Why Context Matters
Copilot relies on context to transform from a generic generator into a personalized coding assistant. Supplying the right information up front helps you:- Improve suggestion relevance by guiding Copilot’s understanding
- Minimize back-and-forth clarifications for a smoother workflow
- Boost development efficiency by reducing post-generation edits
Defining Context
Context includes any data provided to the AI model to help it understand your goals:- Open files, project structure, and selected code in your editor
- Terminal output (error messages, command results)
- Project notes, documentation, or design specs
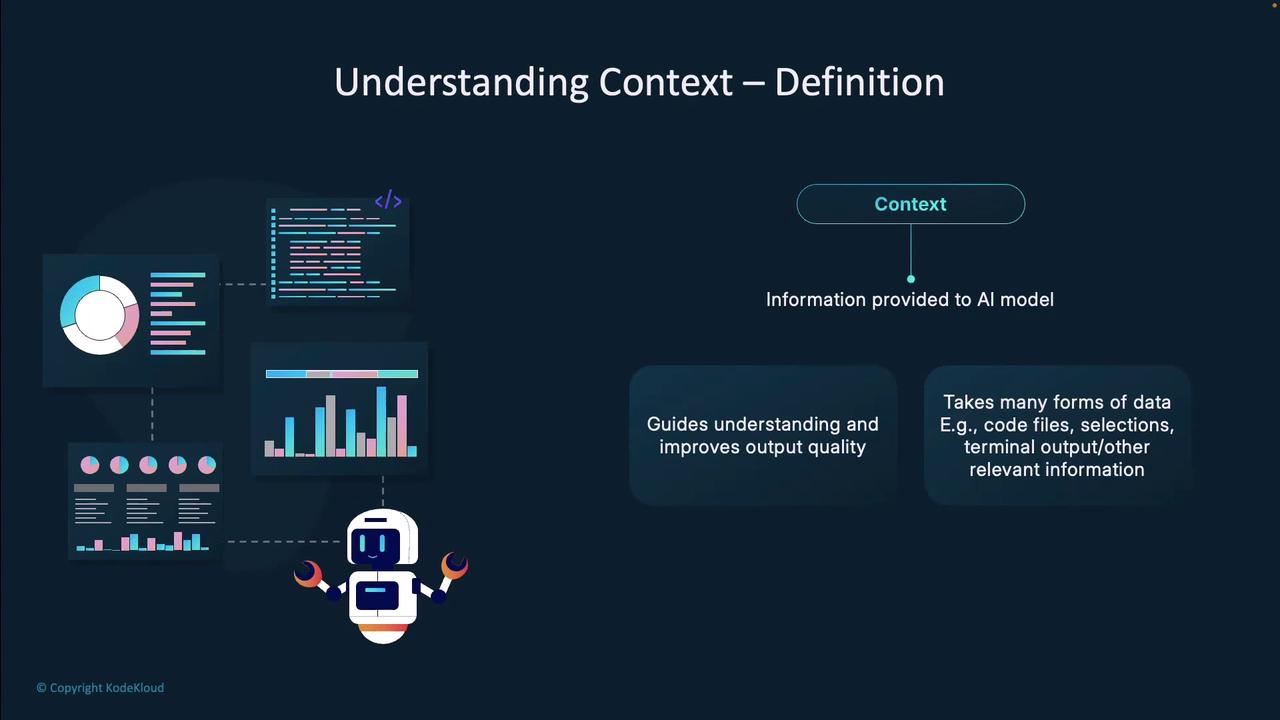
Types of Context
Copilot’s suggestions draw from three primary context sources:| Context Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Files and snippets Copilot auto-selects as relevant | Analyzing prompt to pick matching project files |
| Explicit | Manually supplied via prompts, references, or files | #selection, file attachments |
| Implicit | Derived from open/edited files and selections | Current file buffer and highlighted code |
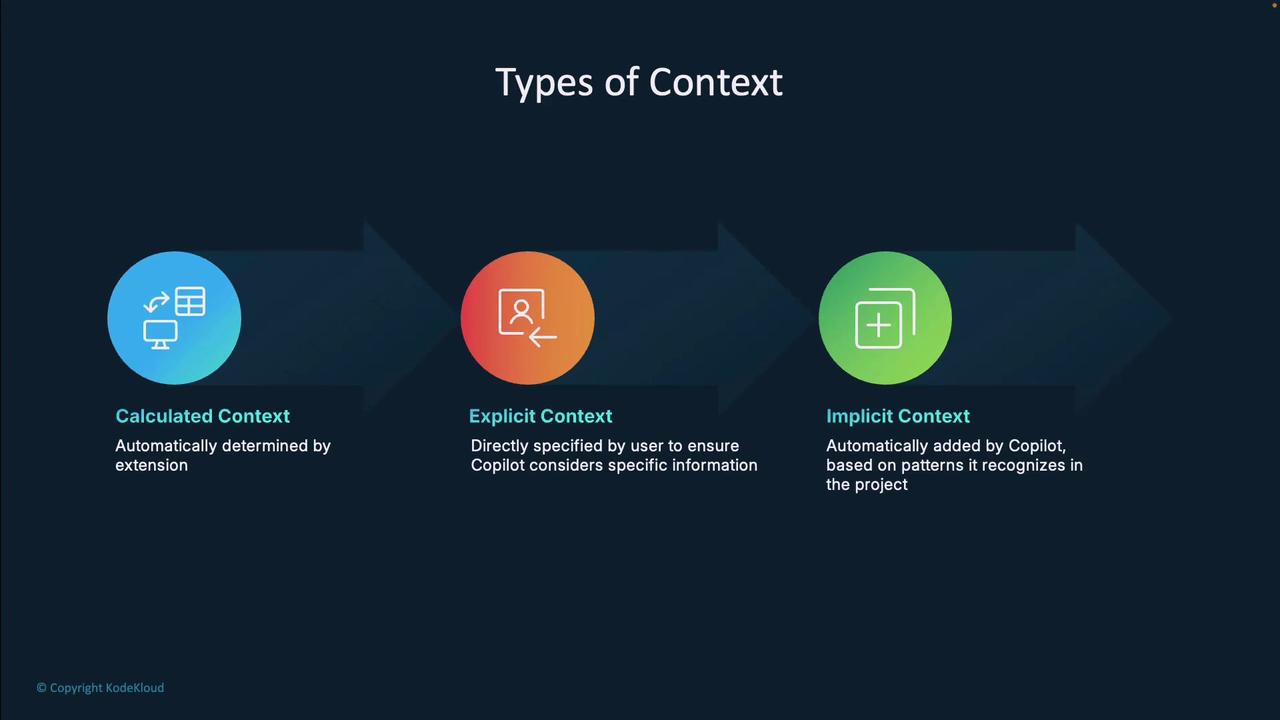
Calculated Context
Calculated context minimizes manual work: Copilot analyzes your request and automatically includes relevant code snippets and files. For instance, in an Agentic Workspace scenario, it selects files that match your prompt criteria.
Explicit Context
Explicit context gives you full control over what Copilot considers. You can specify it by:- Writing clear, descriptive prompts
- Using reference tags like
#selection,#editor, or#file:utils.py - Attaching files or data for Copilot to process
Combine natural language with context references for precise guidance. For example:
“Refactor
“Refactor
#selection to improve error handling in #file:data_loader.py.”Implicit Context
Implicit context is automatically inferred from your workspace activity:- Captures the open file and any selected text
- Can be disabled in settings for more explicit control
In very large codebases, implicit context may include irrelevant files. Disable it in settings to prevent suggestion confusion.

Additional Context Sources
Copilot can reference multiple environment inputs:- Code files & project structure
- Current editor selection
- Terminal output (errors, command results)
- Source control diffs and commits
Specialized Agents
Invoke focused assistants with the@ symbol to tap domain-specific knowledge:
| Agent | Purpose |
|---|---|
| @workspace | Understands project structure & code relationships |
| @terminal | Runs shell commands and interprets output |
| @vscode | Provides VS Code feature guidance |
| @github | Handles GitHub workflows and metadata |
| @azure | (Preview) Assists with Azure service deployments |
Mention
@workspace or @terminal in your query to route questions to the right Copilot agent.
Context Referencing in Prompts
Use these tags to focus Copilot on specific parts of your code:#file:filename.py— Target a particular file#symbol:MyClass— Reference a class, function, or variable#selection— Include only the selected code#editor— Pass the full open file contents
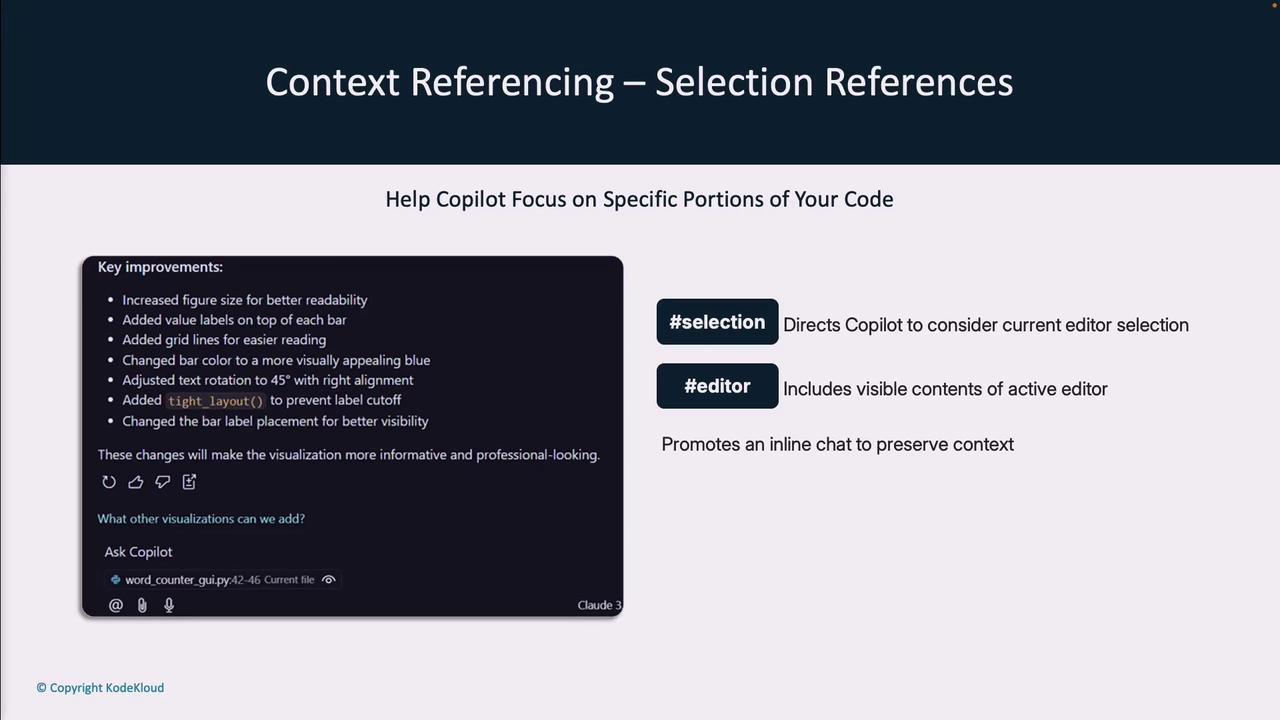
Terminal & Source Control References
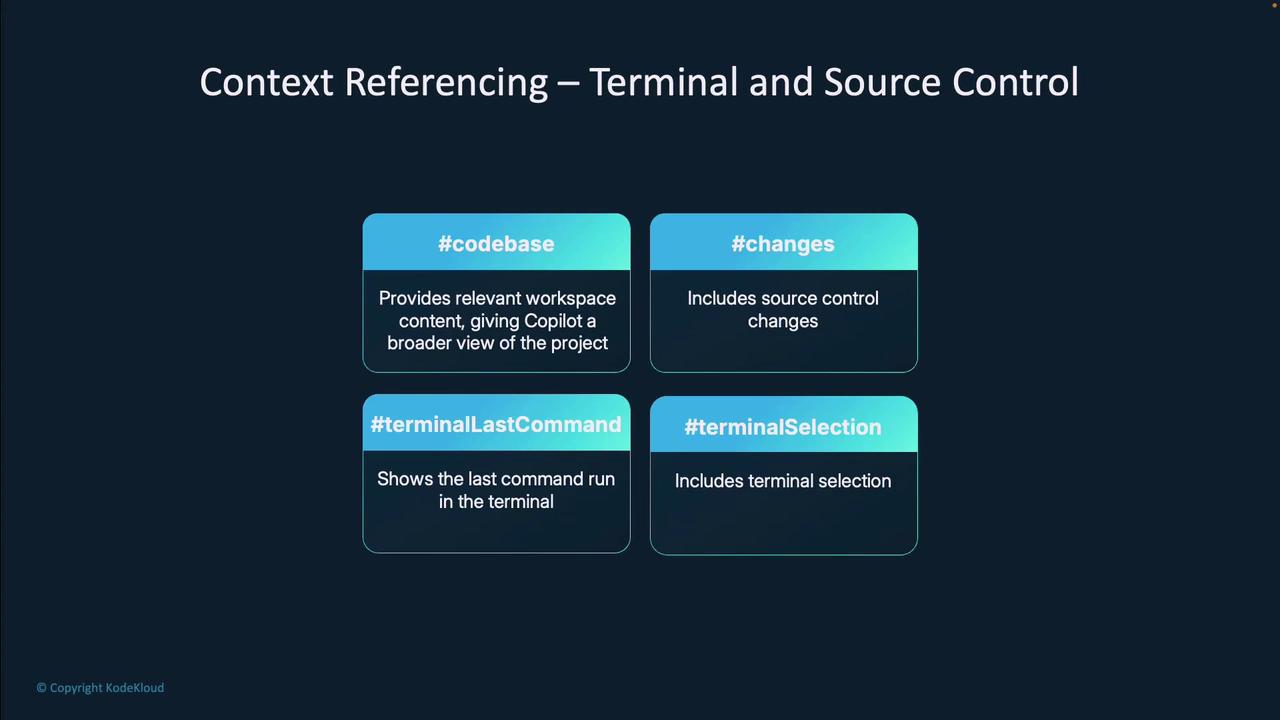
For debugging or reviewing recent changes, include:#codebase— Entire workspace context#changes— Git diffs and staged modifications#terminalLastCommand— Your last executed shell command#terminalSelection— Selected terminal output
Custom Instructions
For ultimate control, add agithub-copilot-instructions.md file in your repo root. Copilot will load these guidelines for every session: