Using rsync for Remote Synchronization
rsync (short for “remote synchronization”) is a powerful tool for backing up data. It efficiently synchronizes directories between a local and remote system by transferring only changed files.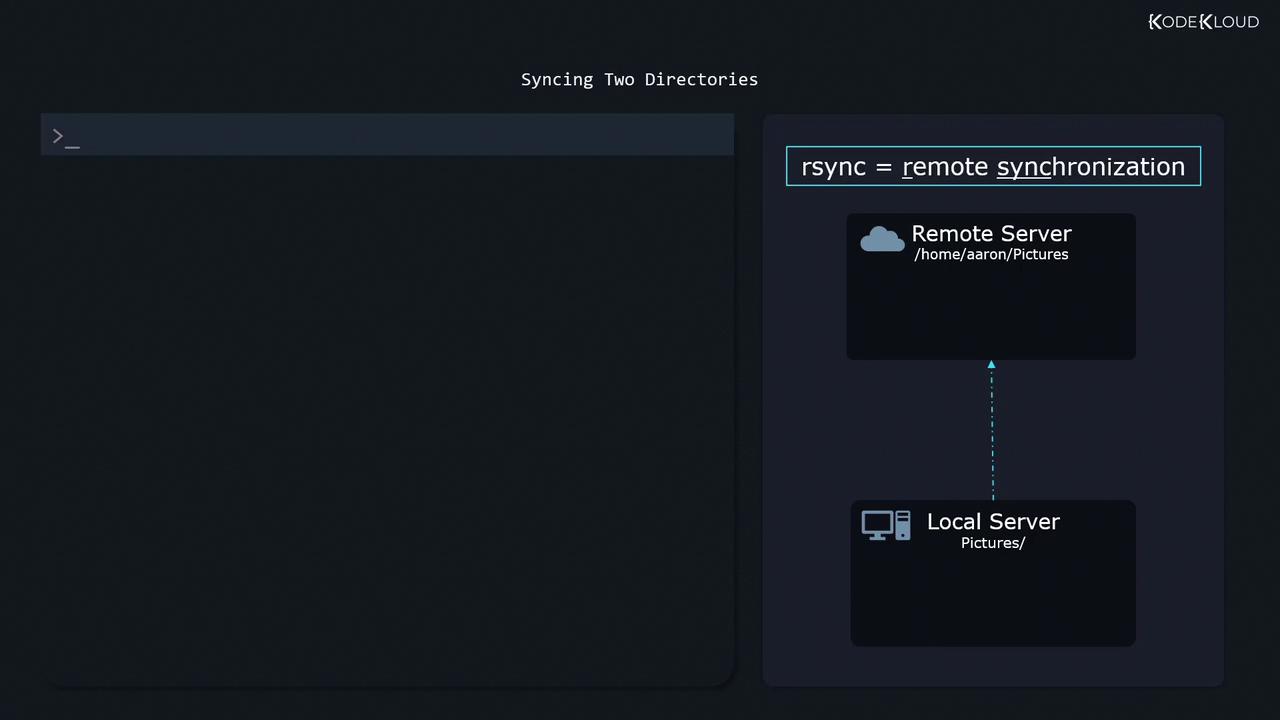
Basic rsync Command Syntax
The general syntax for rsync is:-a (archive) flag ensures that subdirectories, file permissions, modification times, and other attributes are preserved during synchronization.
For example, to synchronize a local “Pictures” directory with a remote “Pictures” directory, you would use:
Using dd for Disk Imaging
When you need to back up an entire disk or partition, instead of just individual files, thedd utility becomes essential. It creates an exact, bit-by-bit copy of a disk or partition, a process commonly referred to as disk imaging.
Before creating a disk image, ensure the disk or partition is unmounted to prevent data modifications during the imaging process.
Creating a Disk Image with dd
Run the following command with root permissions to create a disk image:sudo dd: Runs theddcommand with elevated permissions.if=/dev/vda: Specifies the input file—the disk or partition you want to back up.of=diskimage.raw: Defines the output file where the disk image is saved.bs=1M: Sets the block size to one megabyte, which can enhance the performance of the backup process.status=progress: Displays progress information as the backup operation proceeds.
Restoring a Disk Image
Restoring the disk image is just as straightforward. Reverse the input and output parameters:Restoring a disk image will overwrite the destination disk entirely. Ensure you are restoring to the correct disk to avoid unintended data loss.
Summary
In this lesson, we discussed two essential Linux backup methodologies:| Method | Use Case | Command Example |
|---|---|---|
| rsync | File-level backup and synchronization | rsync -a Pictures/ [email protected]:/home/aaron/Pictures/ |
| dd | Creating and restoring complete disk images | sudo dd if=/dev/vda of=diskimage.raw bs=1M status=progress |