Apache Kafka powers mission-critical, event-driven architectures in the financial services sector. In this guide, we’ll walk through a real-world use case—processing millions of financial transactions in real time—highlighting how Kafka’s scalable, fault-tolerant design enables compliant, low-latency operations.
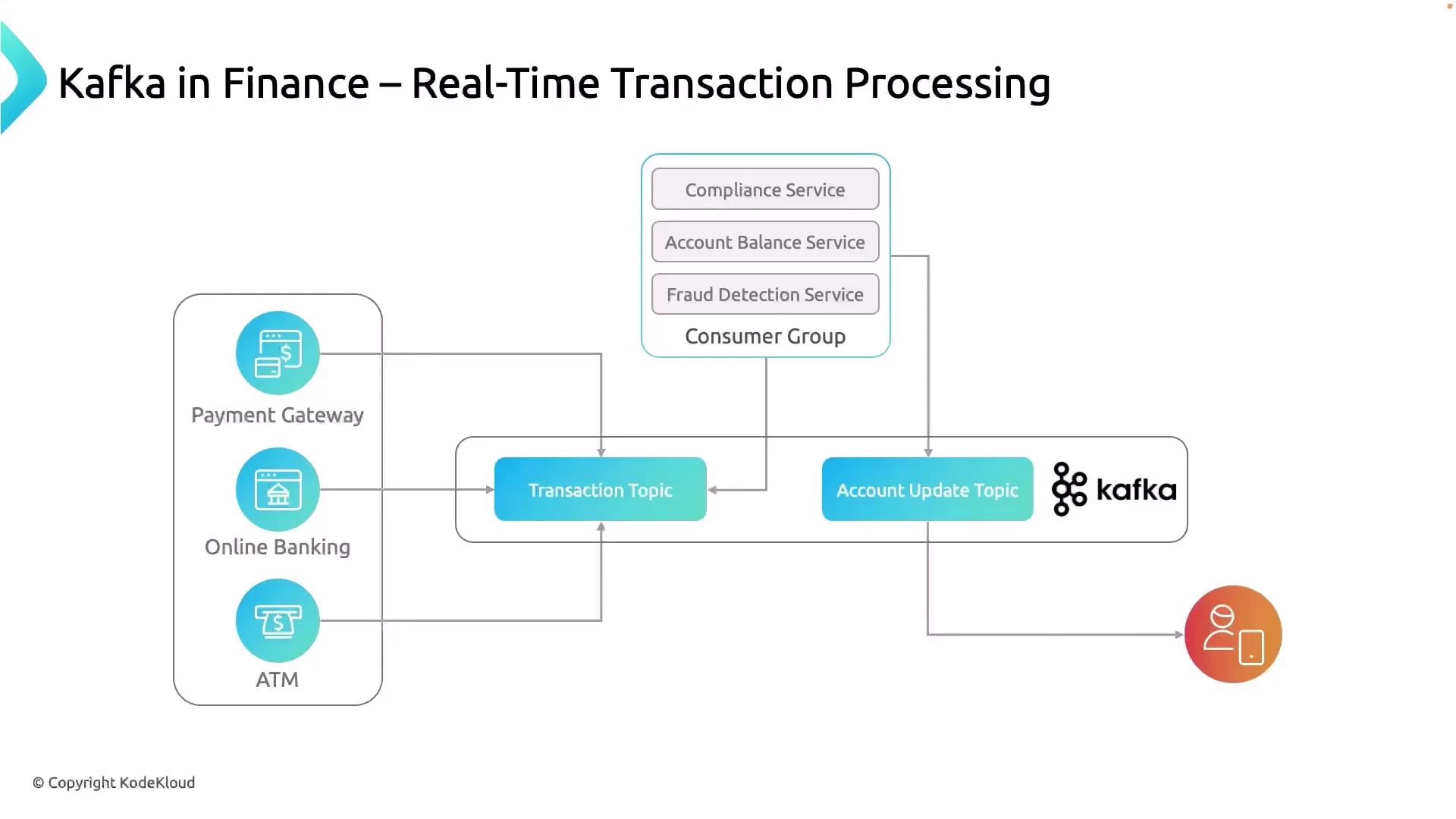
Overview of Transaction Data Flow
Multiple channels (payment gateways, online banking, ATMs) generate transaction events.
Producers publish these events to a central Kafka topic (transactions-topic).
Downstream microservices consume, process, and enrich the data.
Final account updates are emitted to another topic (account-updates-topic) and delivered to end users.
In Kafka, a topic is an ordered, append-only log. Producers write messages to a topic, and consumers read them in the same order they were produced.
Data Producers Channel Description Kafka Topic Payment Gateways Credit/debit cards, UPI, QR code systems transactions-topicOnline Banking Portals Web and mobile banking interfaces transactions-topicATM Networks Cash withdrawals and deposits transactions-topic
Example: Producing a Transaction Event kafka-console-producer \ --broker-list broker1:9092 \ --topic transactions-topic
Once a customer initiates a payment, the event is published here for downstream processing.
Data Consumers Service Responsibility Input Topic Output Topic Compliance Service Enforce regulatory and business rules transactions-topic(none) Fraud-Detection Service Rule-based or ML-driven anomaly detection transactions-topic(none) Balance-Updater Service Update account balances, then publish account state changes transactions-topicaccount-updates-topicNotification Service Notify customers of debits, credits, or holds account-updates-topic(none)
Example: Consuming Account Updates kafka-console-consumer \ --bootstrap-server broker1:9092 \ --topic account-updates-topic \ --from-beginning
End-to-End Flow Diagram Benefits of Kafka for Real-time Transactions Feature Financial Impact High Throughput & Low Latency Process thousands of transactions per second Scalability via Partitioning On-demand scaling for peak loads (e.g., Black Friday) Fault Tolerance & Durability Multi-region replication for high availability Loose Coupling in Microservices Independent SDLC, simplified maintenance and upgrades
Stream millions of events with predictable performance
Meet strict SLA and compliance requirements
Integrate seamlessly with ML models for real-time risk scoring
Additional Use Cases in Finance Beyond transaction processing, Kafka enables:
Real-time market data streaming
Trade reconciliation and clearing
Risk analysis and reporting
Customer 360° profiles via event sourcing
References