Docker Toolbox
Docker Toolbox is the legacy method for running Docker on Windows. Imagine working on a Windows laptop without direct access to a Linux system—whether in a lab or the cloud—but still wanting to experiment with Docker. In such cases, you can install virtualization software (such as Oracle VirtualBox or VMware Workstation) on your Windows machine and deploy a Linux virtual machine (for example, Ubuntu or Debian). Once Docker is installed on the Linux VM, you’re ready to experiment. Docker Toolbox simplifies this process by bundling several components together:- Oracle VirtualBox
- Docker Engine
- Docker Machine
- Docker Compose
- Kitematic (a graphical user interface)

- Your operating system must be 64-bit Windows 7 or higher.
- Virtualization must be enabled on your system.
Docker Toolbox is ideal for legacy Windows systems that do not qualify for the newer Docker Desktop option.

Docker Desktop for Windows
Docker Desktop for Windows is the modern solution that leverages Microsoft’s native virtualization technology, Hyper-V, rather than relying on third-party VirtualBox. During installation, Docker Desktop automatically creates a Linux VM through Hyper-V, on which Docker runs seamlessly. Docker Desktop for Windows is supported only on:- Windows 10 Enterprise or Professional Edition.
- Windows Server 2016.
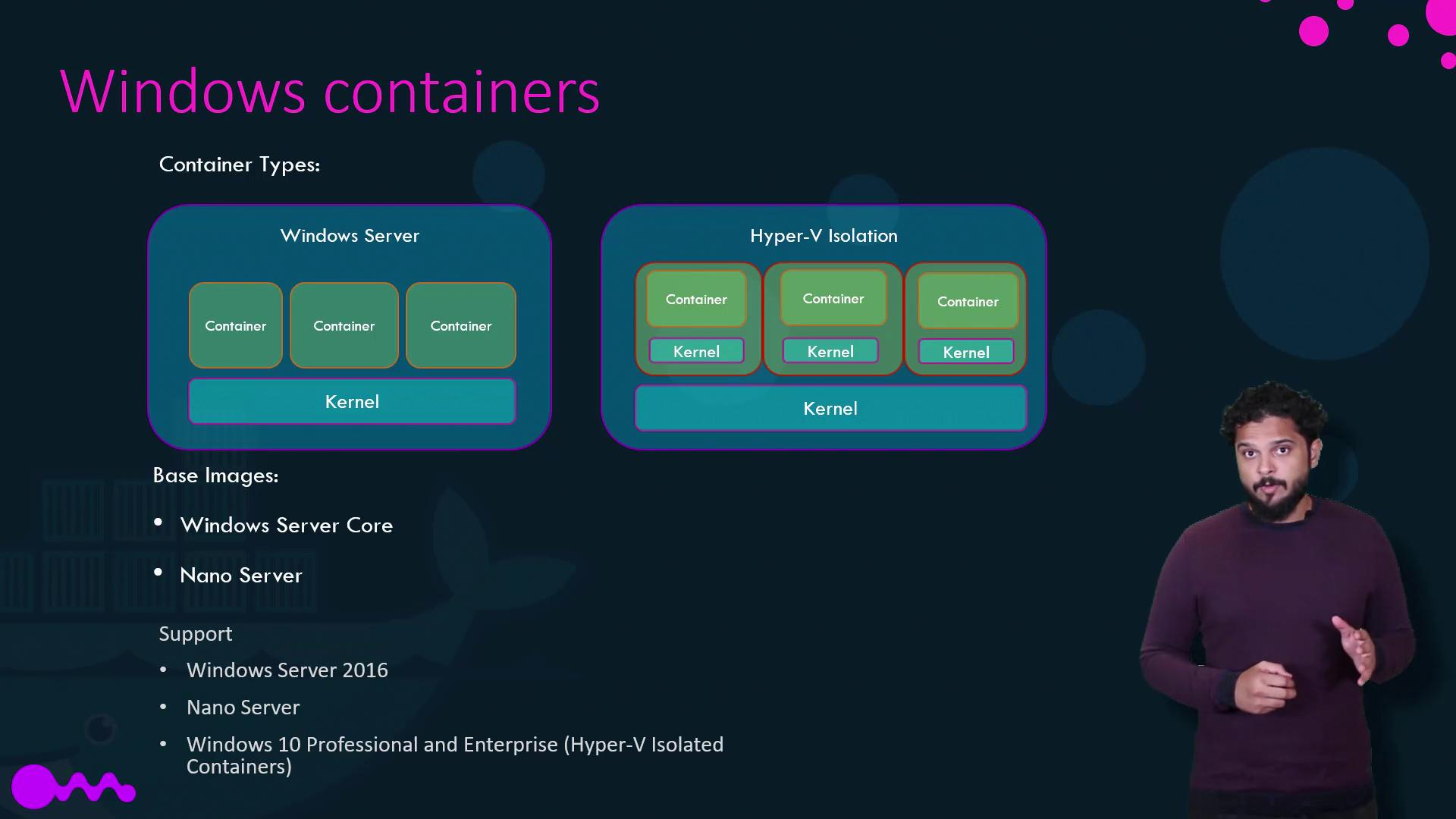
| Container Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Windows Server Containers | Share the host’s kernel, similar to Linux containers. |
| Hyper-V Isolated Containers | Each container runs inside a highly optimized virtual machine for kernel isolation. |
- Windows Server Core
- Nano Server (a lightweight, headless deployment option, akin to Alpine in Linux)
Final Considerations
Before switching between Docker Toolbox and Docker Desktop, be aware of an important limitation:VirtualBox and Hyper-V cannot coexist on the same Windows host. If you initially set up Docker Toolbox using VirtualBox and later decide to transition to Docker Desktop with Hyper-V, you must remove or disable the VirtualBox-based setup. Refer to Docker’s official migration guide for detailed instructions.