Availability Zones vs. Regions
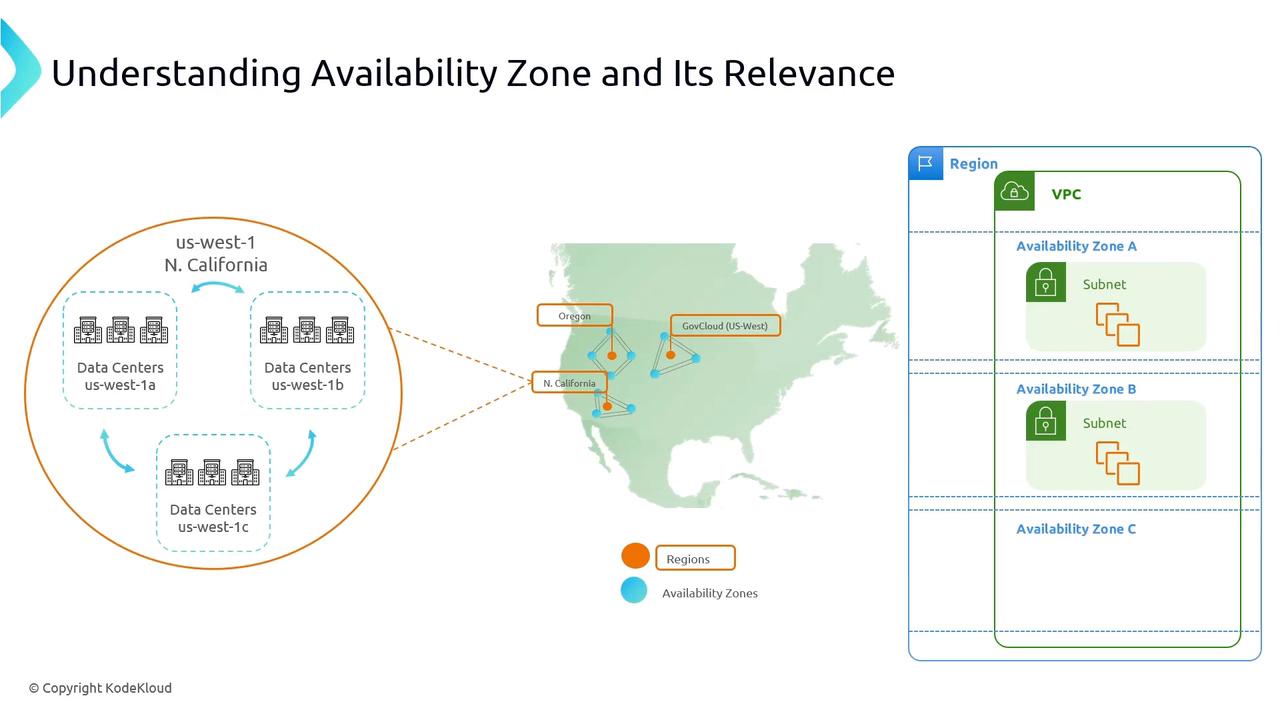
An AWS Region is a geographically isolated area containing multiple, physically separate Availability Zones. Each AZ has its own power, cooling, and network infrastructure, minimizing correlated failures. Key characteristics:- Region: A collection of AZs in the same geographic area (e.g., US West – Northern California
us-west-1). - AZ: A standalone data center within a region, labeled like
us-west-1a,us-west-1b,us-west-1c.
- Fault tolerance: If one AZ suffers a power failure, other AZs in the same region continue operating normally.
- Isolation from regional disasters: An earthquake affecting one region won’t impact other AWS Regions.
| Replication Type | Description | AWS Service Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-AZ replication | Distribute data within the same region | S3, RDS Multi-AZ |
| Cross-region replication | Distribute data across different geographic regions | S3 Cross-Region Replication, RDS Read Replica |
By default, AWS resources are created in the region you select. To replicate resources across regions, you must enable features like S3 Cross-Region Replication or RDS Read Replicas.
AWS Global Regions
AWS operates multiple Regions around the world. Each Region is fully isolated to maximize fault tolerance:| Region | Identifier |
|---|---|
| US West (Northern California) | us-west-1 |
| US West (Oregon) | us-west-2 |
| Asia Pacific (Tokyo) | ap-northeast-1 |
| Asia Pacific (Singapore) | ap-southeast-1 |
| Hong Kong | ap-east-1 |
| …and more | … |
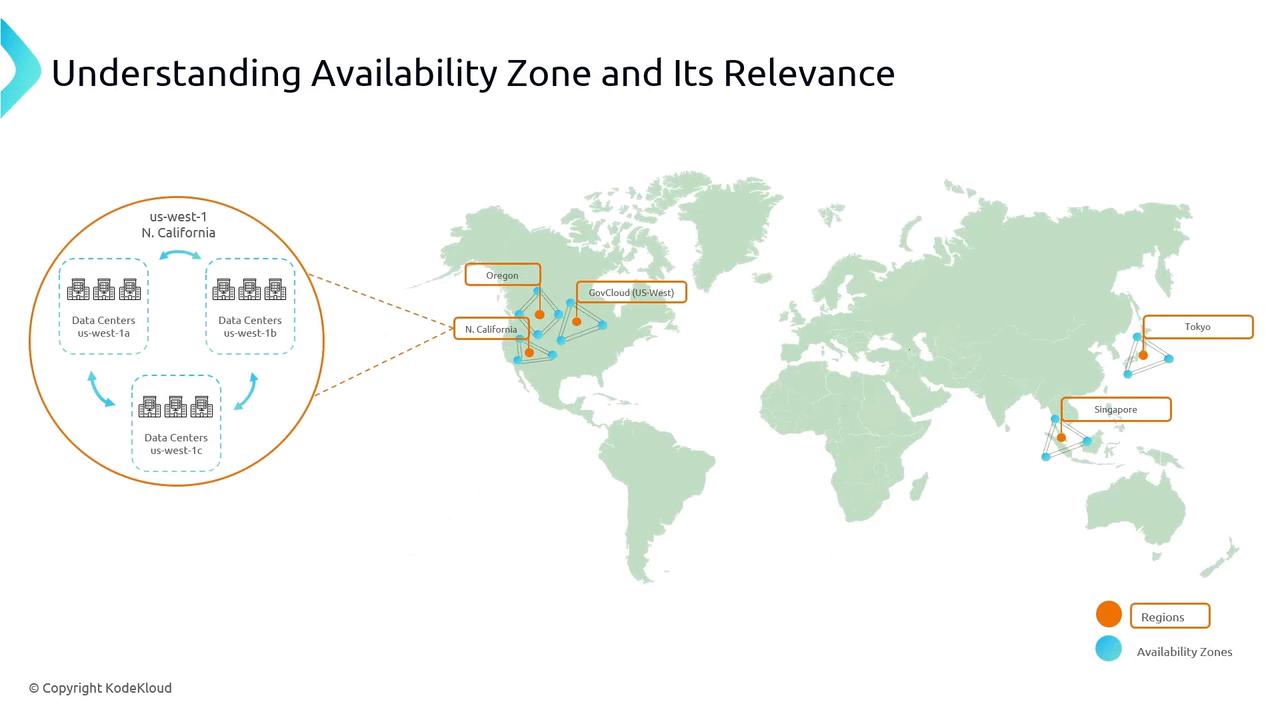
While cross-region architectures deliver maximum resilience against geographic disasters, distributing resources across multiple AZs within a single Region often provides sufficient high availability and lower latency for most applications.