What Is Amazon EFS?
EFS delivers a fully managed, elastic NFS file system that automatically scales storage up and down as you add or remove files. It abstracts away capacity planning and low-level configuration, letting developers focus on applications.EFS provides NFSv4.1/4.2-compatible mounts with POSIX semantics, making it ideal for workloads requiring shared file access across pods and AZs.
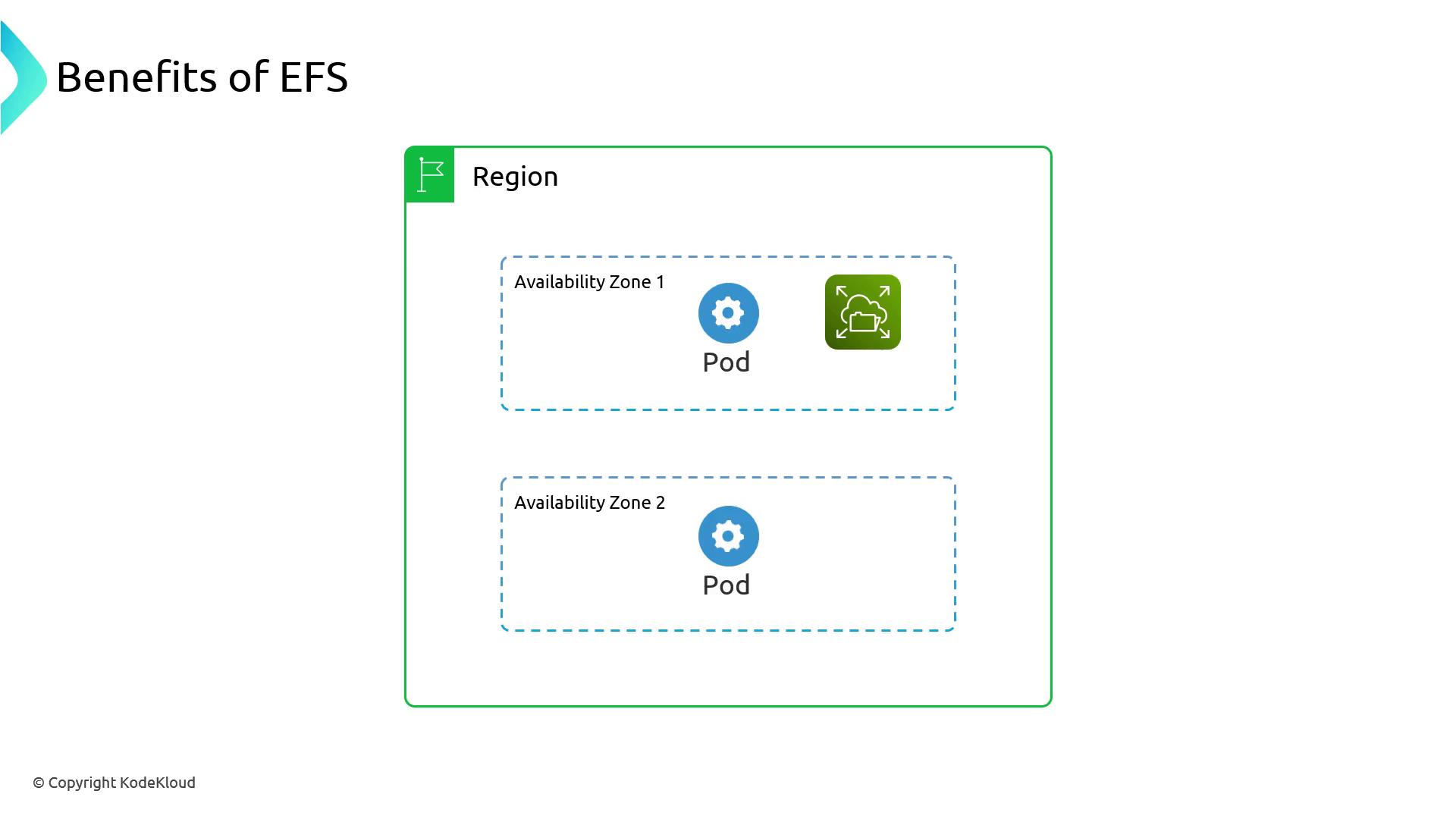
Key Benefits of EFS
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regional Service | Mount the same file system in multiple Availability Zones (AZs). |
| Multi-Writer Access | Support many-to-many mounts—pods in different AZs share one volume. |
| Automatic Scaling | Grow or shrink storage capacity on demand, up to petabyte scale. |
| Fully Managed NFS | AWS handles back-end storage, patches, and availability. |
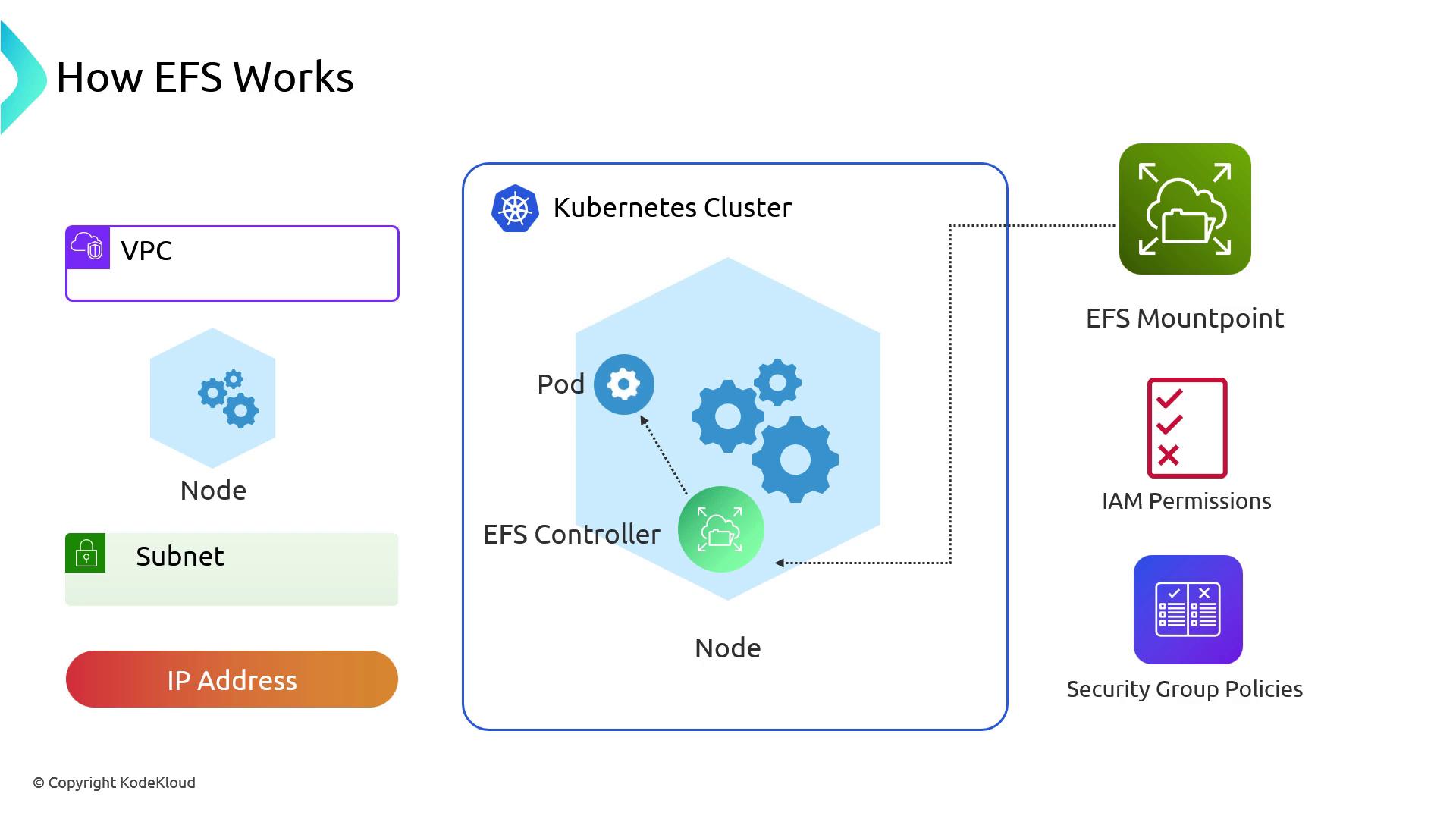
EFS Integration with Kubernetes
To use EFS in EKS, you perform infrastructure setup outside the cluster, then leverage the EFS CSI driver for mounting:-
Provision EFS
- Create an EFS file system and mount targets in each subnet.
- Configure security groups to allow NFS traffic (port 2049) from EKS node subnets.
- Assign IAM roles or policies permitting
elasticfilesystem:ClientMountand related actions.
-
Install the EFS CSI Driver
-
Define PV & PVC
-
Mount in a Pod
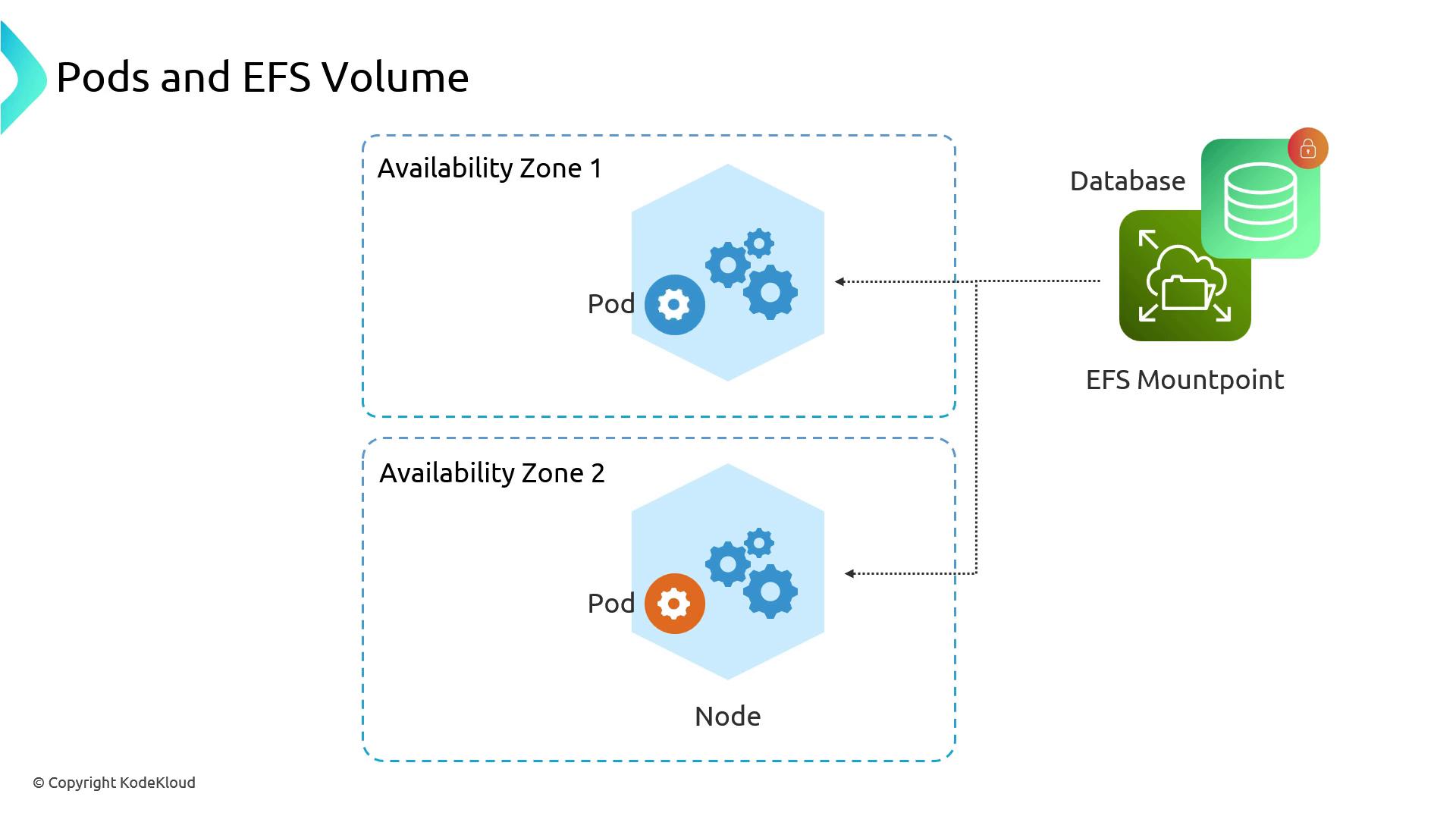
Performance and Workload Considerations
EFS offers shared read/write access but inherits NFS characteristics:- File locking may block concurrent writes on the same file.
- Latency can be higher than block storage for small-file operations.
- Throughput scales with burst credits and Provisioned Throughput modes.
Running high-concurrency databases on EFS can cause I/O contention due to file locks. Evaluate workload patterns and test performance before production use.
Dynamic Provisioning
The EFS CSI driver supports creating subdirectories under one mount target for isolated PVCs. This simplifies management compared to a generic NFS provisioner: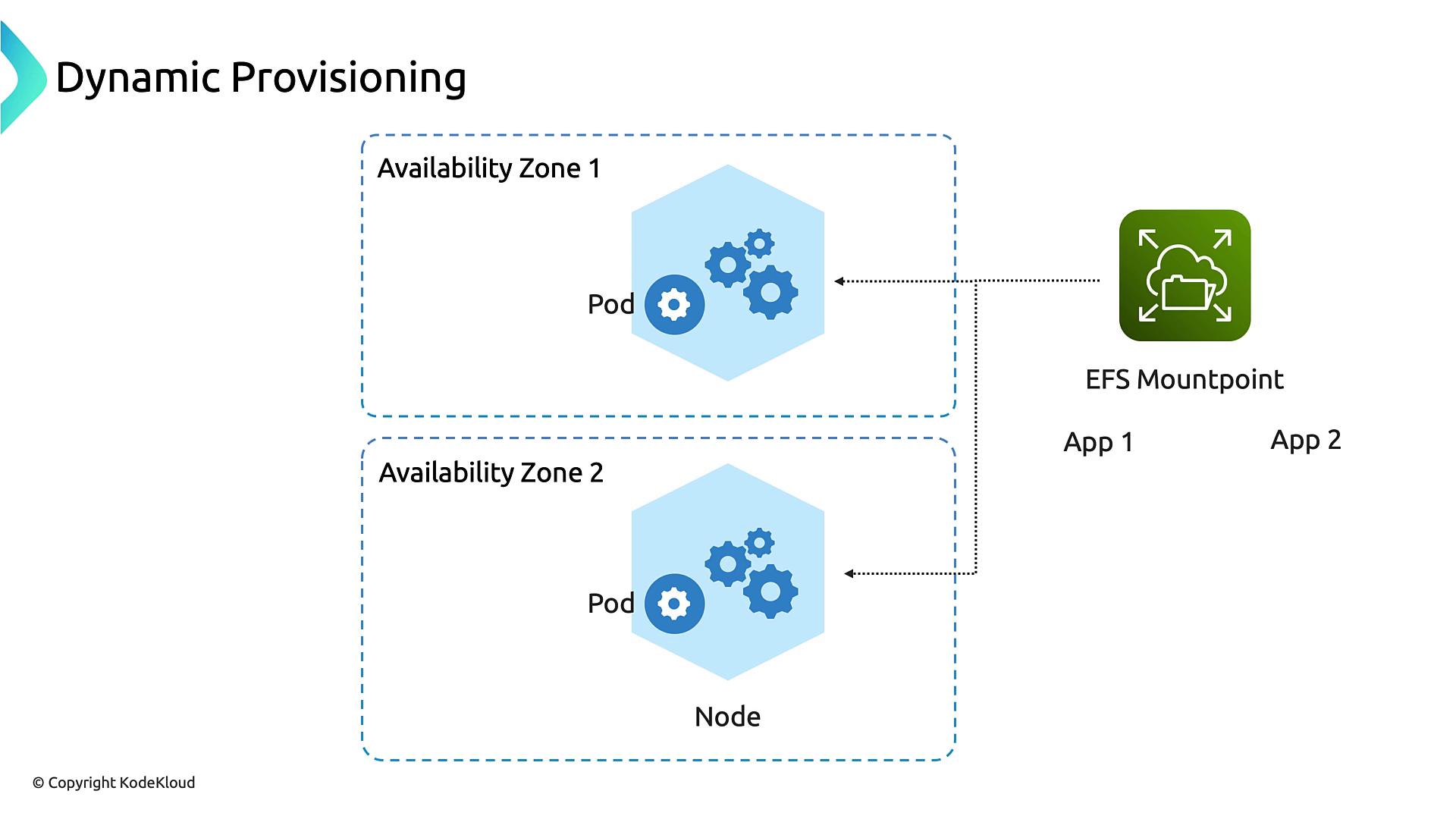
EFS vs. EBS vs. S3: Cost and Capacity Trade-offs
| Storage Type | Access Pattern | AZ Scope | Cost Tier | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EFS | NFS, multi-writer | Regional | $$ | Shared file storage, web assets |
| EBS | Block, single-writer | Single AZ | $ | High IOPS databases, low-latency apps |
| S3 | Object | Regional | $ | Backups, archives, static hosting |
