Service Level Indicators (SLIs)
A Service Level Indicator (SLI) is a quantitative metric that evaluates a specific aspect of the service provided. Essentially, SLIs measure the quality of service from the user’s perspective. Common SLIs include:- Request latency
- Error rate
- Saturation or throughput
- Availability (uptime)
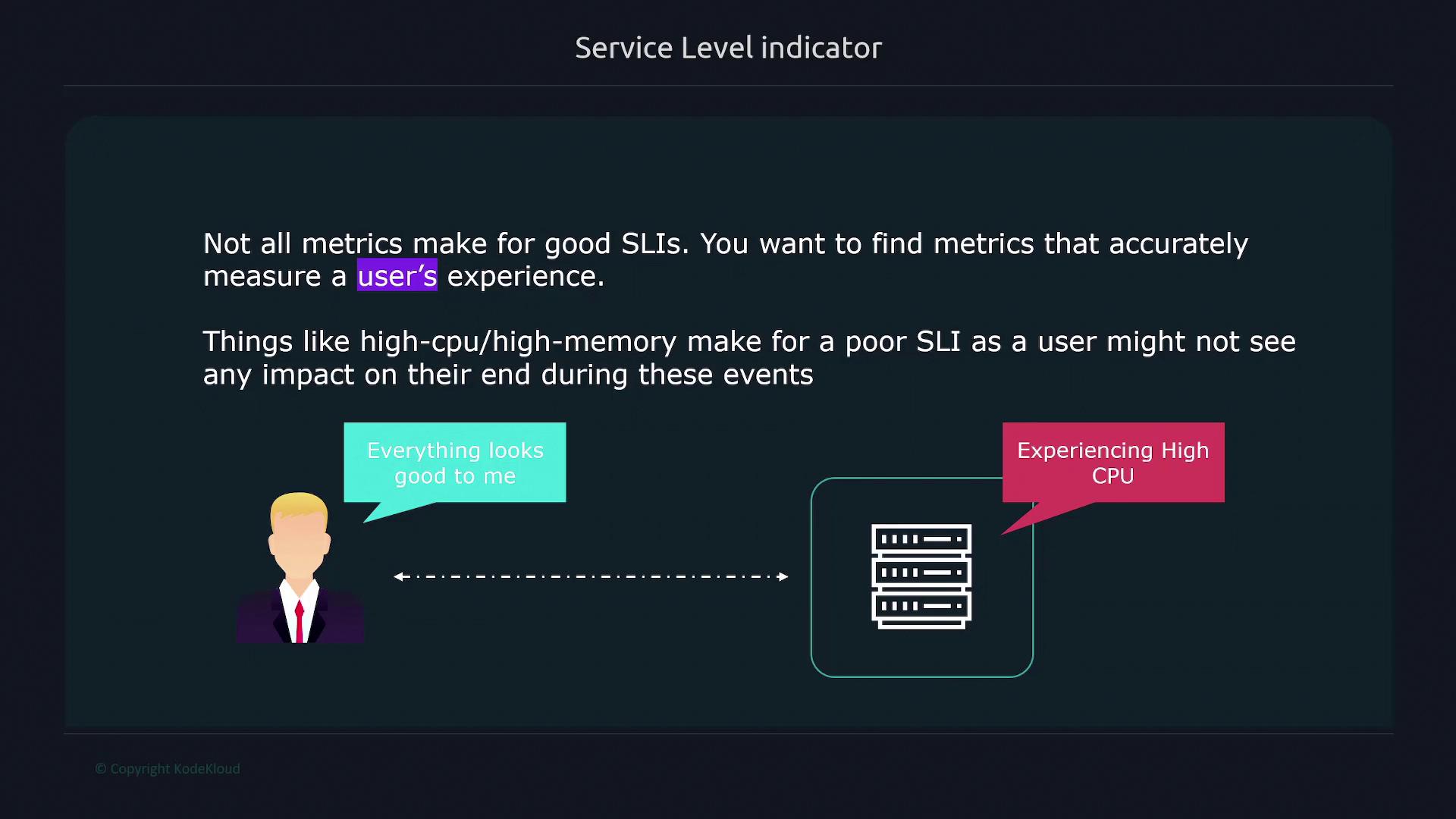
Service Level Objectives (SLOs)
A Service Level Objective (SLO) defines the target value or range for an SLI. For example, if an SLI measures the latency of an application, the corresponding SLO might require that the latency remains below 100 milliseconds. Similarly, an SLO for availability could dictate a minimum of 99.9% uptime. SLOs are set with the customer’s experience in mind, directly quantifying the product’s reliability.
When setting SLOs, it is essential to choose realistic and achievable targets. Overly aggressive goals, such as 100% uptime or 99.999% uptime, can be costly and difficult to maintain.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) formalizes the targets defined by SLOs in a legally binding document. An SLA acts as a contract between a vendor and a user, guaranteeing a specific level of service quality. Should the service fail to meet the predetermined SLOs, the SLA typically outlines penalties, often in financial terms.
In summary, SLIs provide measurable insights into service quality from a user’s perspective, SLOs define the desired performance targets, and SLAs formalize these expectations, ensuring accountability through contractual penalties if the targets are not met.