Key Components of a Resource-Based Policy
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Version | Defines the policy language version (e.g., 2012-10-17). |
| Statement | Contains one or more permission statements. |
| Principal | Specifies the AWS entity (user, role, account, or group) to which the policy applies. |
| Effect | Indicates whether to Allow or Deny specified actions. |
| Action | Lists AWS operations (for example, s3:DeleteObject). |
| Resource | Defines the ARN(s) of the target resource(s). |
Example: Explicit Deny in an S3 Bucket Policy
The following policy blocks theaccounting group from deleting objects or the bucket itself in the accounting1 S3 bucket:
Explicit denies always override any allows. Ensure you review all policies for unintended deny statements.
IAM Policy Evaluation Logic
When multiple statements or policies apply to a request, AWS evaluates them in this order:| Order | Evaluation Step | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Explicit Deny present | Request is denied immediately. |
| 2 | Explicit Allow (no Deny) | Request is granted. |
| 3 | Neither Deny nor Allow | Request is implicitly denied. |
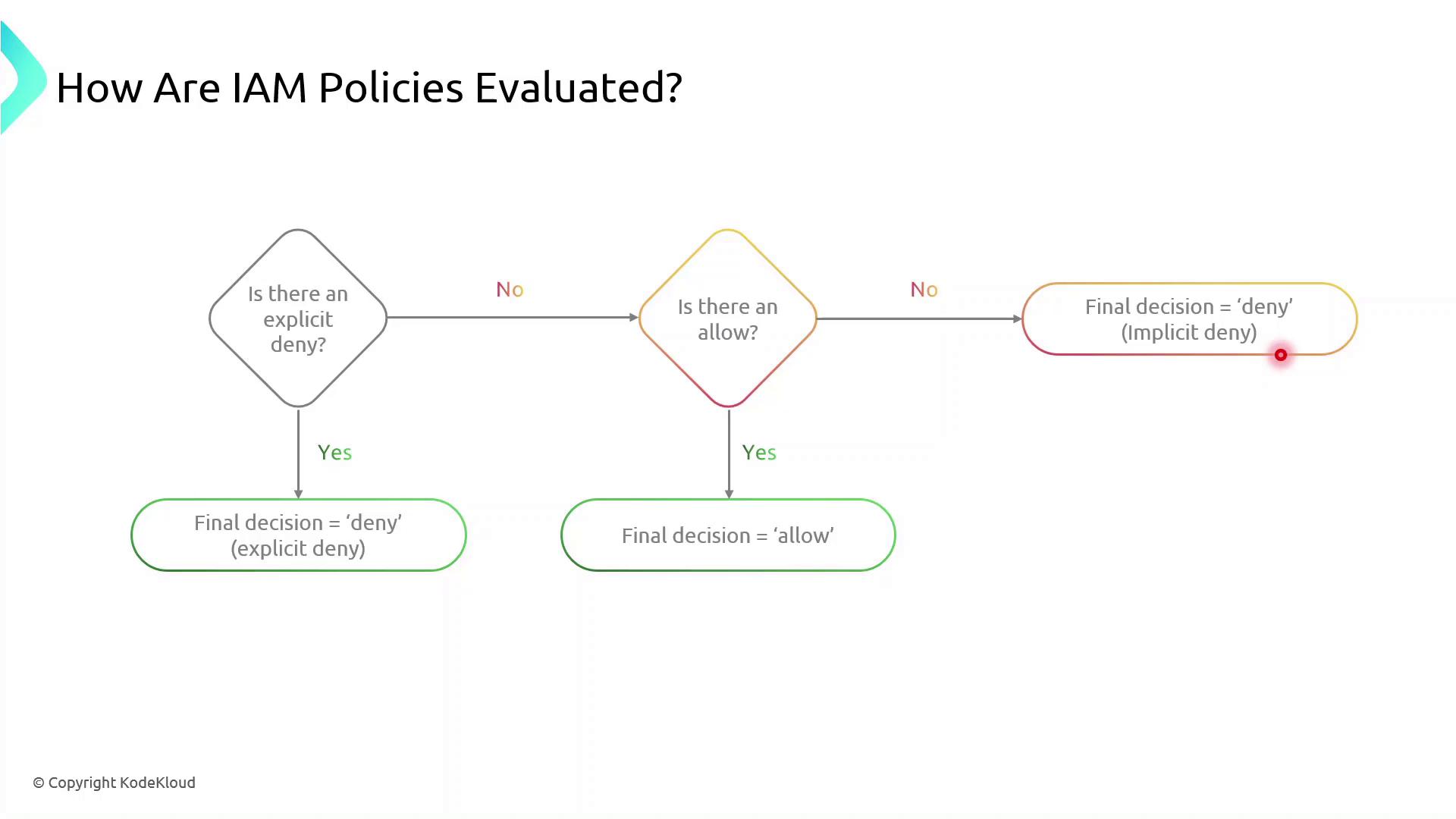
Implicit denies occur when no policy explicitly allows an action. You must explicitly allow all required operations.
Creating and Attaching Your S3 Bucket Policy
Follow these steps to apply a resource-based policy to an S3 bucket:- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- Open the IAM service and choose Policies.
- Click Create policy, then select JSON.
- Paste your policy document and review.
- Attach the policy to the target S3 bucket under the Permissions tab.
Make sure you have the necessary IAM permissions to create and attach policies. Failure to do so will result in authorization errors.