as Splunk or CloudTrail.
Key Takeaways for Docker Interviews
- Logs Persistence: When you start, stop, or restart a container, the logs persist.
- Log Rotation Consideration: Depending on your application’s log rotation strategy, executing the
docker logscommand might display output from a new log file if logging restarts. - Container Deletion: Deleting a container will also delete any logs stored inside it.
- Best Practices: Use external log storage solutions to safeguard logs when a container is deleted.