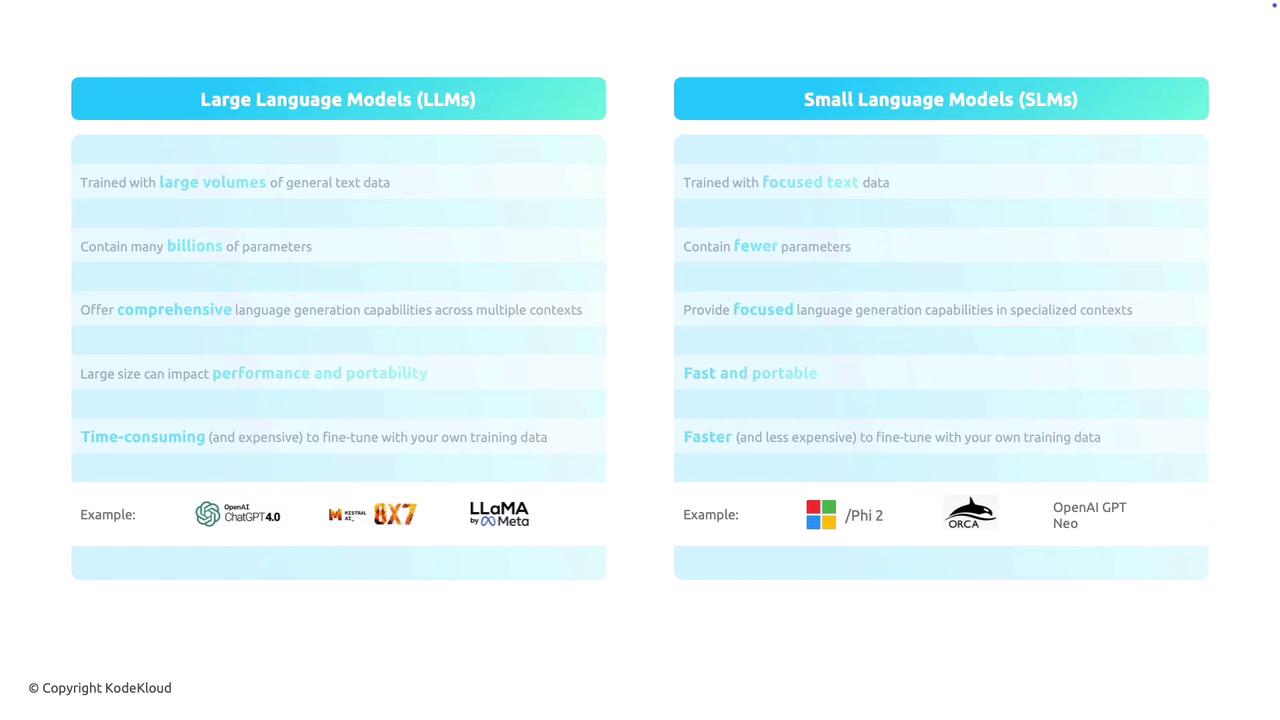
Data and Training
LLMs are trained on extensive, diverse datasets that provide a broad understanding of language. This general training enables them to handle various contexts and subjects. In contrast, SLMs are developed using focused datasets, often tailor-made for specific topics or tasks. This targeted training makes SLMs highly effective within their specialized domains.Model Parameters
One of the defining differences between these models is the number of parameters:- LLMs: Often contain billions of parameters. These extensive parameter sets allow them to model complex language patterns and generate detailed, nuanced text.
- SLMs: Feature fewer parameters, resulting in simpler yet robust models that perform well in their specialized areas.
Capabilities
Each model type excels in different areas:-
LLMs:
- Provide versatile language generation capabilities across multiple contexts.
- Are suitable for a wide range of applications, from creative writing to technical documentation.
-
SLMs:
- Deliver focused language generation that specializes in a particular industry or subject matter.
- Are optimized for efficiency and speed, particularly in targeted use cases.
Performance and Portability
Due to their large size, LLMs typically require significant computational resources, which may limit their portability and affect real-time performance. SLMs, with their leaner architectures, generally offer faster processing and greater portability. These advantages make SLMs ideal for deployment on devices with limited resources.When deciding between an LLM and an SLM, consider the trade-off between the model’s versatility and deployment efficiency.
Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning is a critical step in adapting a model for specific tasks:- LLMs:
- Fine-tuning these expansive models can be resource-intensive and expensive due to their complexity.
- SLMs:
- Their streamlined design allows for quicker and less costly fine-tuning, making them practical for targeted applications.
Examples
Below are examples of models in each category:Large Language Models (LLMs)
Examples include:- OpenAI’s GPT-4.0
- Mistral 7b
- LLaMA 3
Small Language Models (SLMs)
Examples include:- Microsoft Copilot
- ORCAD 2
- OpenAI GPT Neo