Creating a go.mod File
To initialize a new Go module, run the following command in your project’s root directory:module followed by a unique module path (in this case, “example.com/learn”). The file also specifies the minimum compatible Go version (“1.19” here).
Setting Up a main.go File
Next, create a main.go file as the entry point for your module. Start by declaring the package asmain and defining the main function:
uuid.NewRandom() generates a new UUID, which is then printed to the console using fmt.Println.
Synchronizing Dependencies with go.mod
At this point, although the code references a third-party package, it hasn’t been downloaded yet. To update your dependencies and the go.mod file, run the command:go mod tidy command scans your source code for all required dependencies and adds any that are missing. You may see output similar to the following:
require section listing the dependencies along with the appropriate versions. An updated file might resemble this:
require section ensures that the correct module versions are used. Notice that the dependency on github.com/google/uuid is marked as indirect because it is used by one of the dependencies rather than directly by your code.
The
go mod tidy command not only downloads missing dependencies but also cleans up any unused ones, ensuring your module remains lean and up-to-date.Running Your Application
Before executing the program, verify that the correct function name (NewRandom()) is used from the UUID package. To run the application, execute:
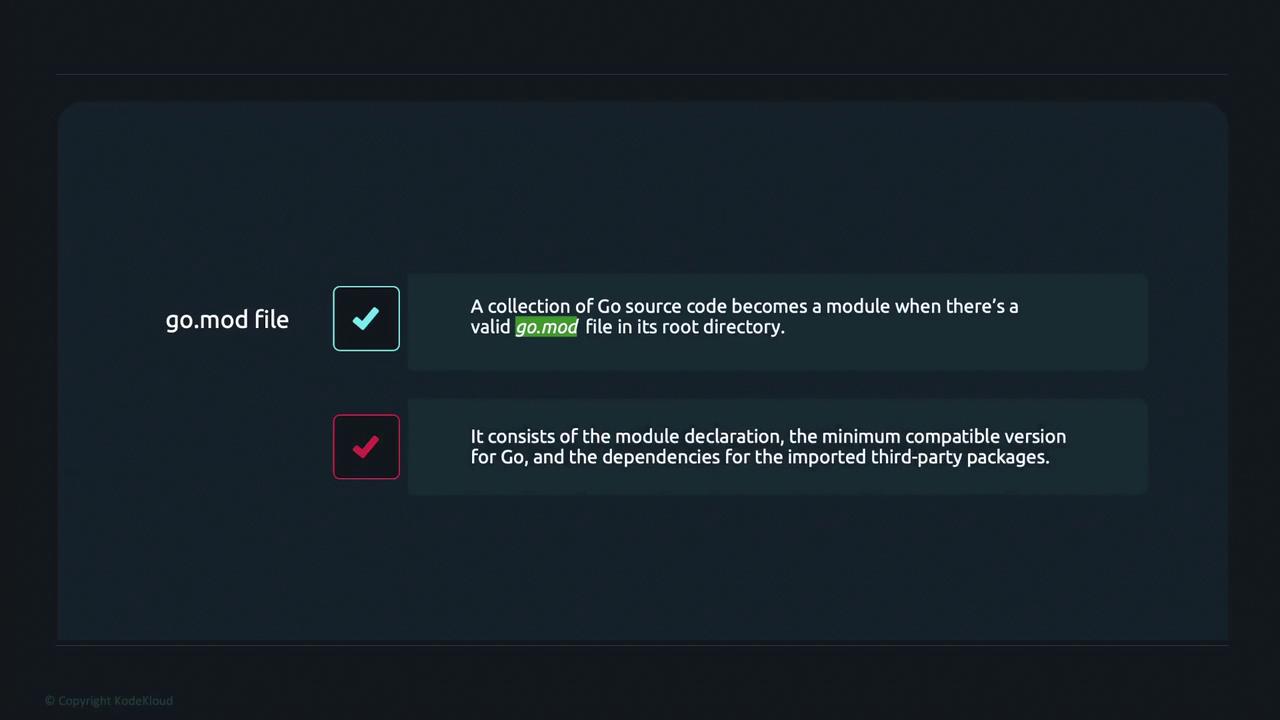
Summary
A Go module is simply a collection of source files managed by a go.mod file. This file includes:- The module declaration with a unique module path.
- The required Go version.
- Dependencies listed with their correct versions.