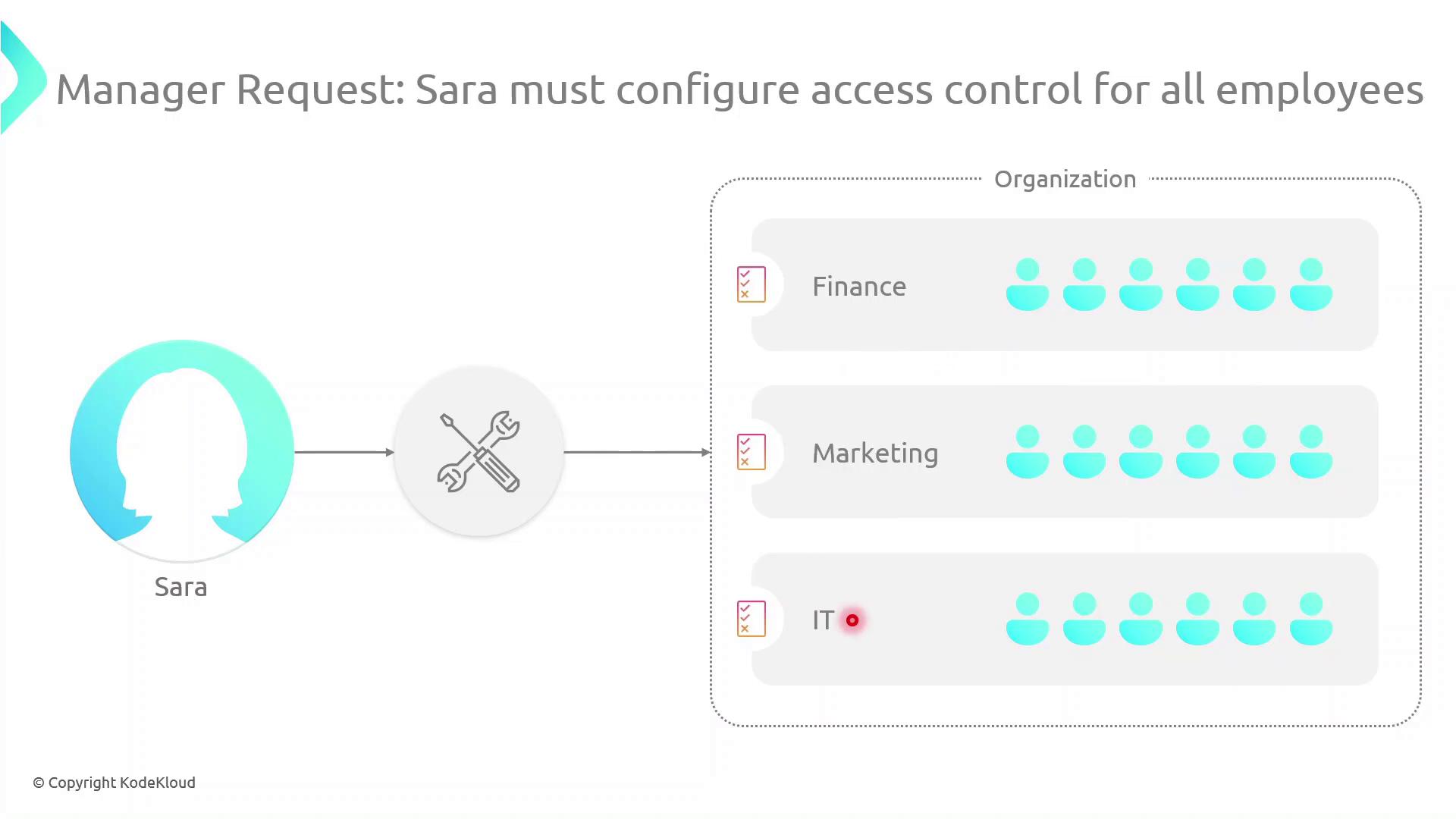
Scenario: Organizing Roles and Permissions
Sarah must implement access controls across multiple departments. Her workflow includes:- Mapping each department and listing team members’ responsibilities (e.g., John in HR handles onboarding).
- Identifying required AWS resources and permission levels for every user.
- Crafting IAM policies—collections of permissions tied to resources.
- Creating IAM groups for teams with similar roles and attaching the appropriate policies.
- Attaching inline policies to users, groups, or roles for unique scenarios.
- Applying resource-based policies (e.g., for S3 buckets) where needed.

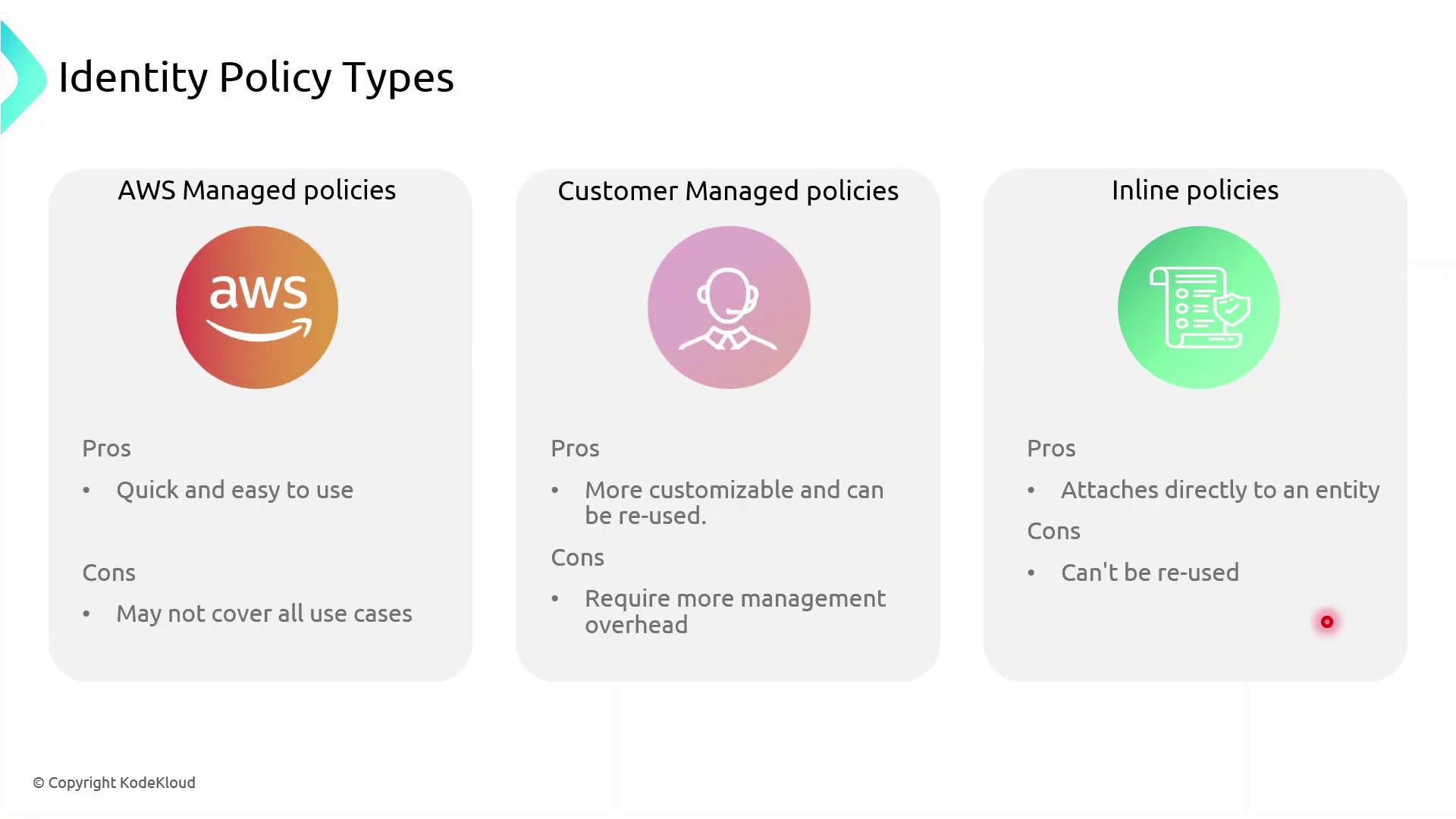
Types of Identity-Based Policies
AWS IAM supports three identity-based policy types:- AWS Managed Policies: Predefined and maintained by AWS.
- Customer Managed Policies: Custom, reusable policies you create and maintain.
- Inline Policies: Embedded within a single user, group, or role; not reusable.
Policy Comparison Table
| Policy Type | Maintenance | Reuse | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Managed Policy | AWS-maintained | High | Common permissions across multiple accounts |
| Customer Managed Policy | Customer-maintained | Medium | Tailored permissions shared across teams or projects |
| Inline Policy | Entity-specific | None | One-off exceptions and tightly scoped use cases |
AWS managed policies simplify administration, but they may not cover every custom scenario. Use customer managed policies for greater control, and reserve inline policies for exceptional cases.
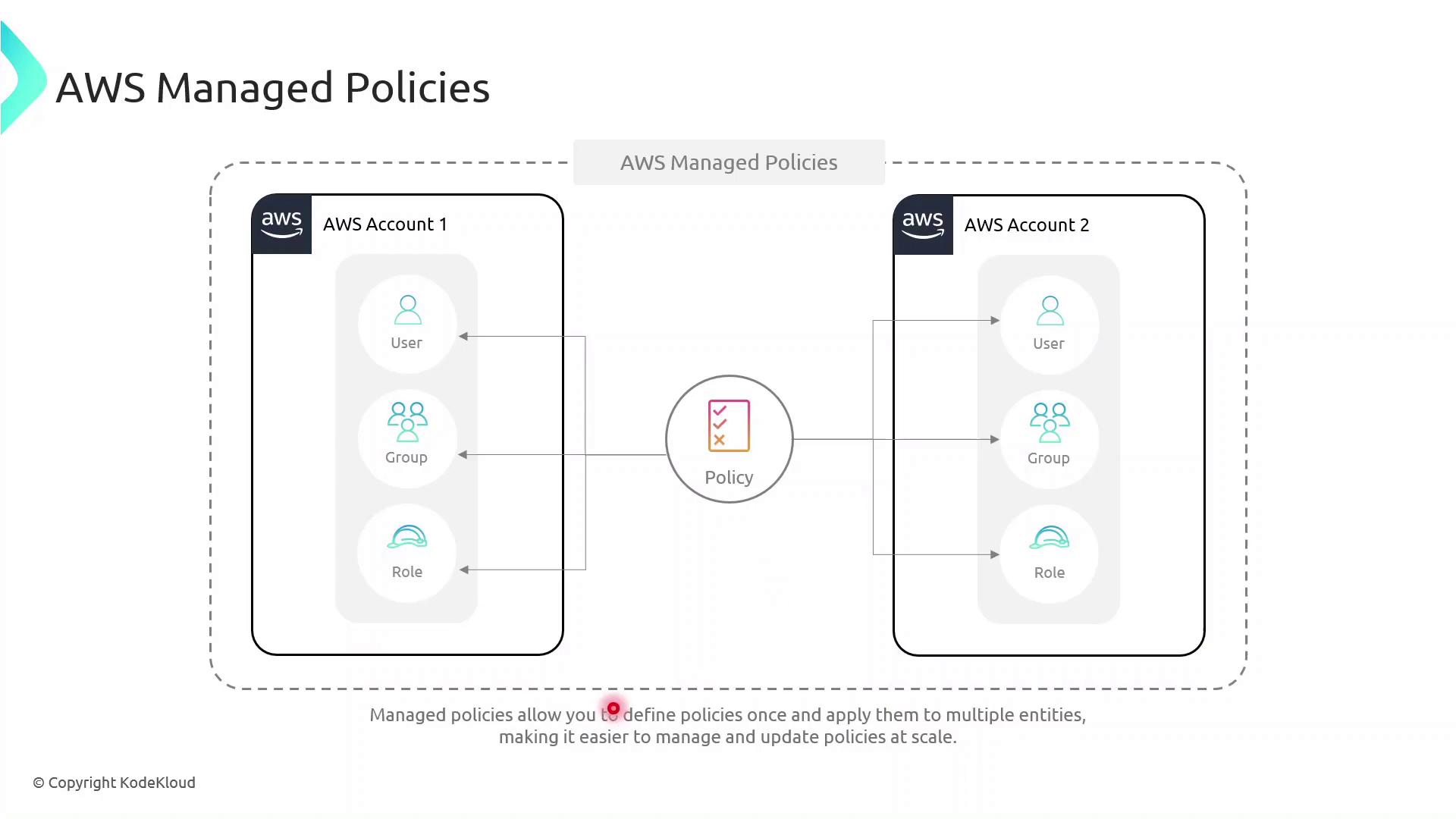
Inline vs Managed: Key Differences
- Inline Policies attach directly to a single IAM entity (user, group, or role).
- AWS Managed Policies exist as separate objects and can be attached to multiple entities, even across AWS accounts, reducing duplication.
Demo: Granting Temporary S3 Access
In this example, we give the DevOps engineer, Alice, limited S3 access until year-end using a customer managed policy with a date-based condition. Create the JSON policy documenttemporary_s3_access_policy.json:
Replace
123456789012 with your actual AWS account ID before running these commands.Next Steps
- Explore multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Learn about identity federation and STS for single sign-on.
- Configure AWS Resource Access Manager to share resources across accounts.
- Set up VPC endpoints to control network traffic to AWS services.