- Inbound flow: ingesting, securing, and preparing prompts
- Outbound flow: validating and delivering generated code
- Security & filtering: protecting users and the system
- Feedback loops: driving continuous Copilot improvements
Dual Flow Process
Copilot architecture follows a two-way pipeline:- Inbound Flow captures your prompt, gathers context, and applies pre-filters.
- Outbound Flow runs security checks and quality validations before returning suggestions.
| Flow Type | Key Actions | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound | Prompt ingestion, context gathering, toxicity checks | Secure, contextual input |
| Outbound | Post-processing, quality & security validation | High-quality code suggestions |
Why Data Flow Matters
- Better prompts lead to more accurate code.
- Security stages protect sensitive information.
- Aligned workflows boost development efficiency.
Step 1: Secure Prompt Transmission
All interactions between your editor and Copilot use HTTPS, ensuring end-to-end encryption. Copilot handles:- Chat queries in the sidebar
- Natural-language comments directly in code
HTTPS encryption safeguards your intellectual property and keeps credentials and proprietary code confidential.
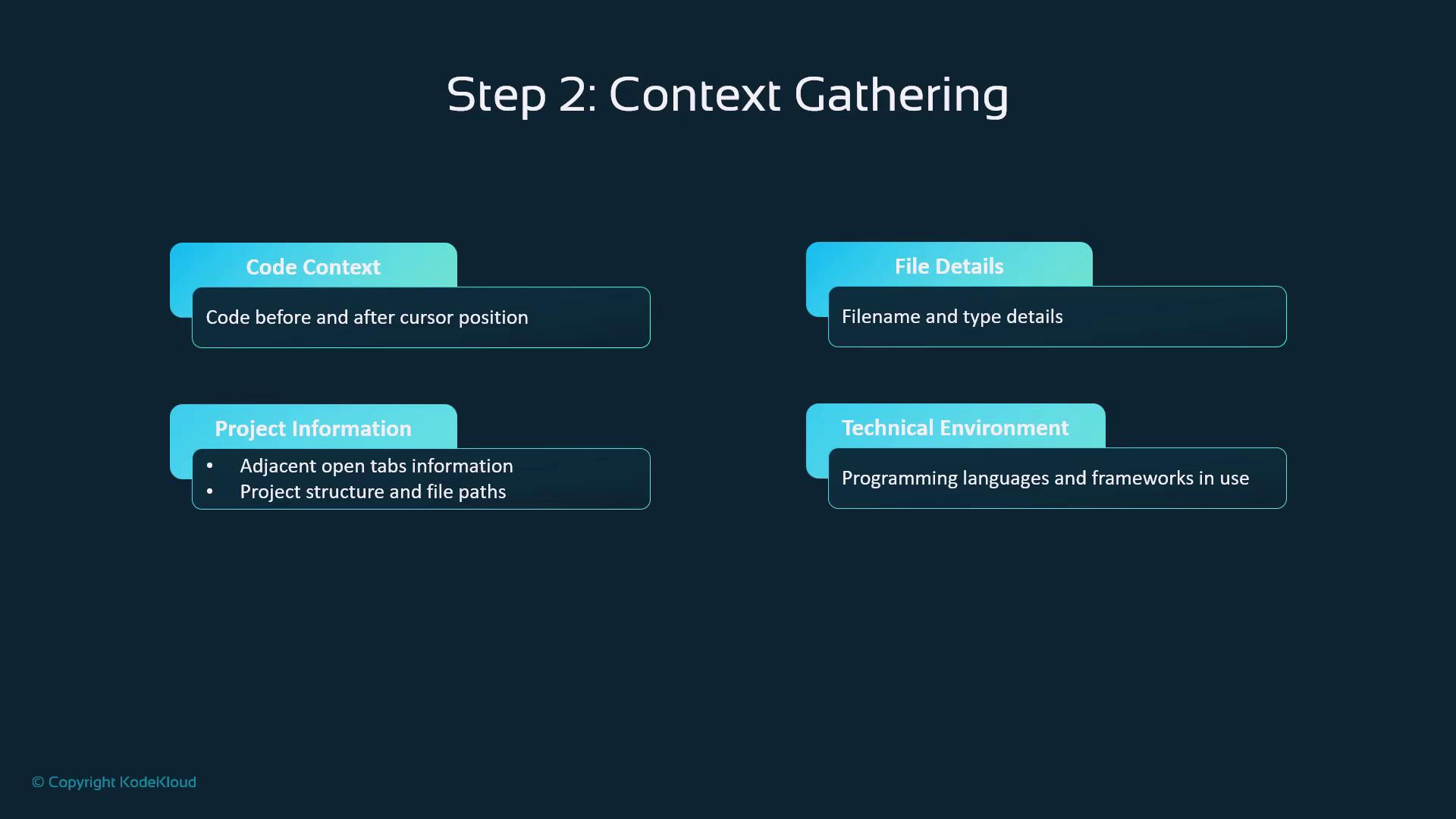
Step 2: Context Gathering
Copilot enriches each prompt with:- Code Context: Surrounding lines of code
- File Details: Name, type, and language
- Project Scope: Open files, folder structure
- Environment: Frameworks, dependencies, settings
Step 3: Proxy Filtering
Your request travels through a GitHub-owned proxy on Microsoft Azure that:- Blocks malicious traffic
- Enforces integrity guardrails
Step 4: Toxicity Filtering
Before the LLM sees the prompt, Copilot screens for:- Hate speech or harassment
- Personal/sensitive data
- Ethical compliance
- Consistent policy enforcement
Step 5: Code Generation with LLM
At the heart of Copilot is a large language model that:- Processes the filtered prompt
- Integrates project context
- Generates code snippets
- Aligns output to your coding style

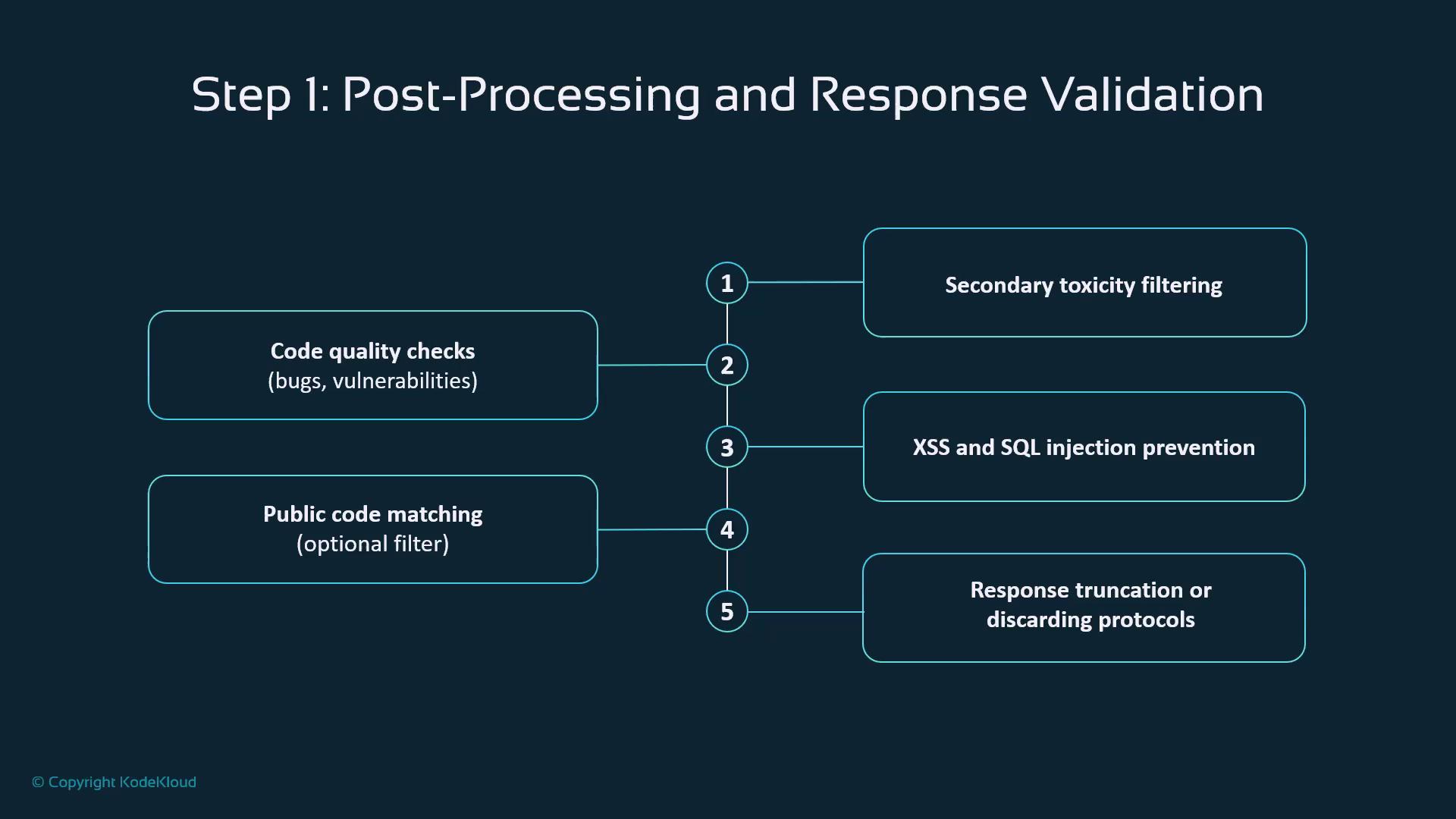
Post-Processing & Validation
Generated code then moves through these checkpoints:| Validation Step | Purpose | Example Threat |
|---|---|---|
| Secondary Toxicity Filtering | Detect inappropriate outputs | Offensive content |
| Code Quality Checks | Identify bugs and vulnerabilities | Memory leaks, logic errors |
| Security Scans | Prevent XSS, SQL injection, etc. | Injection attacks |
| Enterprise Code Matching | Block reuse of proprietary snippets | License or IP violations |
| Truncation/Discard Policy | Remove low-quality or unsafe results | Poorly formed code |
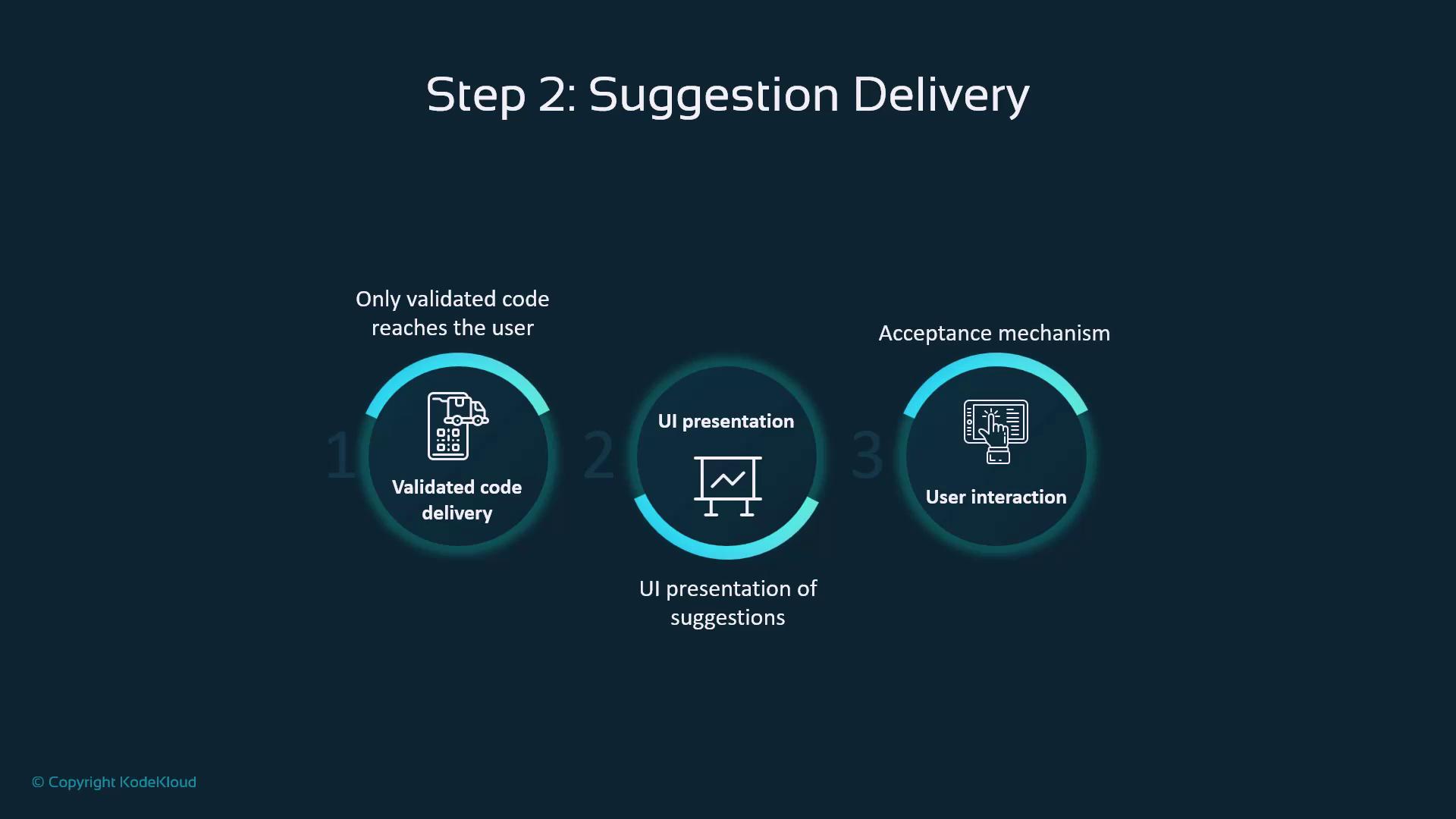
Suggestion Delivery
Once approved, suggestions follow a three-step flow:- Delivery: Transmit validated code
- UI Presentation: Show inline hints in your IDE
- User Interaction: Accept, modify, or reject via shortcuts
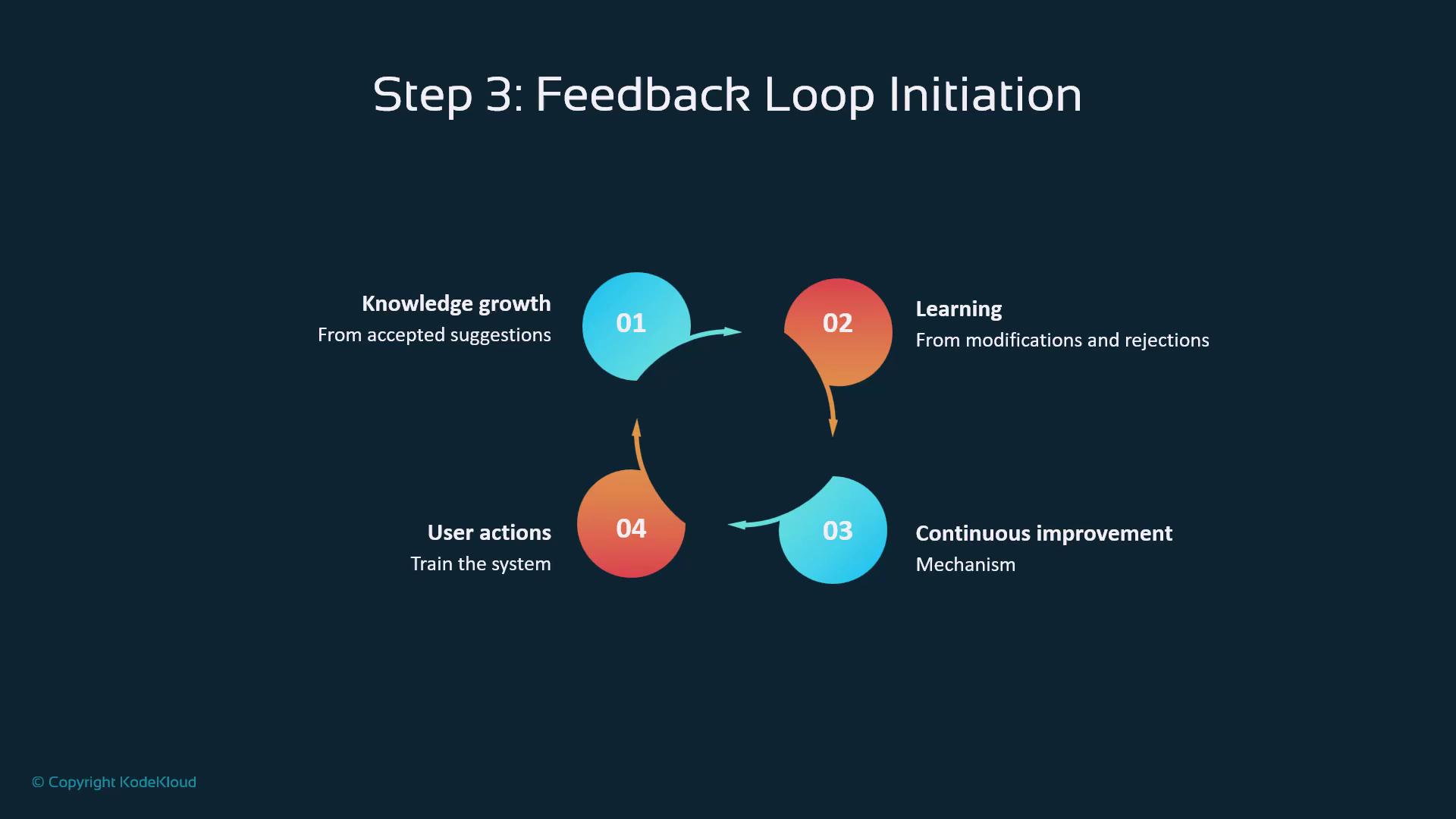
Feedback Loop & Continuous Improvement
Every action—acceptance, edits, or rejections—feeds back into Copilot’s learning system:- Knowledge Growth: Reinforces successful patterns
- Model Learning: Adapts to your coding preferences
- Continuous Refinement: Improves accuracy over time
- User Signals: Shape future suggestions
Writing Effective Prompts
To optimize suggestions:- Be specific about functionality
- Add context via comments
- Include edge cases
- Specify file type and language

Clear, detailed prompts help Copilot deliver precise code snippets. For more guidance, see GitHub Copilot documentation.
Common Prompt Patterns
- Function Descriptions: Define purpose and parameters
- Bug Fixes: Describe current vs. expected behavior
- Refactoring: Specify improvements and structure
- Test Generation: Outline features and frameworks
Prompt Security Best Practices
- Avoid embedding sensitive credentials or proprietary algorithms
- Handle any required sensitive data with care
- Adhere to corporate AI policies
- Uphold data privacy at all times

Never share API keys, secrets, or confidential data directly in your prompts.
Learning Mechanisms
Copilot refines its model through:| Level | Scope |
|---|---|
| Global | Aggregated learnings from all users |
| Project-Specific | Patterns unique to your repository |
| Language & Stack | Framework and language fluency |
| Pattern Recognition | Reusable code structures and idioms |
Administrator Controls
Enterprise settings include:- Public Code Matching filters
- Policy Management for usage standards
- Security Configurations and role-based access
- Compliance Tools for regulatory adherence
Key Takeaways
- Copilot’s pipeline is a secure, multi-stage flow.
- Built-in safeguards maintain quality, security, and ethics.
- Your feedback drives continuous improvement.
- Understanding this flow helps you craft better prompts.
