awk to customize the field separator when processing structured text. By default, awk splits records on whitespace, but -F lets you define any character or regular expression as the delimiter.
1. Default Field Splitting
By default,awk treats any whitespace as the field separator:
2. Changing the Field Separator with -F
To use a colon (:) as the separator:
awk:
3. Why Quote or Escape the Separator
Certain characters (for example,|, &, *, <, >) have special meanings to the shell.
Always quote or escape the field separator to prevent shell interpretation.Incorrect:This fails because
| is seen as a pipe.Correct: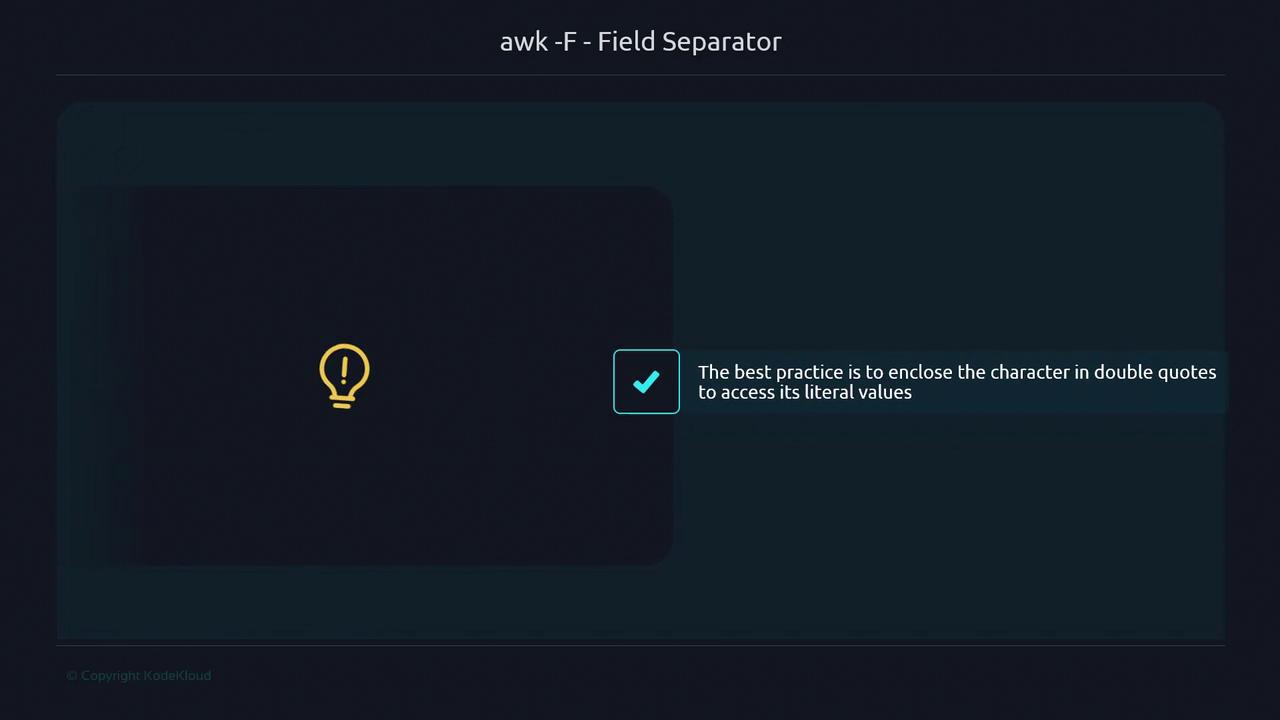
4. Common Field Separators
| Separator | Shell Meaning | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| : | None | /etc/passwd |
| , | None | CSV export |
| | | Pipe (must escape) | Database output |
| \t | Tab (escape \t) | TSV files |
| = | Assignment (escape) | Key-value configs |

5. Example: Processing Database Output
Here’s a Bash script (db.sh) that runs a PostgreSQL query inside Docker, trimming each field:
See the GNU Awk User’s Guide for more
awk options.Next Steps
Next, we’ll explore the -v option to declare variables withinawk: