Testing the Default Response
-
Map
example.comto127.0.0.1by editing/etc/hosts: -
Curl over HTTP to see the redirect:
-
Fetch only headers from HTTPS:
-
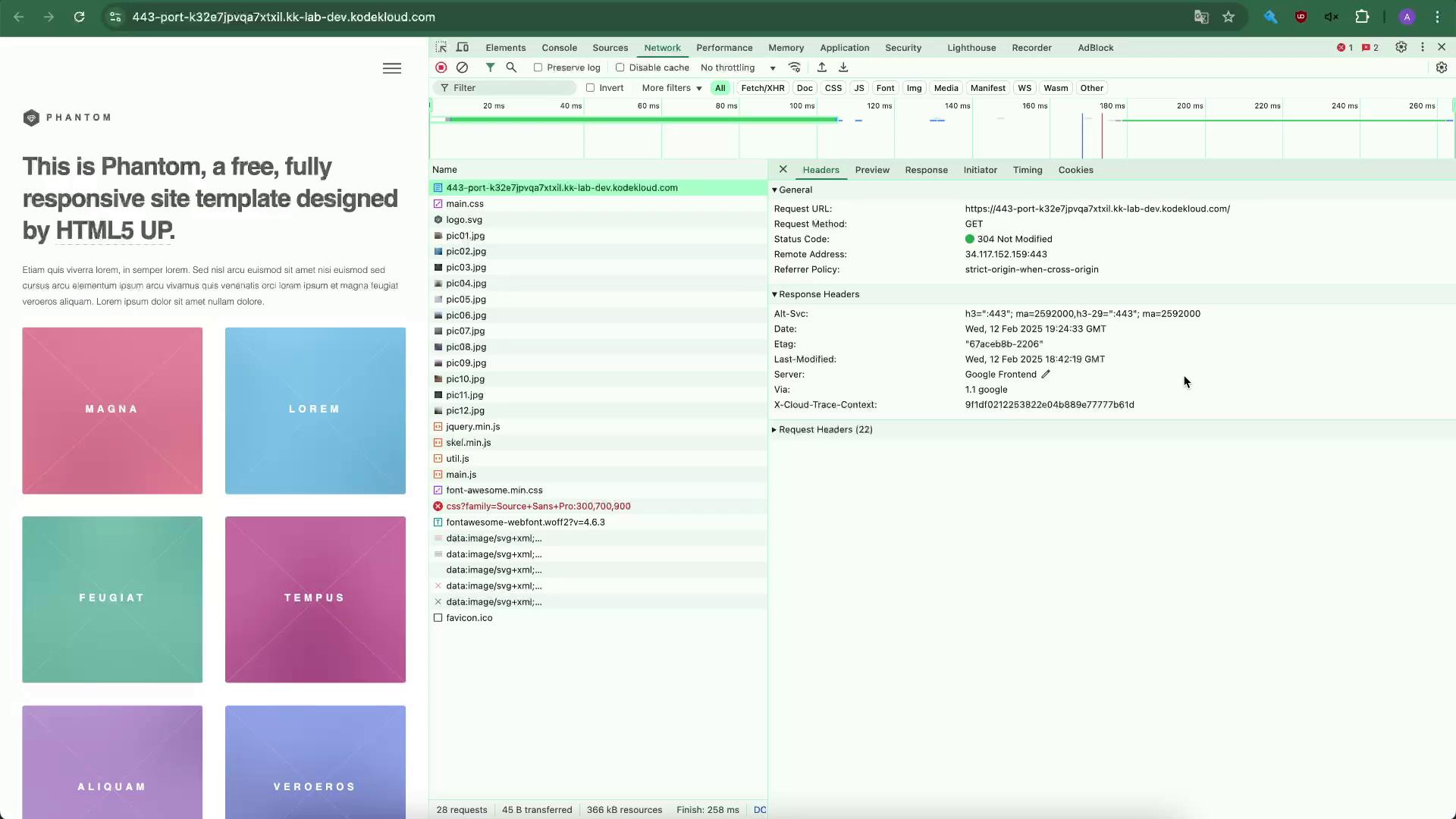
Open your browser’s developer tools (Network tab) and refresh. You’ll see only default headers like
Server,Date, etc.
Adding Security Headers
Edit your HTTPS server block (e.g.,/etc/nginx/sites-available/example-https):
server { ... } listening on port 443, add these headers:
Always test your configuration before reloading:
Summary of Security Headers
| Header | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Strict-Transport-Security | Enforce HTTPS connections |
| X-Frame-Options | Prevent clickjacking |
| Content-Security-Policy | Restrict resource loading to same origin |
| Referrer-Policy | Control Referer header information |
Configuring NGINX as a Load Balancer
Now we’ll distribute traffic to two Apache backends and forward client information.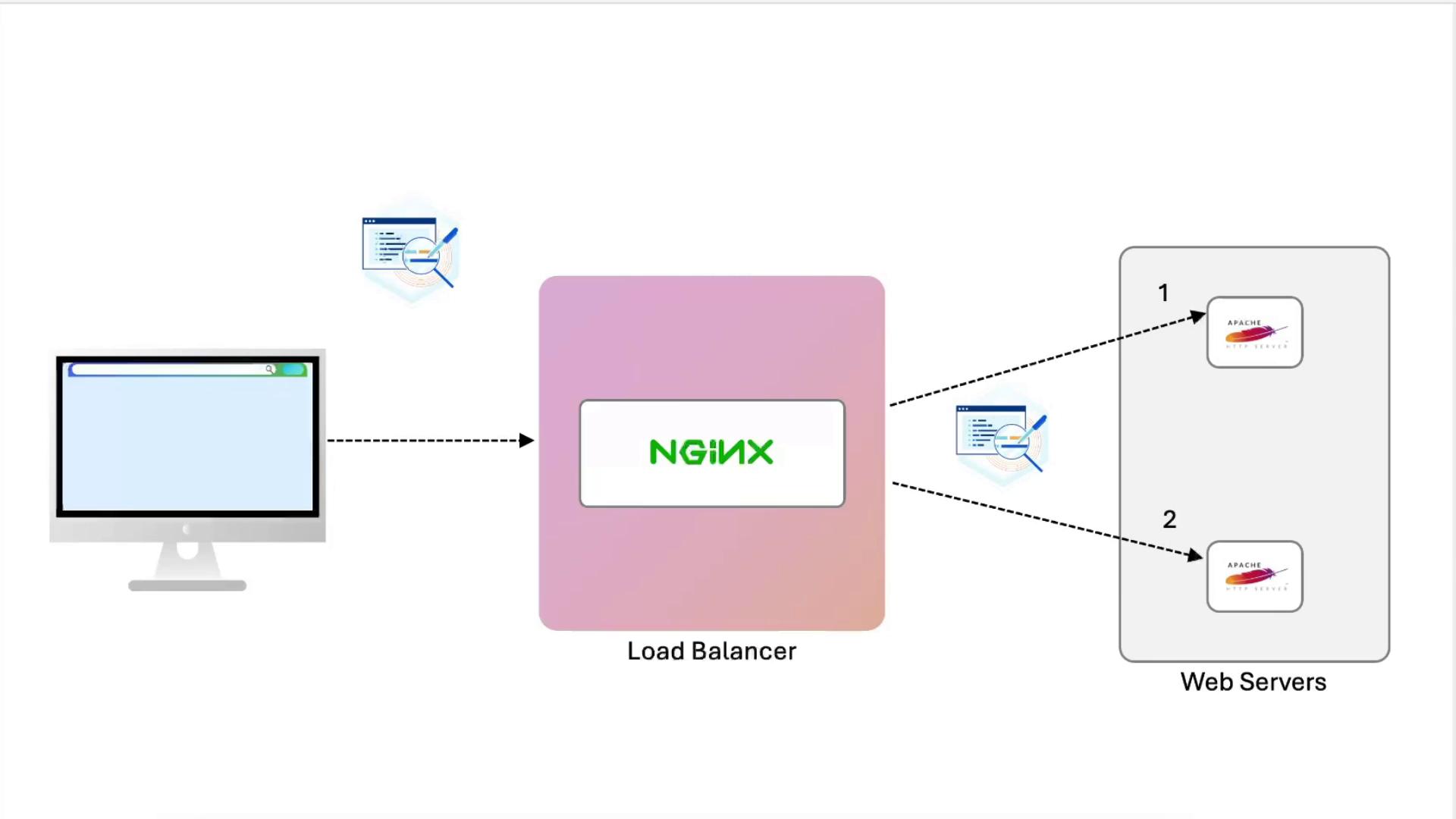
1. Define the Upstream
Add at the top ofnginx.conf or inside your site file:
2. Initial Proxy Test (No Headers)
Replace thelocation / block:
3. View Apache Access Logs
Passing Proxy Headers
Update the samelocation / block to forward client data:
After changing log formats, always test Apache before restarting:
4. Update Apache Log Format (on node01)
In/etc/apache2/apache2.conf or your vhost:
5. Compare Logs
- node02 (unchanged): logs show only the load balancer’s IP.
- node01: logs include:
X-Real-IP: immediate client IPX-Forwarded-For: full proxy chainX-Forwarded-Proto: original protocol
Recap
- Tested default NGINX headers.
- Added security headers (
HSTS,X-Frame-Options,CSP,Referrer-Policy). - Configured NGINX as an SSL-terminating load balancer.
- Forwarded proxy headers (
X-Real-IP,Host,X-Forwarded-For,X-Forwarded-Proto). - Updated Apache
LogFormatto capture these headers.