s (substitute) command in sed is a powerful tool for search-and-replace operations on text streams. Whether you’re updating configuration files, automating code refactoring, or cleaning log files, mastering sed substitution will streamline your workflow.
By default,
sed reads from stdin or an input file and writes to stdout. Use the -i option for in-place editing.Table of Contents
- Basic Syntax
- Quick Reference Commands
- Practical Example: Updating a Salary
- Substitution Scope
- Targeting Specific Occurrences
- Line Addressing
- In-Place Editing (
-i) - Inserting Text with
i - Conclusion
- References
Basic Syntax
Use the following pattern to substituteold_string with new_string:
s— substitute commandold_string— search pattern (regular expression supported)new_string— replacement text/— delimiters (can be any character)- By default, only the first match per line is replaced.
Quick Reference Commands
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
s/original/replacement/ | Substitute first match on each line | sed 's/foo/bar/' file.txt |
-n '/pattern/p' | Print only lines matching a pattern | sed -n '/Error/p' /var/log/syslog |
/pattern/d | Delete lines matching a pattern | sed '/^#/d' config.conf |
Practical Example: Updating a Salary
Given anemployees.txt file:
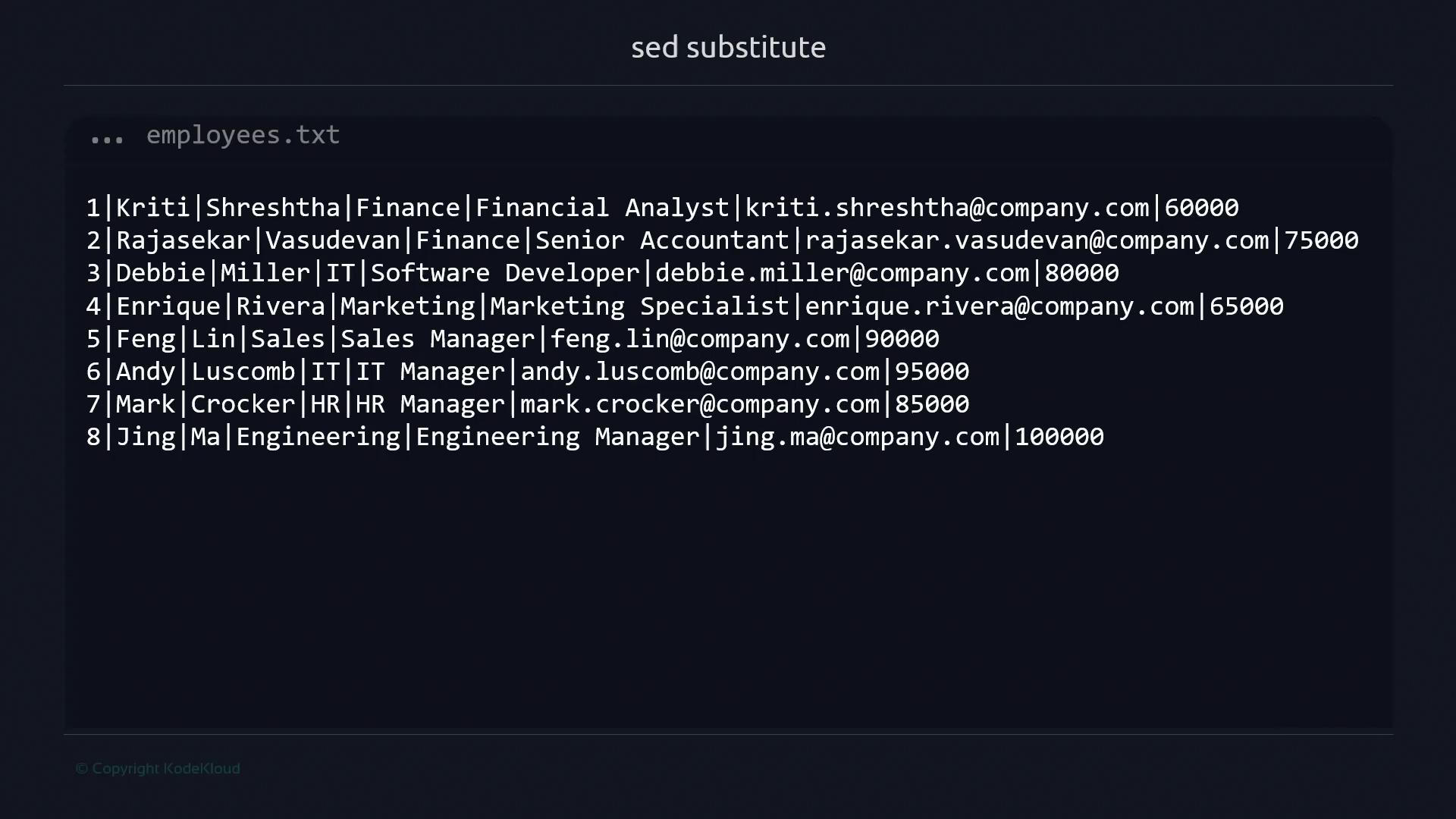
65000 to 85000, run:
65000 on each line and prints the result to stdout.
Substitution Scope
Global Replacement
Append theg flag to replace all matches in each line:
First-Match Only
Withoutg, only the first match is replaced:
Targeting Specific Occurrences
You can replace only the nth occurrence on each line by specifying a number:IT per line.
Line Addressing
Limit substitutions to certain lines or ranges:-
Single line (line 7):
-
Line range (lines 1–3):
-
Another single line (line 5):
In-Place Editing (-i)
Modify the file directly using -i:
company in employees.txt.
When using This creates
-i, changes are irreversible unless you create a backup:file.txt.bak before editing.Inserting Text with i
The i command inserts lines before the current pattern space or at a specified line:
i, sed throws an error:
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned how to:- Use
s/old/new/for basic substitution - Leverage
gand numeric flags for global or specific replacements - Address lines and ranges for targeted edits
- Apply in-place editing with
-i(and backups) - Insert new lines using the
icommand
sed.