1. Review Aurora PostgreSQL Cluster Configuration
Ensure your Aurora PostgreSQL cluster is deployed regionally with the following setup:| Instance Role | Availability Zone | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Writer | us-east-1a | Available |
| Reader | us-east-1b | Available |
2. Establish Baseline Metrics in CloudWatch
Before running an FIS experiment, capture steady-state performance metrics:- Open the AWS Console and navigate to CloudWatch → X-Ray Trace Map.
- Select your target database (e.g., the
adoptionPostgreSQL cluster). - Set the time range to the last 30 minutes.
| Metric | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Latency | ~2 ms |
| Request Rate | ~26 requests/min |
| Faults | None |
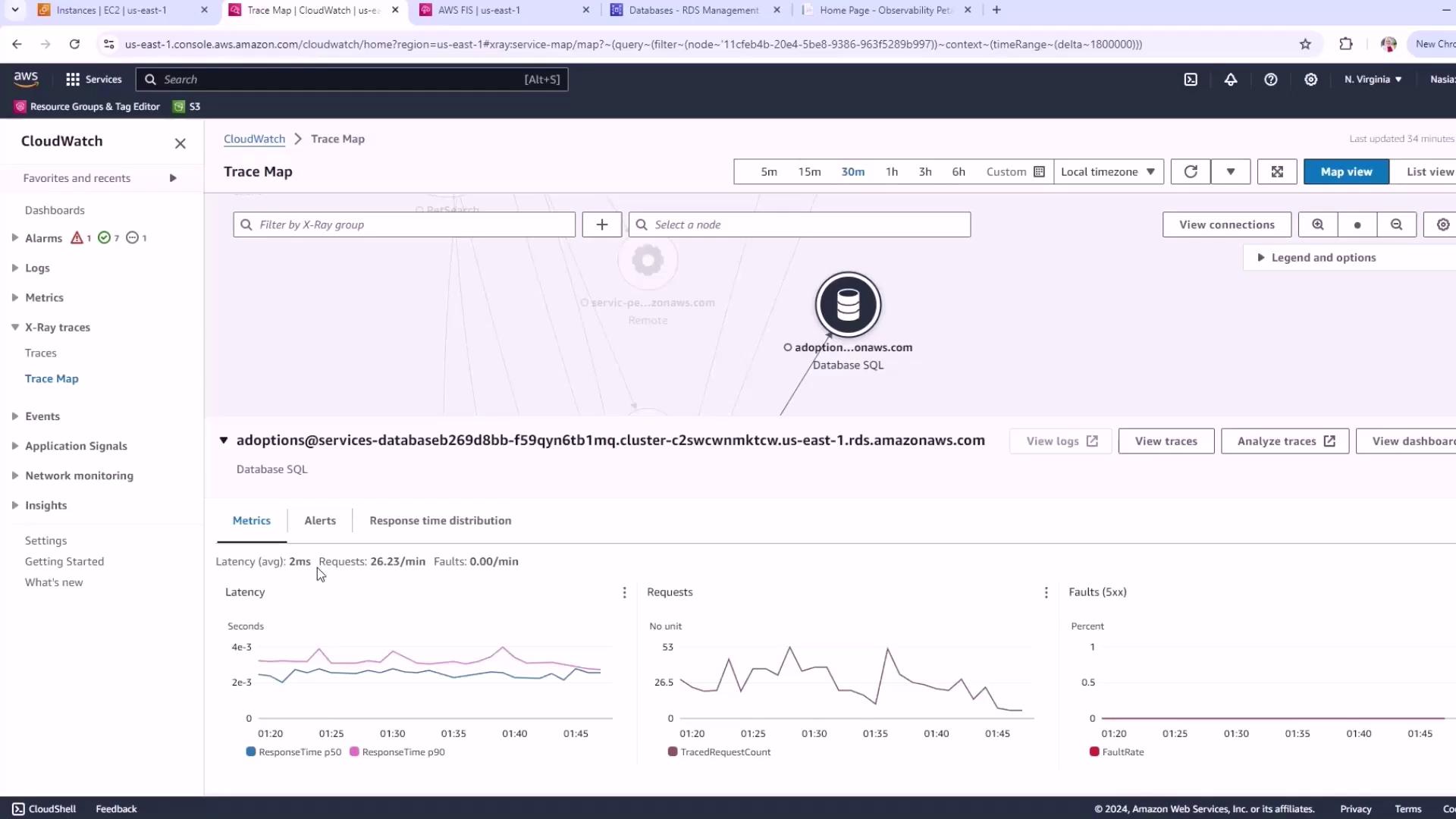
Recording baseline metrics is essential for measuring the impact of your FIS experiments. Always capture steady-state data first.
3. Create an IAM Role for FIS
AWS FIS needs permission to act on your RDS resources and write logs. Follow these steps:- Navigate to IAM → Roles → Create role.
- Under Trusted entity, choose AWS service, then select FIS.
- For Use case, pick RDS.
-
Name the role
FISRDSRole. -
In the Trust policy editor, replace the JSON with:
-
Attach the managed policy
CloudWatchLogsFullAccess(or a least-privilege equivalent) to enable logging.
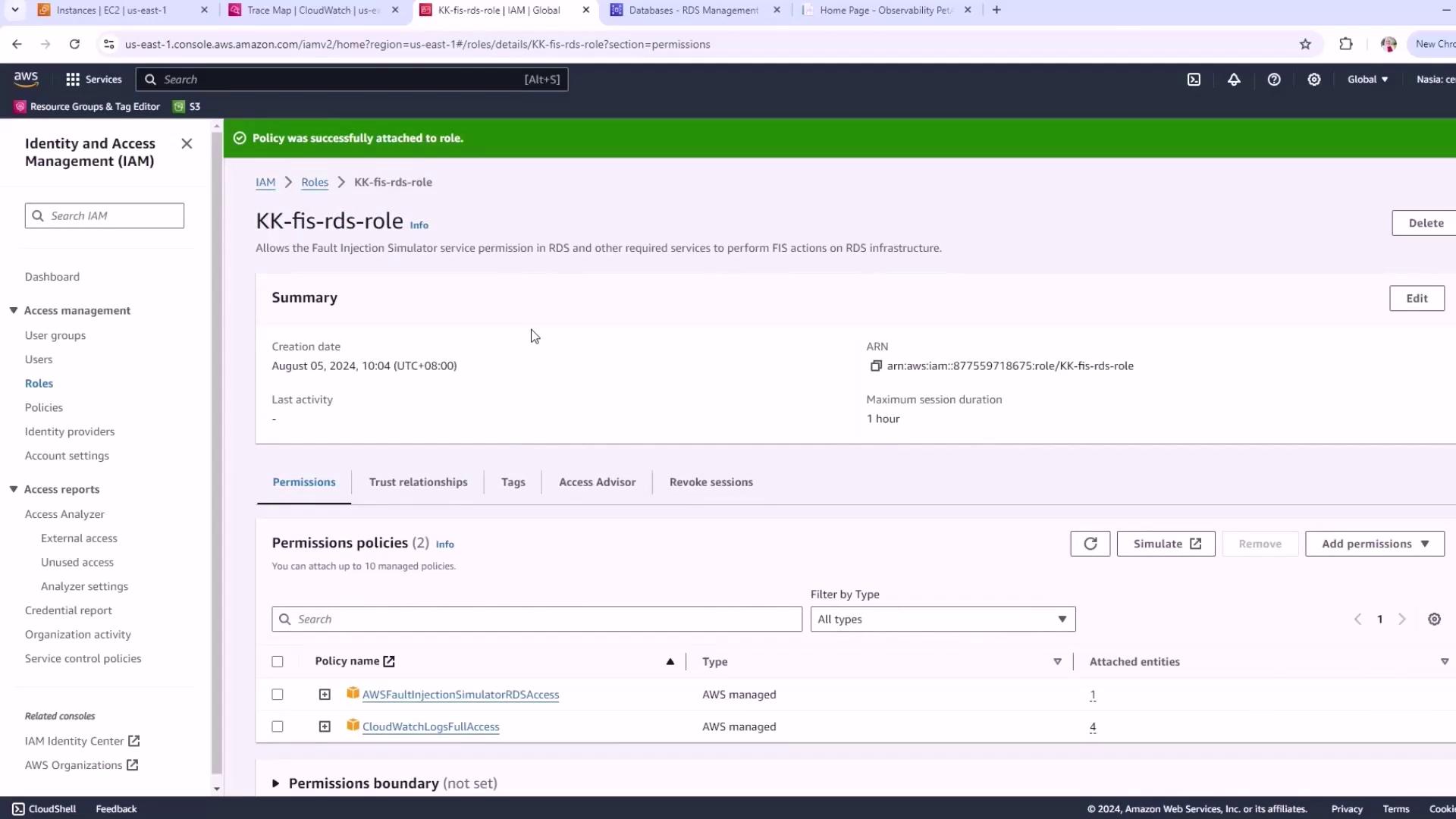
Always follow the principle of least privilege. Grant only the permissions necessary for your FIS experiments to reduce security risks.