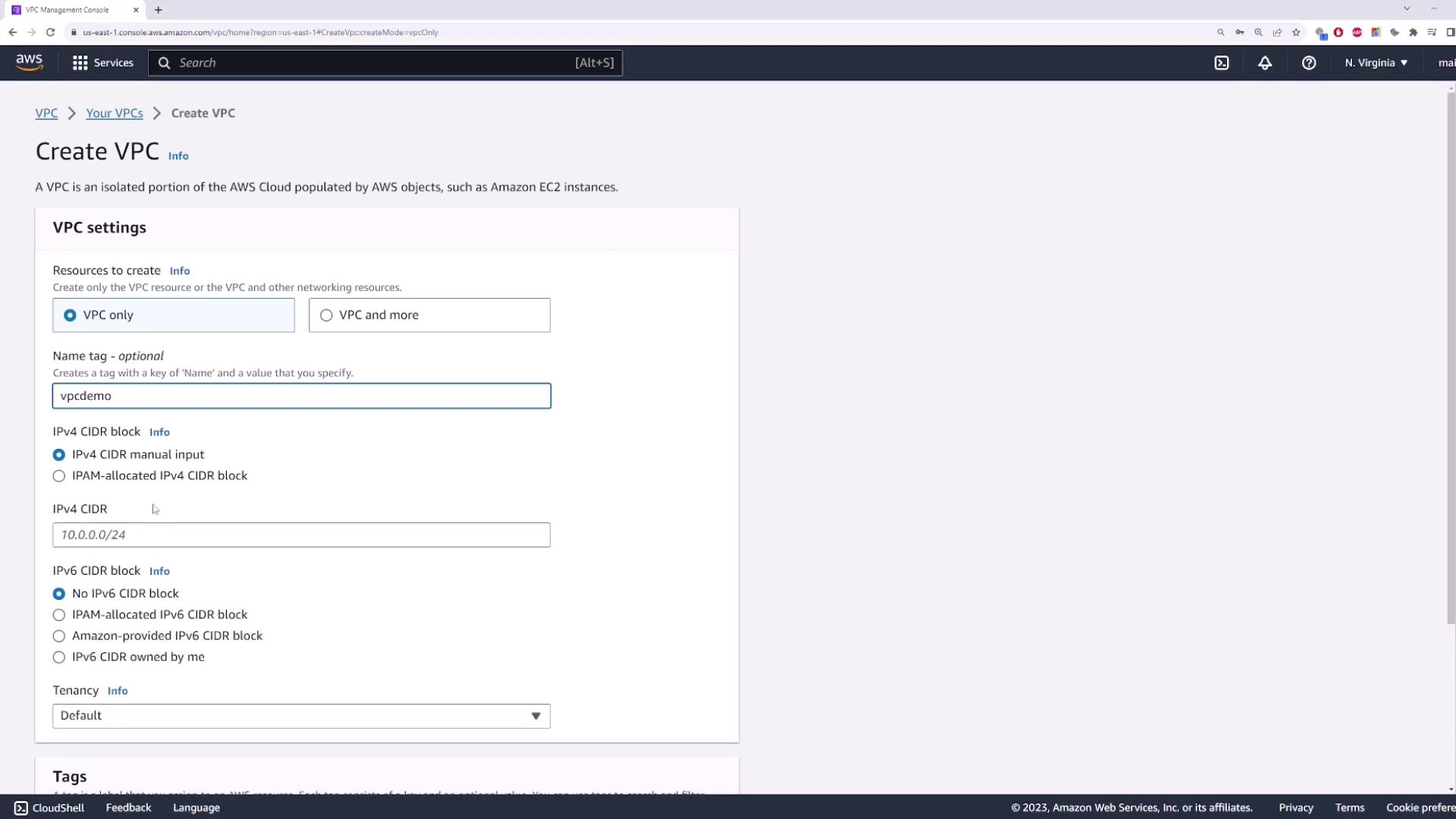
1. Create a New VPC
- Open the VPC console and select Create VPC.
- Enter a Name tag (e.g.,
demo-vpc) and set the IPv4 CIDR block to10.0.0.0/16. - Leave IPv6 settings disabled and click Create.
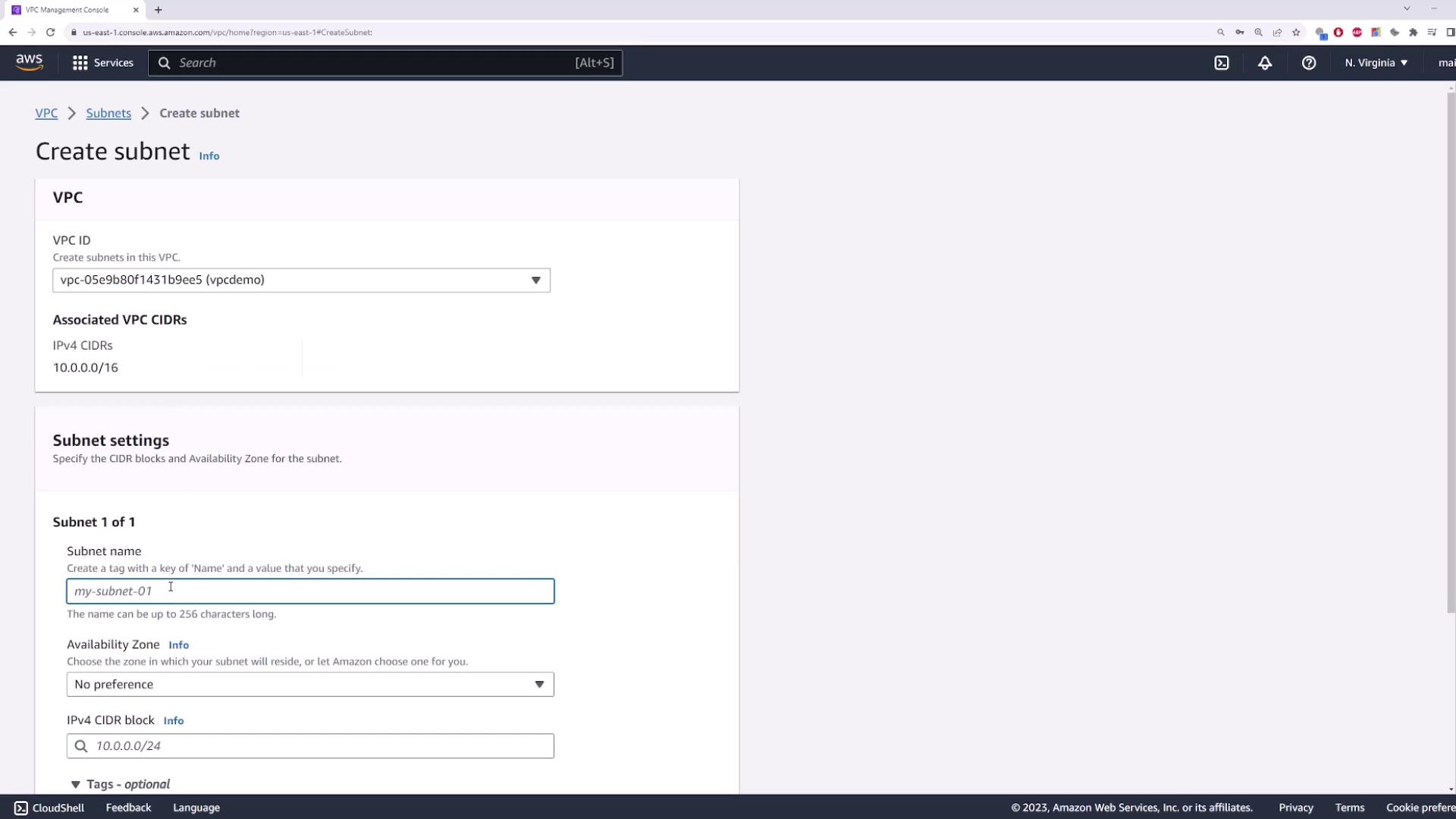
2. Create a Private Subnet
This subnet will host your EC2 instance without a public IP.- Name:
private-subnet - Availability Zone: e.g.,
us-east-1b - IPv4 CIDR block:
10.0.1.0/24
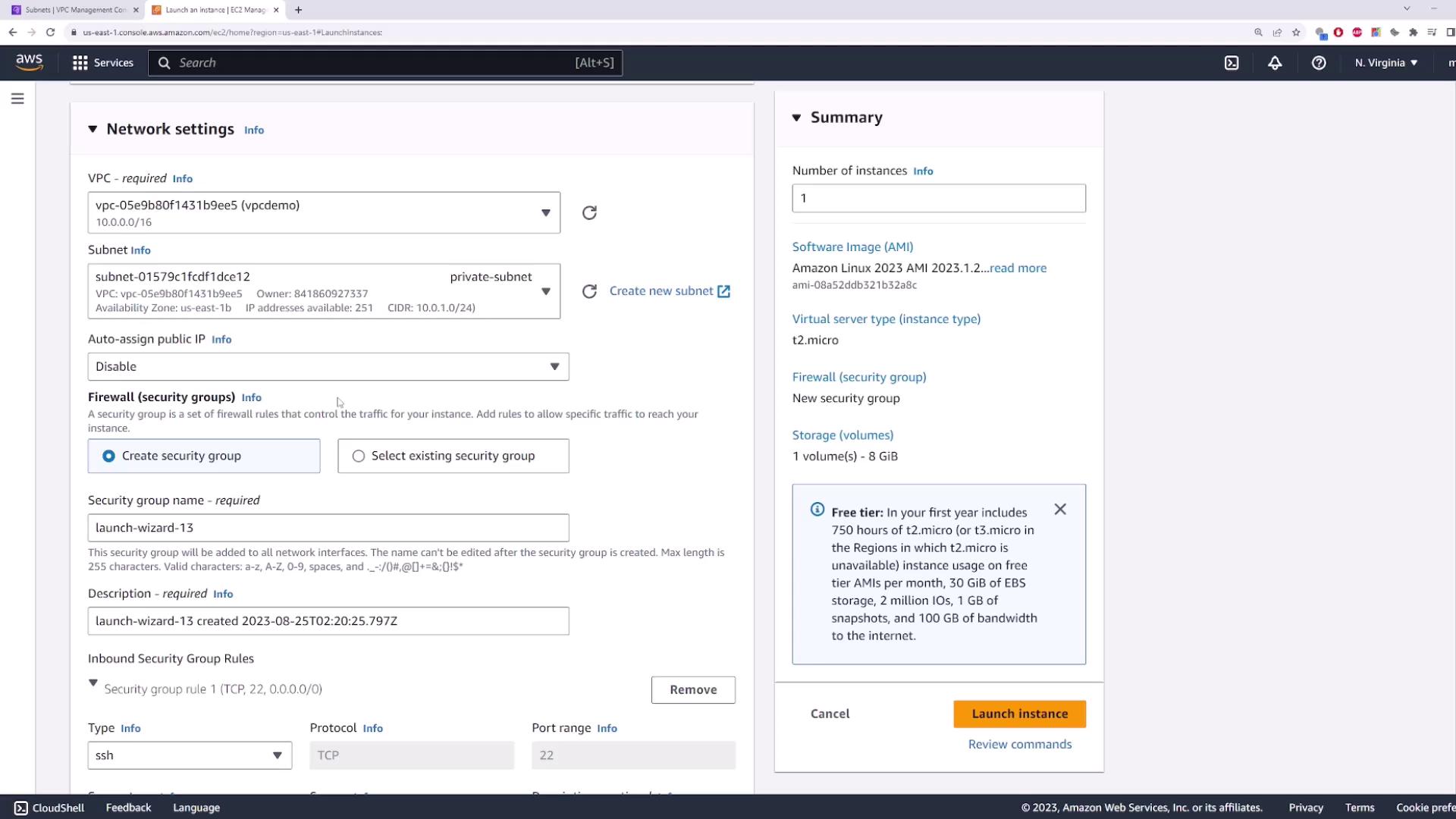
3. Launch an EC2 Instance in the Private Subnet
- Navigate to the EC2 console → Launch Instance.
- Select the Amazon Linux 2 AMI (or your preferred AMI).
- Under Network settings:
- Choose your demo-vpc and the private-subnet.
- Disable Auto-assign Public IP.
- Configure or select a security group (default settings are fine).
- Review and Launch. Name it
private-server.
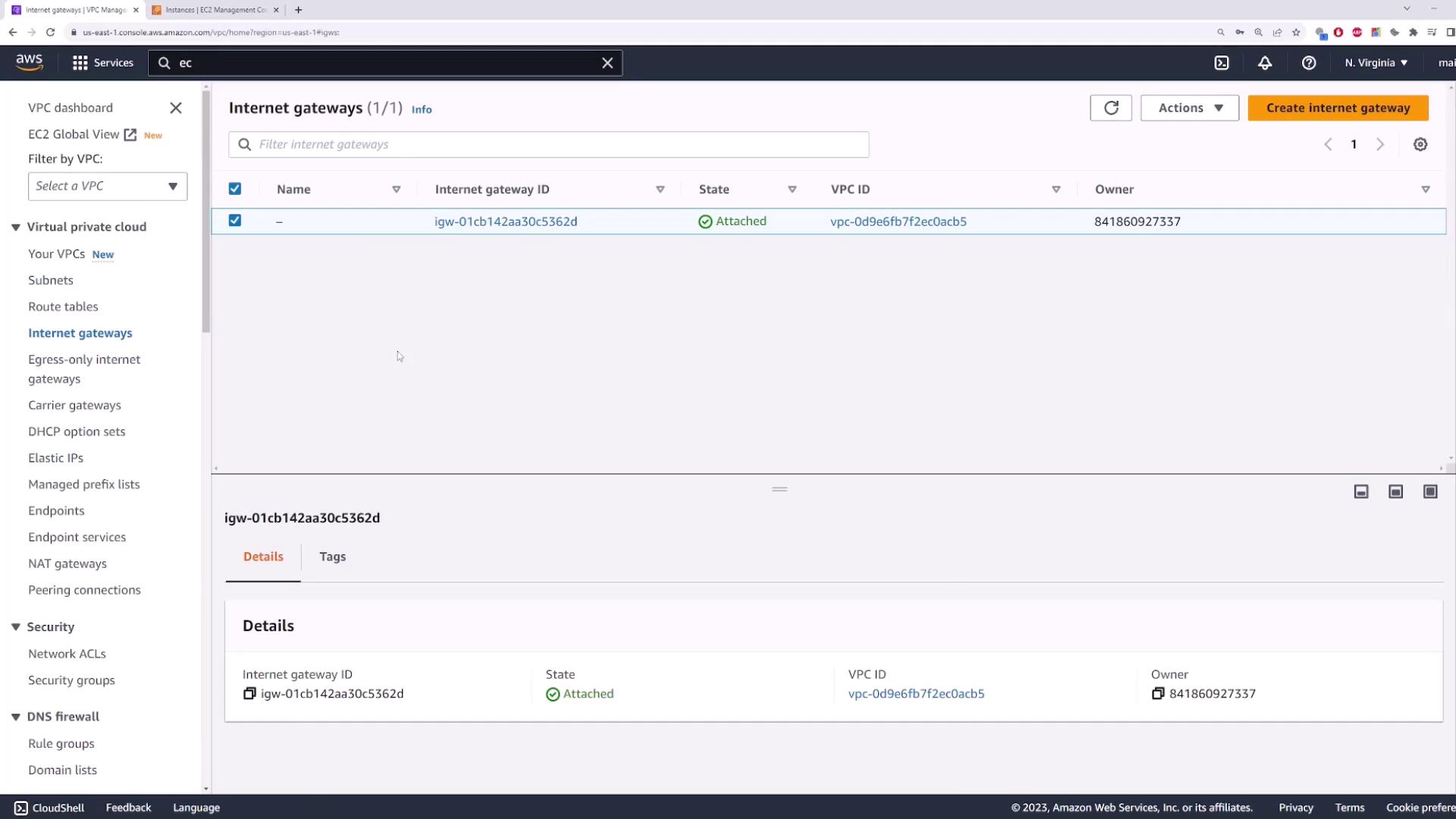
4. Create and Attach an Internet Gateway
An Internet Gateway (IGW) is required to give public subnets internet access.- In the VPC console, go to Internet Gateways → Create Internet Gateway.
- Name it
my-igwand click Create. - Select the new IGW → Actions → Attach to VPC → choose
demo-vpc.
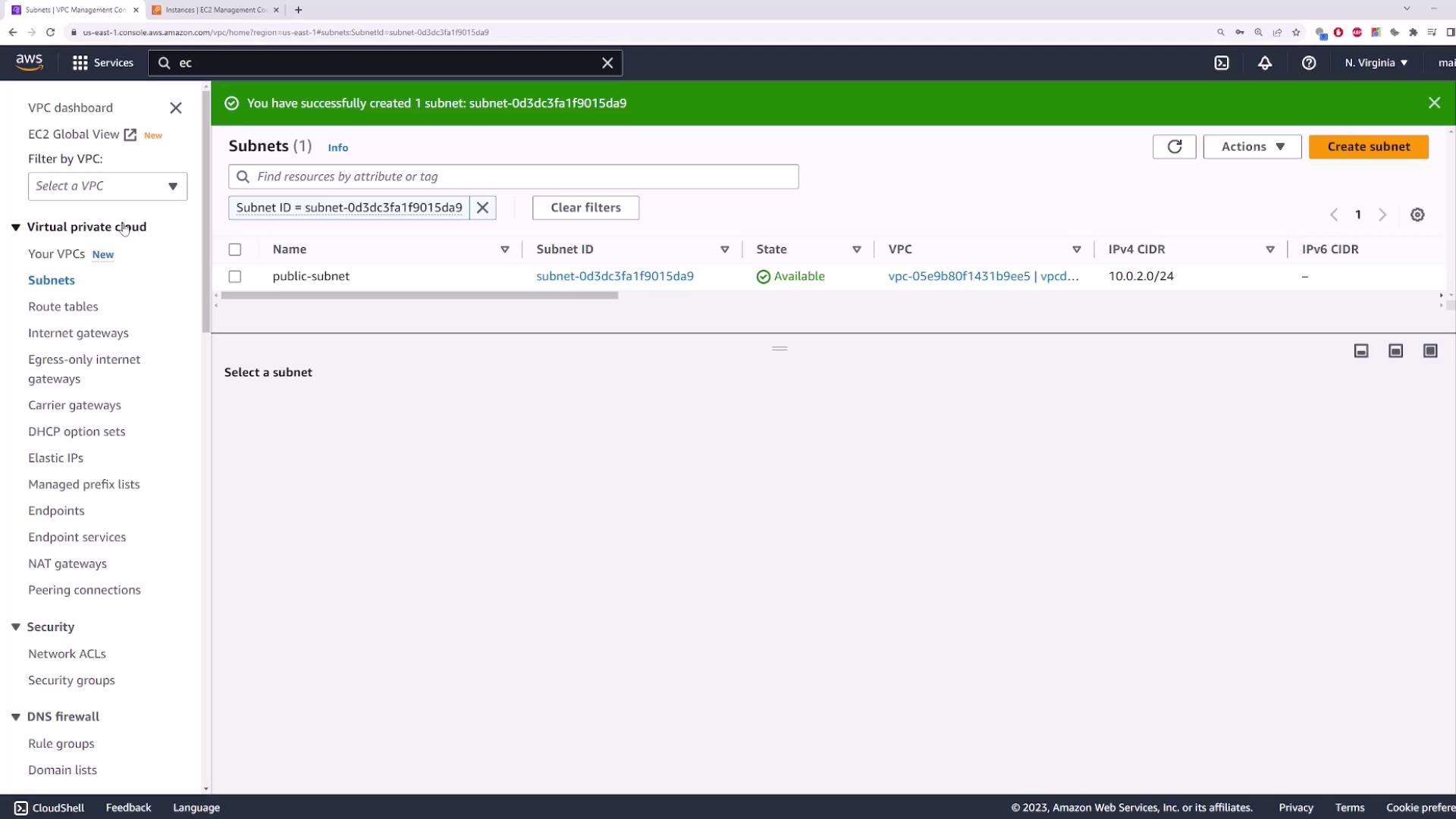
5. Create a Public Subnet
This subnet will host the NAT Gateway and must have a route to the IGW.- Name:
public-subnet - Availability Zone: same or different (e.g.,
us-east-1b) - IPv4 CIDR block:
10.0.2.0/24
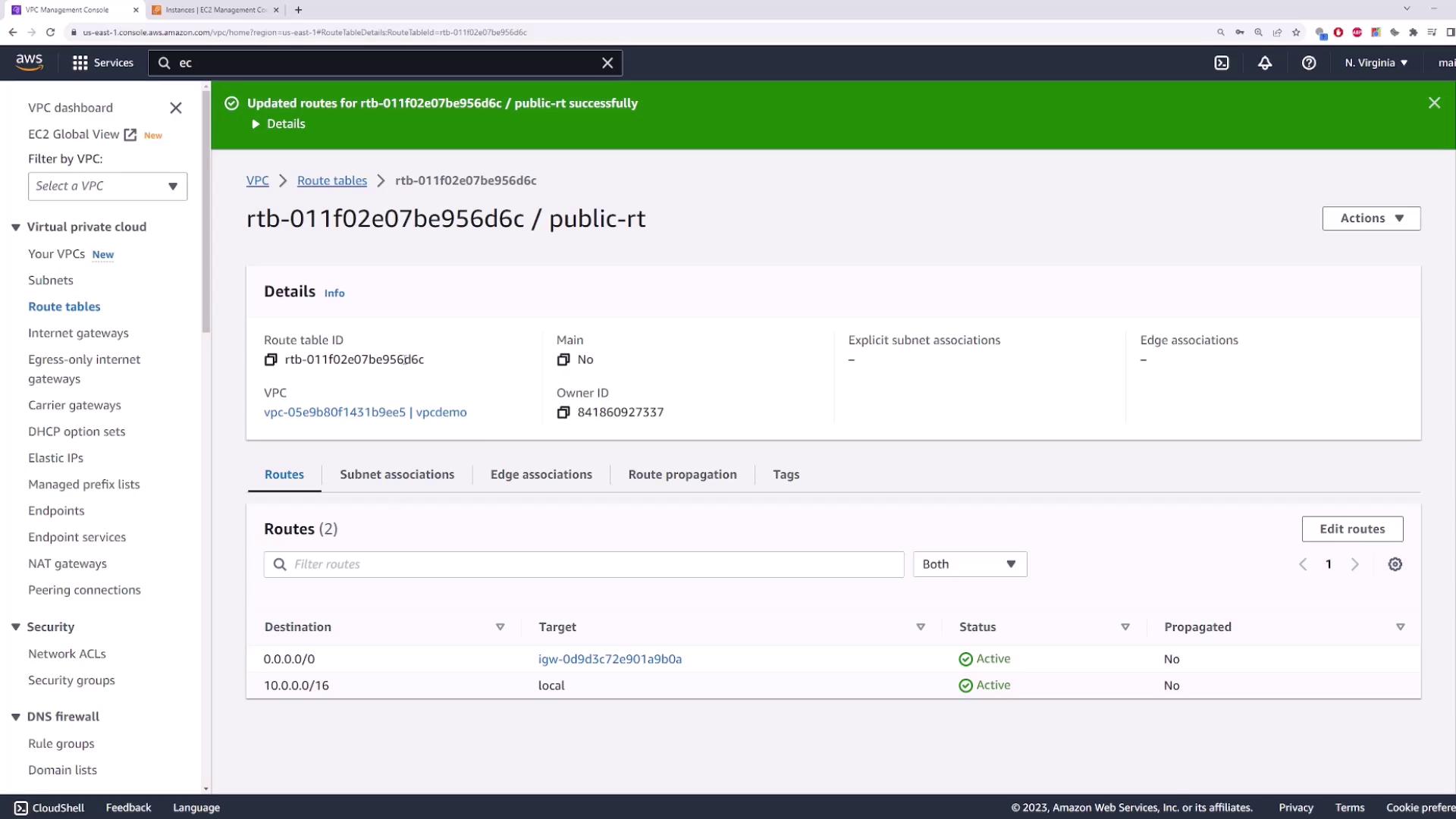
6. Configure Route Tables
You need two route tables: one public and one private.Separate route tables help isolate internet-facing and internal traffic.
| Route Table Name | Associated Subnet | Default Route Target |
|---|---|---|
| public-route-table | public-subnet | Internet Gateway (my-igw) |
| private-route-table | private-subnet | (added after NAT creation) |
Steps
- Create
public-route-table→ selectdemo-vpc→ Create. - Edit routes → Add route
0.0.0.0/0→ Target: Internet Gateway → choosemy-igw→ Save. - Associate with
public-subnet. - Create
private-route-table→ selectdemo-vpc→ Create. - Associate with
private-subnet(no default route yet).
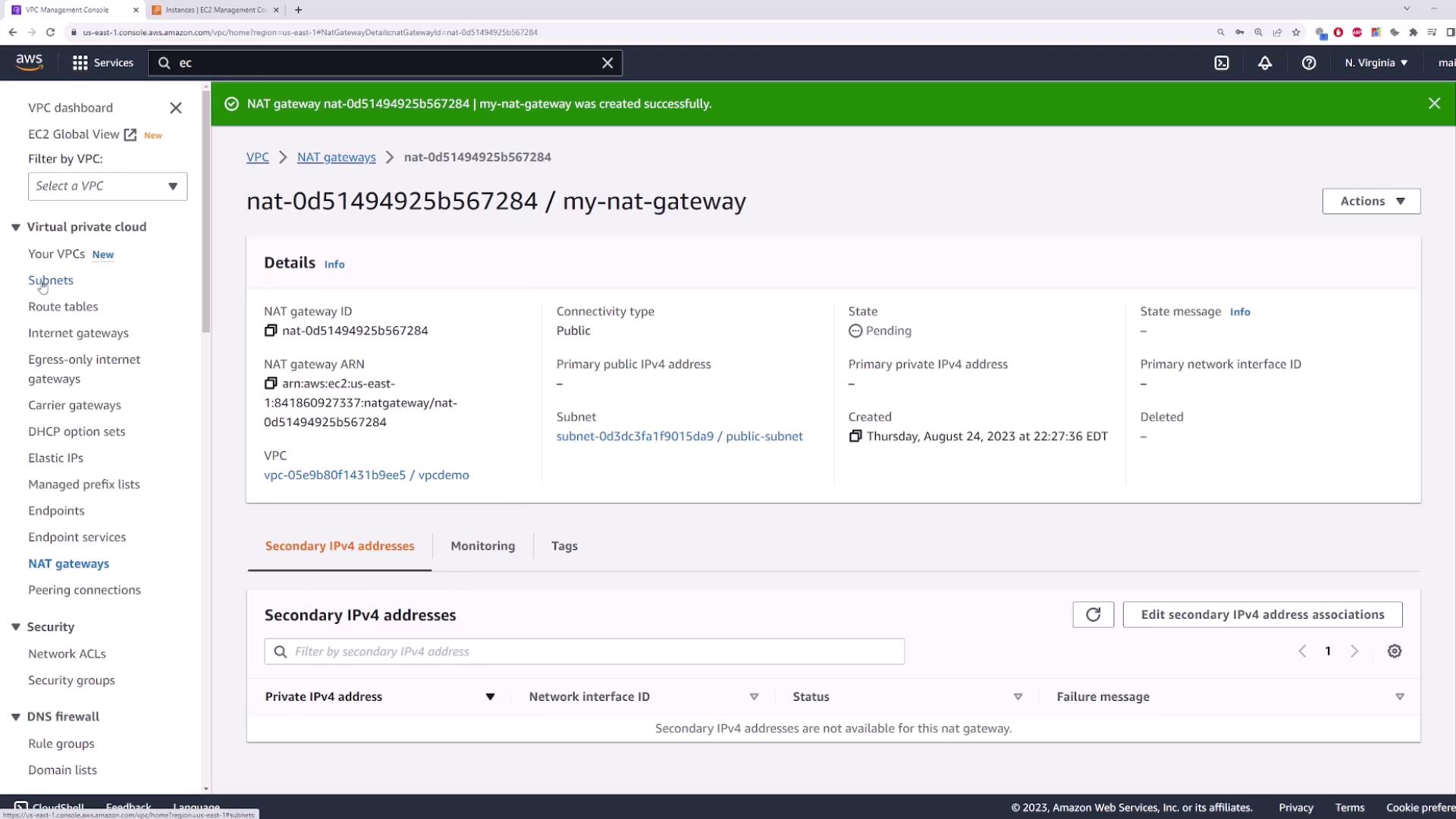
7. Deploy a NAT Gateway
In a public subnet, NAT Gateways allow private instances to access the internet securely.- Go to NAT Gateways → Create NAT Gateway.
- Name it
my-nat-gateway. - Subnet: public-subnet.
- Allocate a new Elastic IP.
- Click Create NAT Gateway.
8. Update the Private Route Table
After the NAT Gateway becomes available:- Open
private-route-table→ Edit routes. - Add route
0.0.0.0/0→ Target: NAT Gateway → selectmy-nat-gateway. - Save.
private-subnet will send outbound traffic through the NAT Gateway while remaining inaccessible from the internet.
9. Plan for High Availability
NAT Gateways are zonal resources. To avoid a single point of failure:- Deploy one NAT Gateway per Availability Zone.
- Update each private route table to point to the NAT Gateway in its own AZ.
If the AZ with your NAT Gateway goes down, all instances using it lose internet access.