Data Poisoning and Training Data Integrity
Data poisoning is a major threat that compromises the integrity of training data. When adversaries corrupt training data—for example, by altering true positives to false negatives—they can cause mislabeling that affects the overall behavior of the model. This type of attack is particularly dangerous in sensitive fields such as healthcare diagnostics and fraud detection.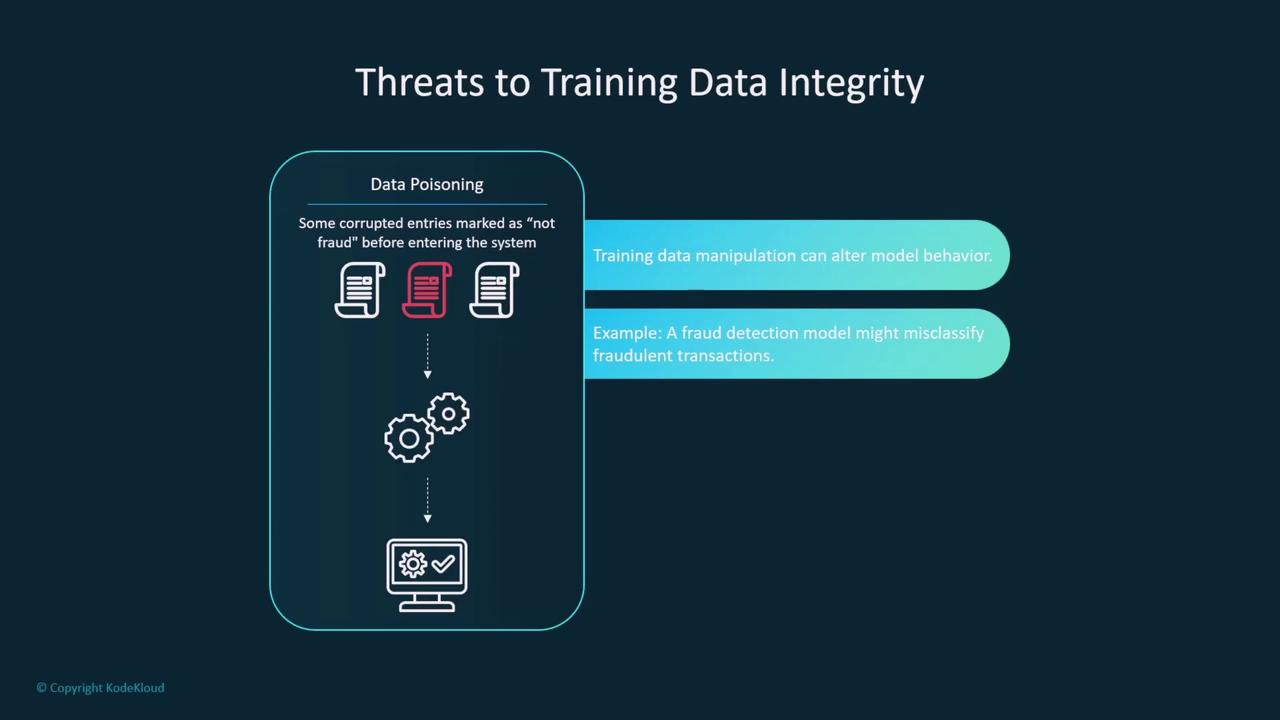
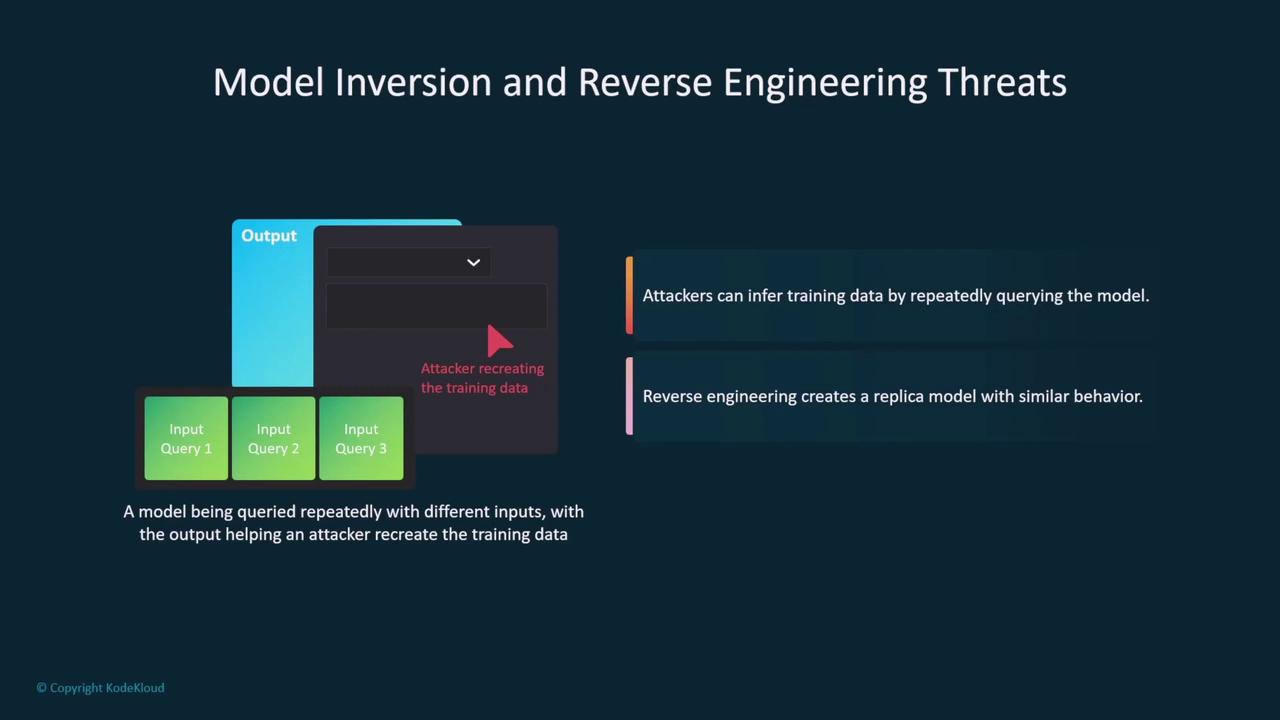
Adversarial Inputs in Facial Recognition
Another significant risk involves attackers introducing subtle alterations in input data. In facial recognition systems, minor changes to facial images can trigger false negatives, potentially allowing unauthorized access.
Prompt Injection Attacks
Prompt injection attacks are a particular concern for large language models. These attacks involve injecting malicious inputs that manipulate the model’s output, potentially exposing sensitive internal information like system prompts or data sources. In worst-case scenarios, this can result in a ‘jailbroken’ model.
Ensure that your AI systems are equipped with robust input validation and monitoring mechanisms to defend against prompt injection and related vulnerabilities.
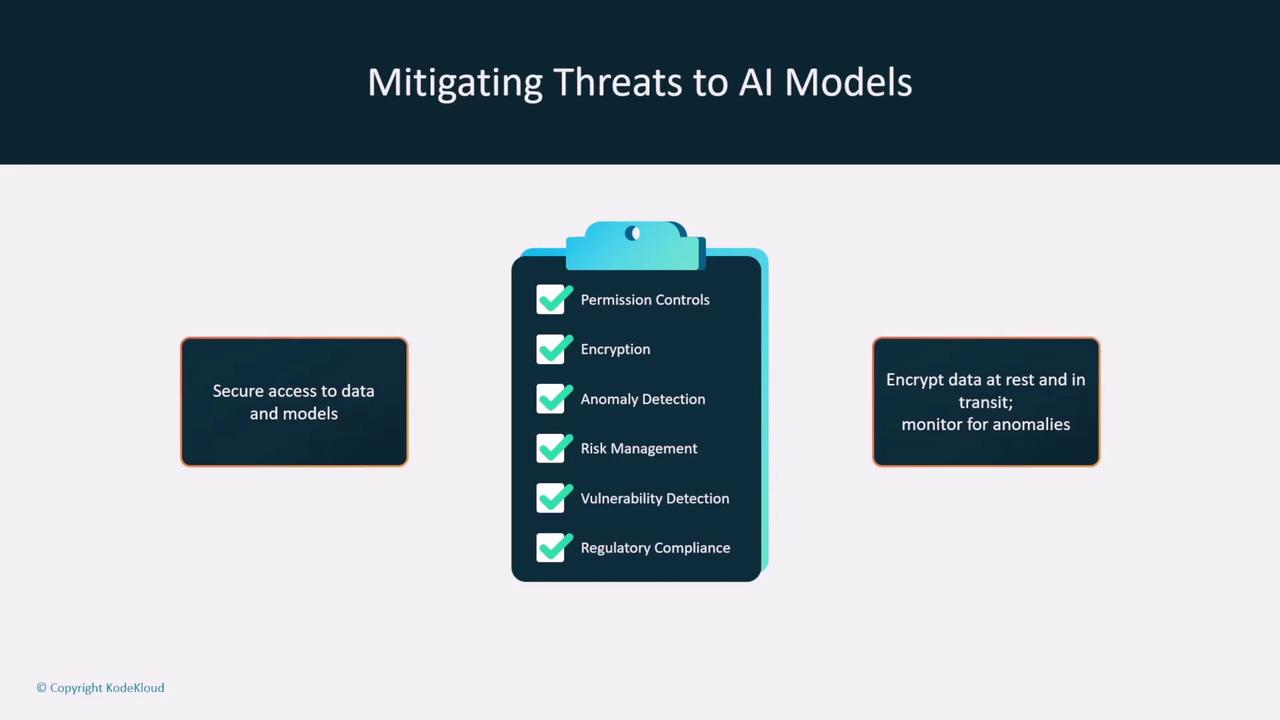
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate these security threats, consider employing the following strategies:- Access Controls and Encryption: Implement strict permission policies and use encryption to protect data both at rest and in transit. Services like AWS KMS and ACM are excellent tools for managing these security measures.
- Anomaly Detection and Guardrails: Utilize tools such as Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor to continuously assess data quality, detect drift, and identify anomalies in real time. Implement guardrails similar to those provided by AWS Bedrock to maintain a secure operational environment.
- Prompt Injection Protection: Enhance your models’ resilience by training them to detect harmful prompt injection patterns. Set up monitoring systems that trigger alerts upon detecting suspicious input behavior.

Monitoring and Continuous Evaluation
Maintaining the security of deployed models requires continuous monitoring. Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor, for example, can compare incoming data to baseline quality metrics, identify performance drift, and raise alerts if deviations are significant. This service continuously evaluates model inferences against labeled data, pinpointing any issues related to data quality or security breaches.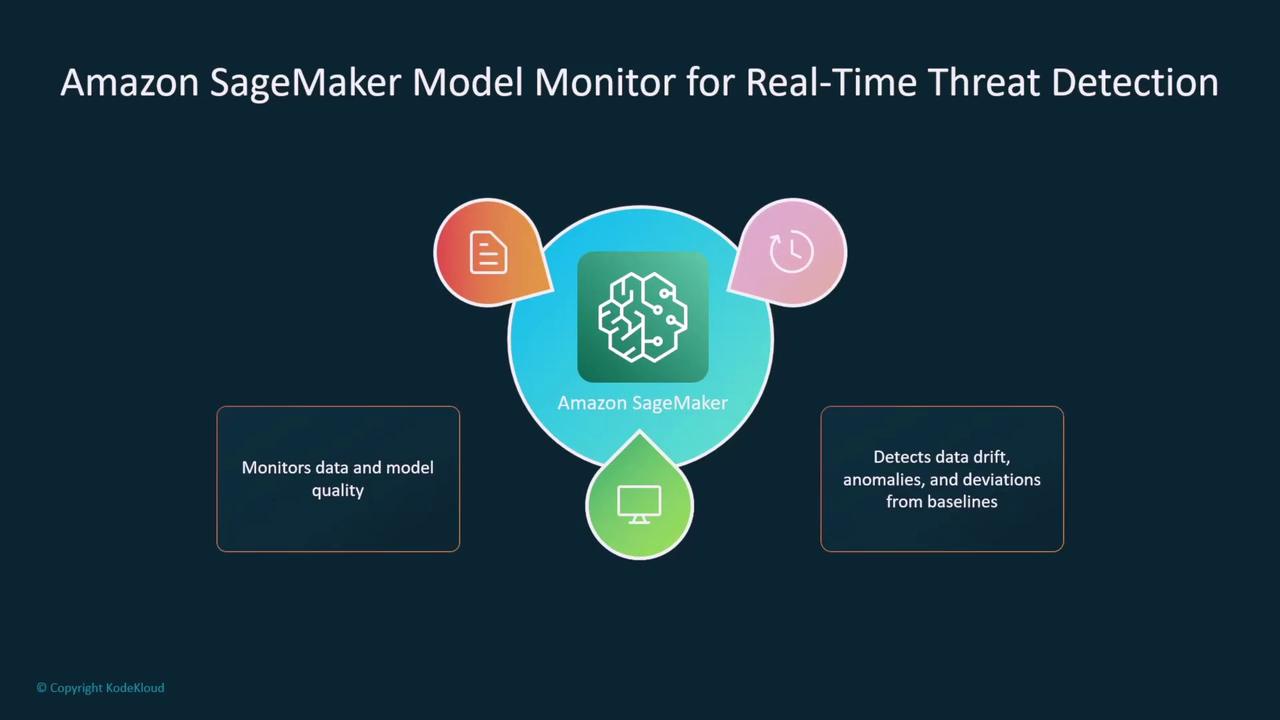
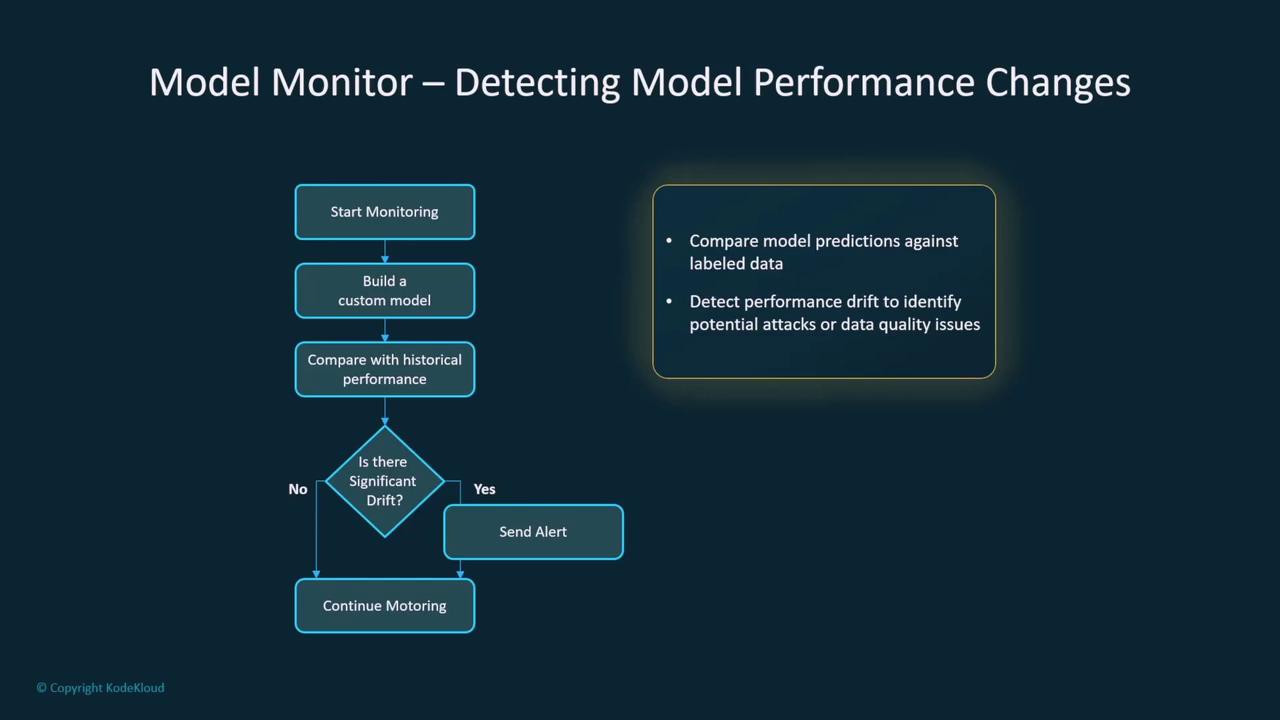
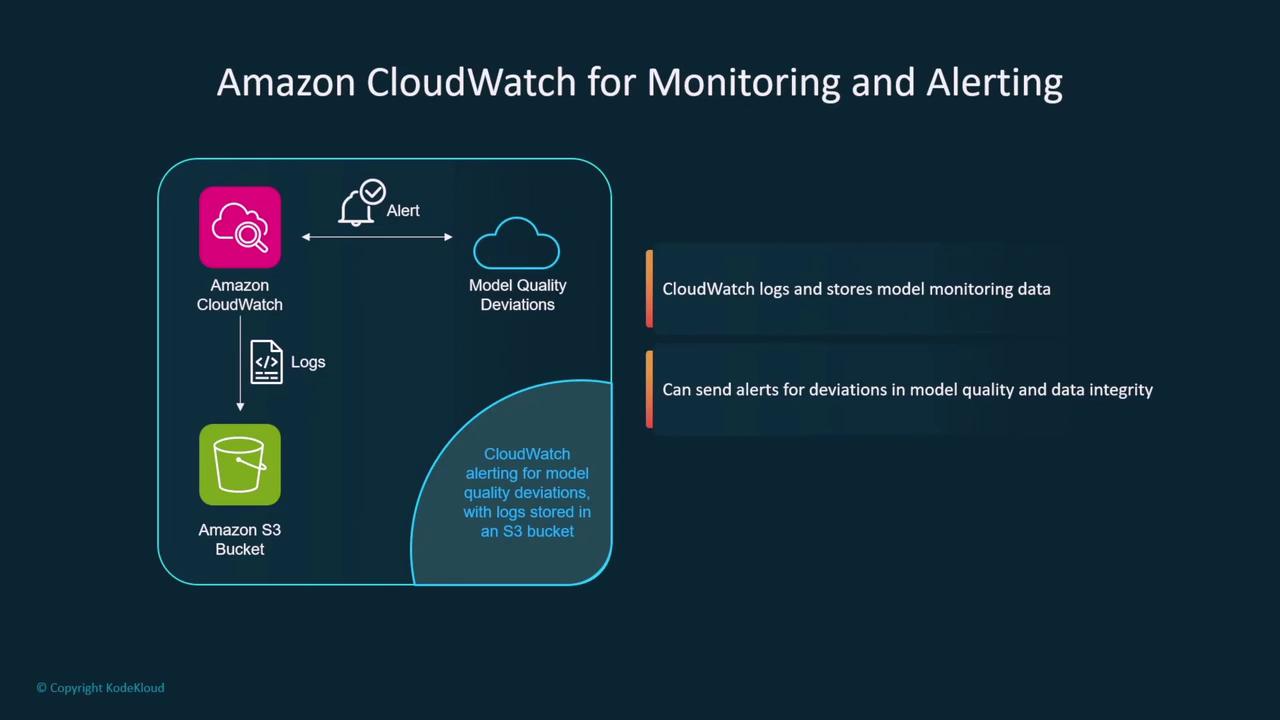
Regular monitoring and updates are crucial for maintaining a secure AI environment. Incorporate routine evaluations and leverage automated tools to ensure continuous protection.