Creating the Jenkins Project
Begin by logging in to your Jenkins instance and navigating to the dashboard. Click on “New Item” (or the plus icon) to create a new job. You will be prompted to enter a name for your project and choose the type of job. The available options depend on the plugins installed on your Jenkins server. For this tutorial, select the Freestyle Project and name it “generate ASCII artwork.”
Configuring the Job
After selecting the Freestyle Project, you will see several configuration sections:- General
- Source Control Management (SCM)
- Build Triggers
- Build Environment
- Build Steps
- Post-build Actions

Adding the Build Steps
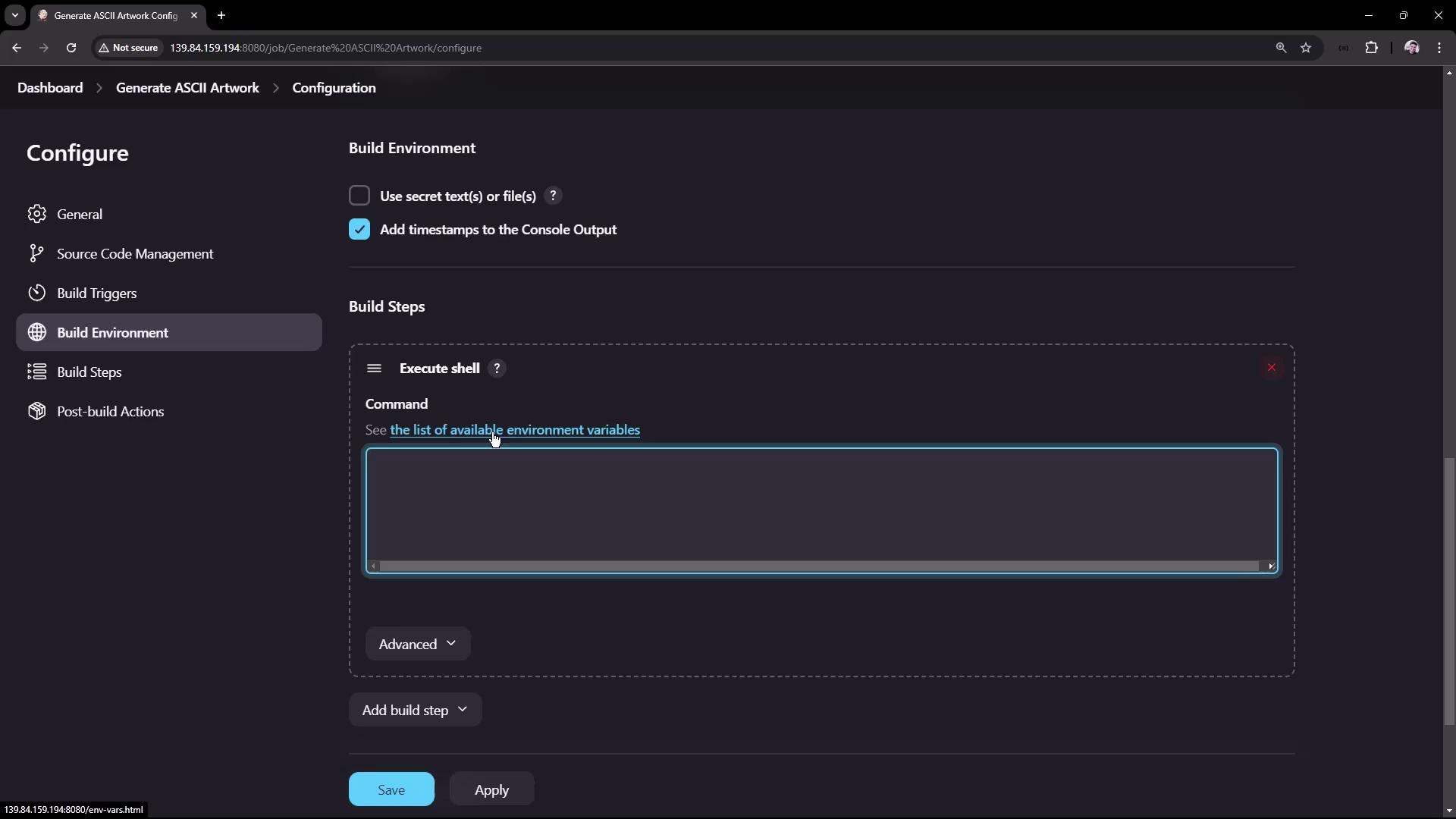
Within the Build Steps section, add a new build step by selecting the shell script execution option. Depending on your environment, you can choose either a Windows batch command or a shell script. In this example, we are using shell commands.
- Fetches advice from the AdviceSlip REST API and saves it as a JSON file.
- Uses the jq tool to extract the advice text and verifies if it contains more than five words.
- Installs the cowsay library if it is not already installed.
- Updates the PATH variable so that Jenkins can locate the cowsay command.
- Pipes the advice text through cowsay to generate the ASCII artwork output.
Ensure that your Jenkins instance has the necessary plugins installed, such as the Timestamp Plugin, and that the system has access to both the jq tool and curl command.
Understanding the Shell Script
When the build is triggered, the following steps occur:-
The script uses
curlto fetch a piece of advice from the API, saving the JSON output toadvice.json. A typical JSON response looks like this: -
The jq command extracts the advice (
.slip.advice) from the JSON file and stores it inadvice.message. - A word count check is performed on the extracted advice. If the advice contains more than five words, a confirmation message is printed; otherwise, an error message is output, potentially marking the build as failed.
-
The script installs the cowsay library using
apt-get(if it is not already installed) and updates the PATH variable to include directories where the cowsay command is located. This update is necessary because the Jenkins environment might not include/usr/gamesor/usr/local/gamesin its PATH. -
Finally, the advice is piped through cowsay, which randomly selects a cow file from
/usr/share/cowsay/cows(usingshuf) to generate ASCII artwork in the Jenkins console output.
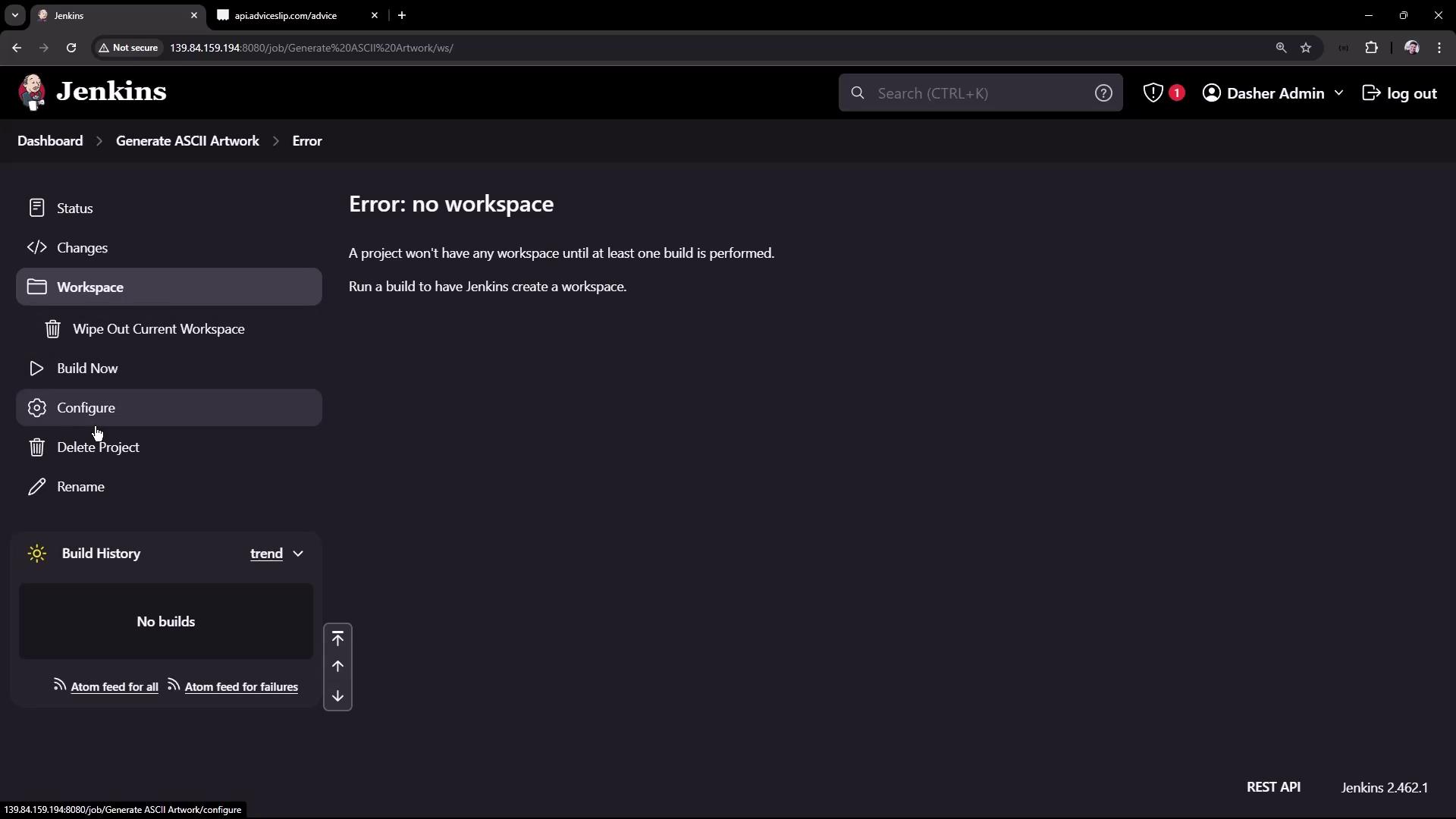
Build Execution and Diagnostics
Once you save the configuration, the project dashboard will display the project description, build status, and workspace details. The workspace is created under the Jenkins home directory, storing any generated files likeadvice.json and advice.message.
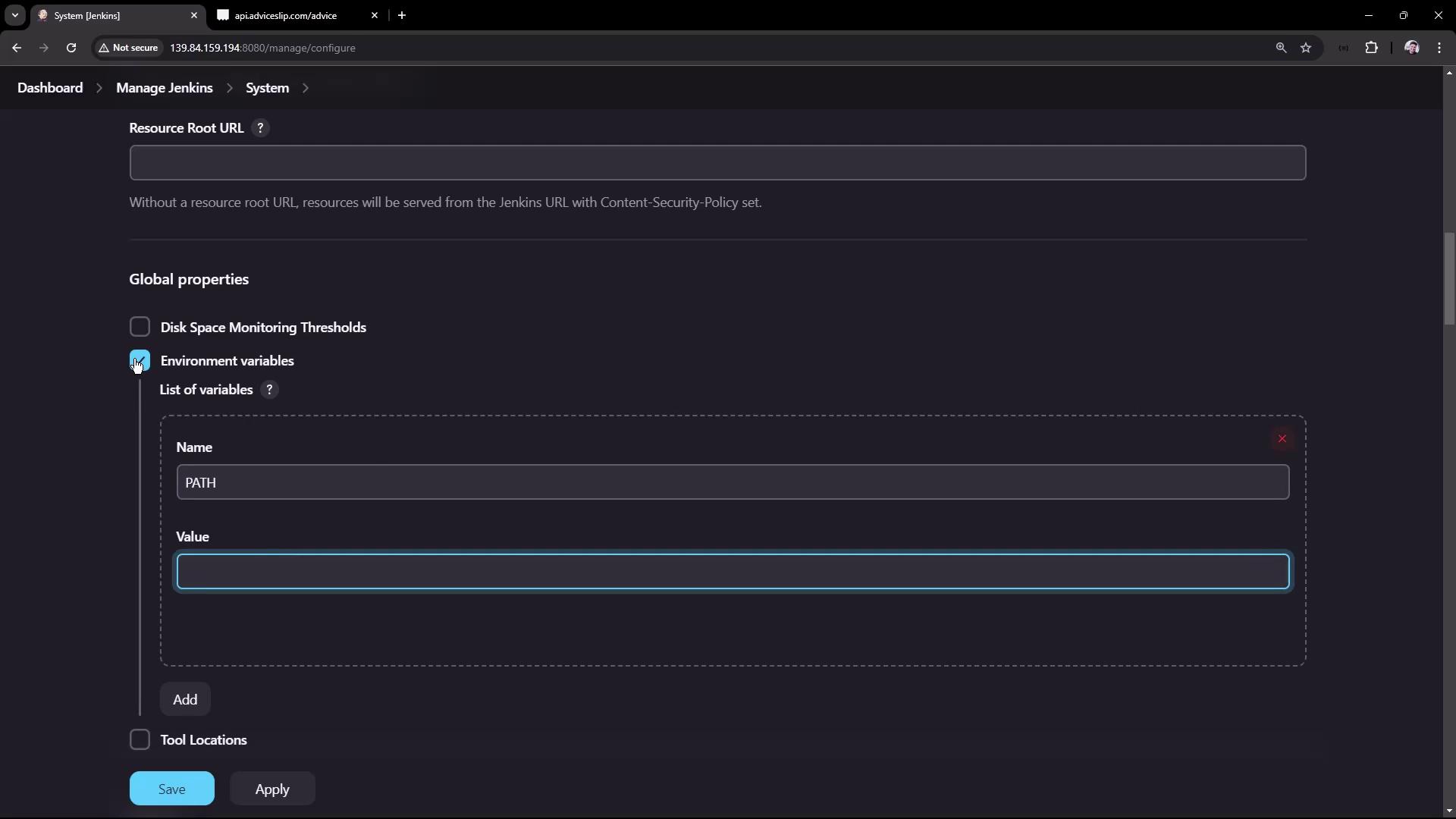
cowsay command was not found. The solution is to update the PATH variable inside your job configuration (as shown in the script above) or configure the global environment variables in Jenkins to include the required directories.
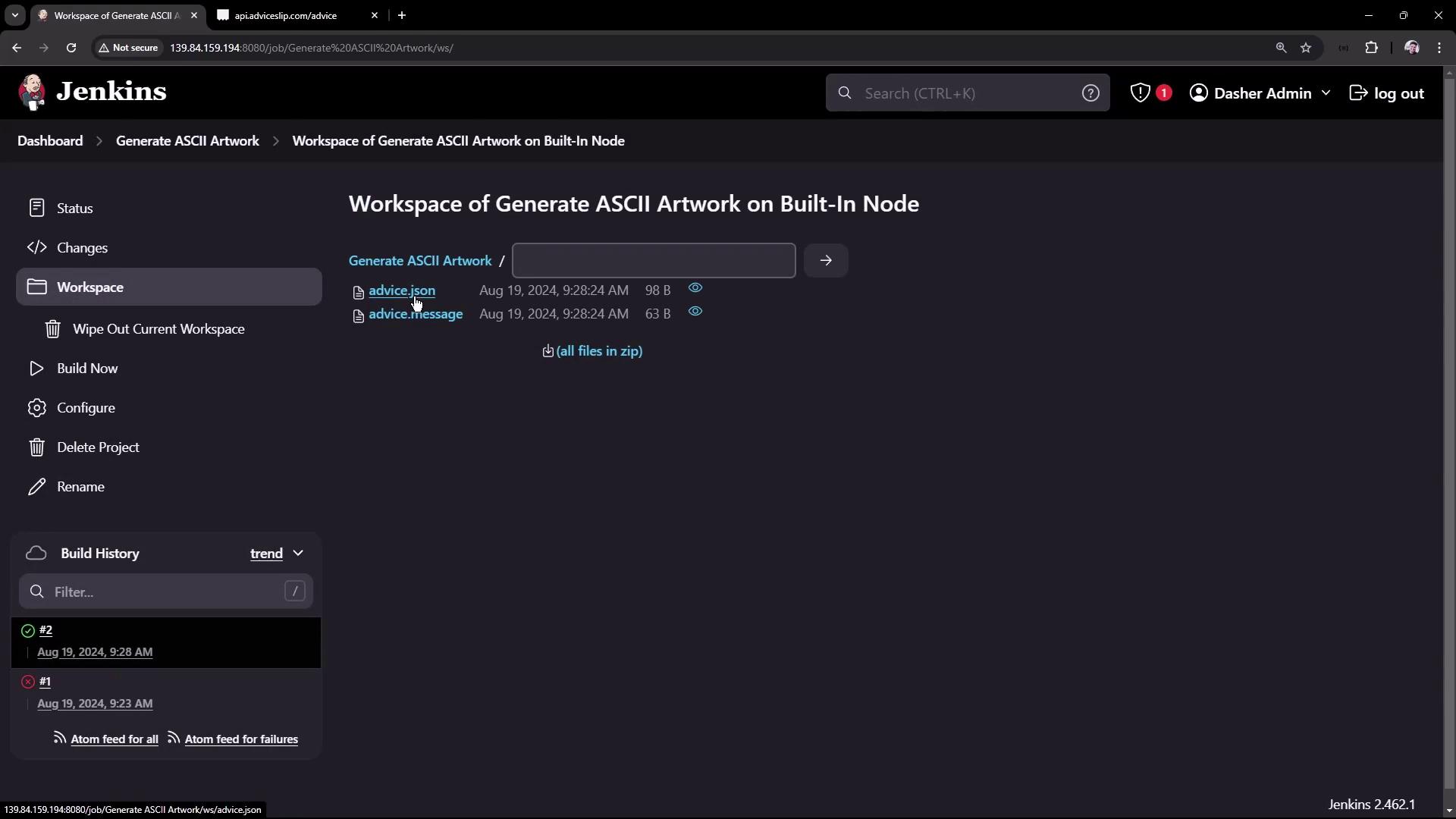
Reviewing the Workspace
After a successful build, the workspace will include the generated files (advice.json and advice.message). These files can be reviewed on the Jenkins workspace page or accessed directly via SSH/terminal on the Jenkins server. Below is an example of a sample advice.json:
Summary
In this article, you learned how to set up a Jenkins Freestyle Job that:- Fetches dynamic data from a REST API.
- Processes JSON data using the jq tool.
- Validates the advice message to ensure it meets a minimum word count.
- Installs and utilizes the cowsay library to render the advice as ASCII artwork.