The Power of Generative AI
Generative AI and LLMs are versatile, general-purpose technologies that can be adapted to meet highly specific domain requirements. They enable a wide range of applications—from content generation and customer service to data analysis—making them cost-effective and scalable solutions for many organizations.


Lowering Barriers in AI Development
Conventional AI development presents significant challenges, including high costs and complex processes. In contrast, generative AI streamlines the development process, democratizing access to advanced AI solutions and fostering innovation across companies of all sizes.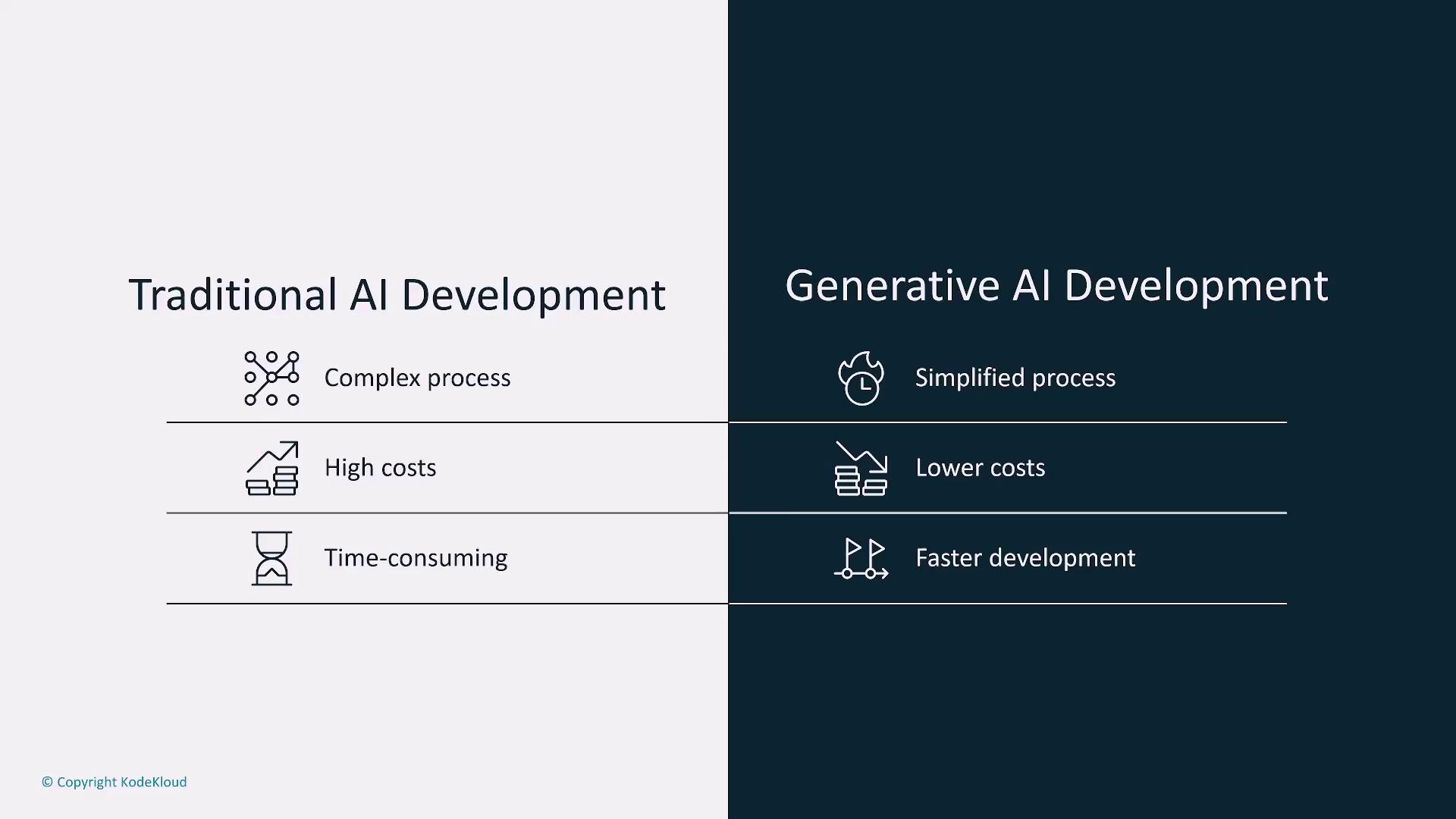
Recognizing Limitations and Challenges
Despite its many benefits, generative AI has notable limitations. It cannot replace the nuanced expertise of human professionals and lacks intrinsic ethical or contextual understanding.While AI systems can be precisely trained for specific tasks, ongoing human oversight is essential—especially when dealing with sensitive or ethically complex domains.
Effective Prompting and Fine-Tuning
Crafting clear, complete, and context-driven prompts is vital when working with LLMs. For instance, a vague instruction like classifying an email may lead to inaccurate results. Fine-tuning the model with multiple examples and specific contextual details significantly improves performance.
Implement robust safeguards to mitigate issues like hallucinations and toxicity, particularly in sensitive applications such as legal or medical advice.
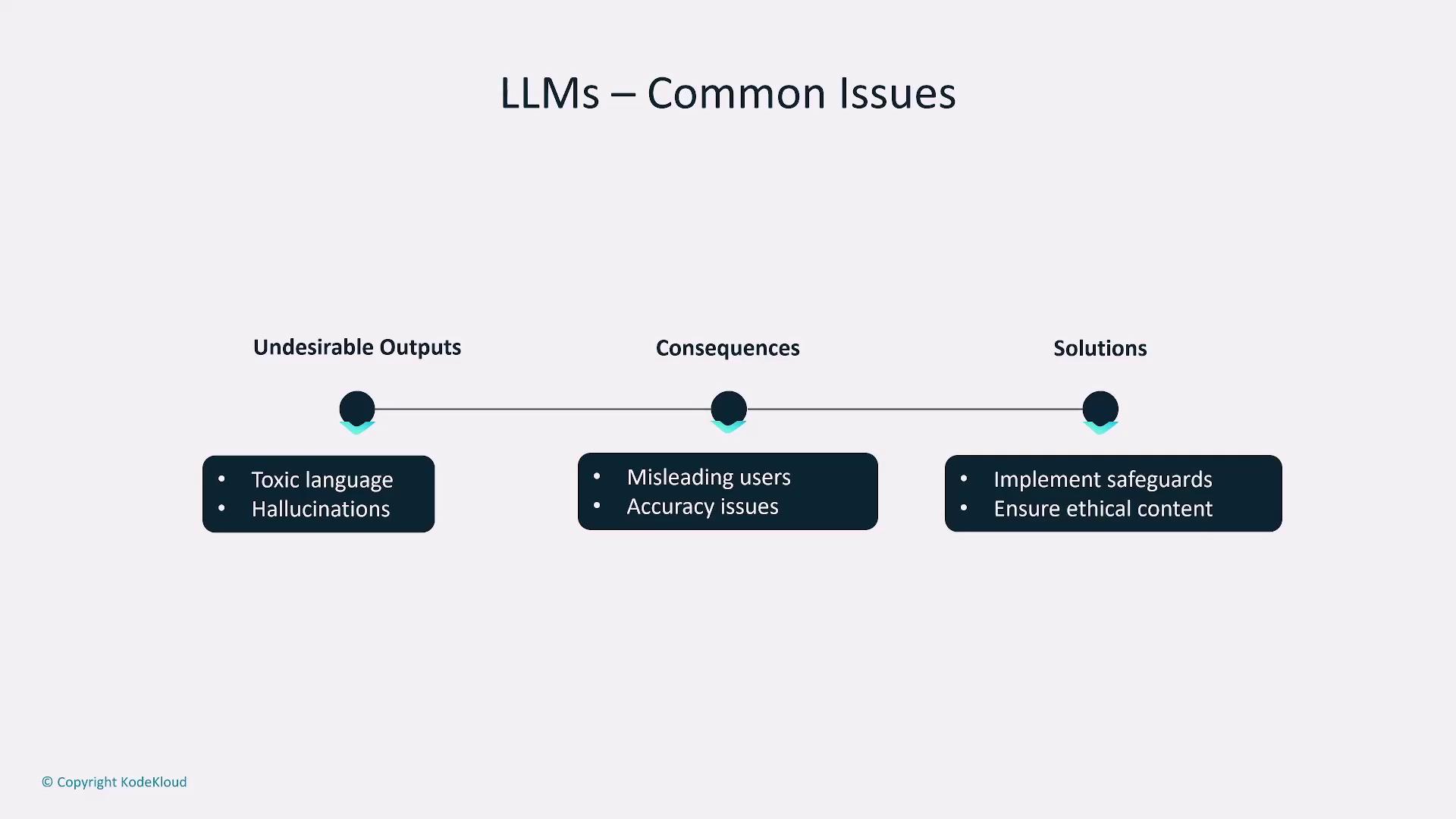
Evaluating LLM Performance
Performance evaluation of language models depends on the specific task. For summarization, metrics like ROUGE (Recall Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation) are used to verify how effectively a summary conveys the intended content. For translation tasks, the BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) score is applied to measure accuracy.
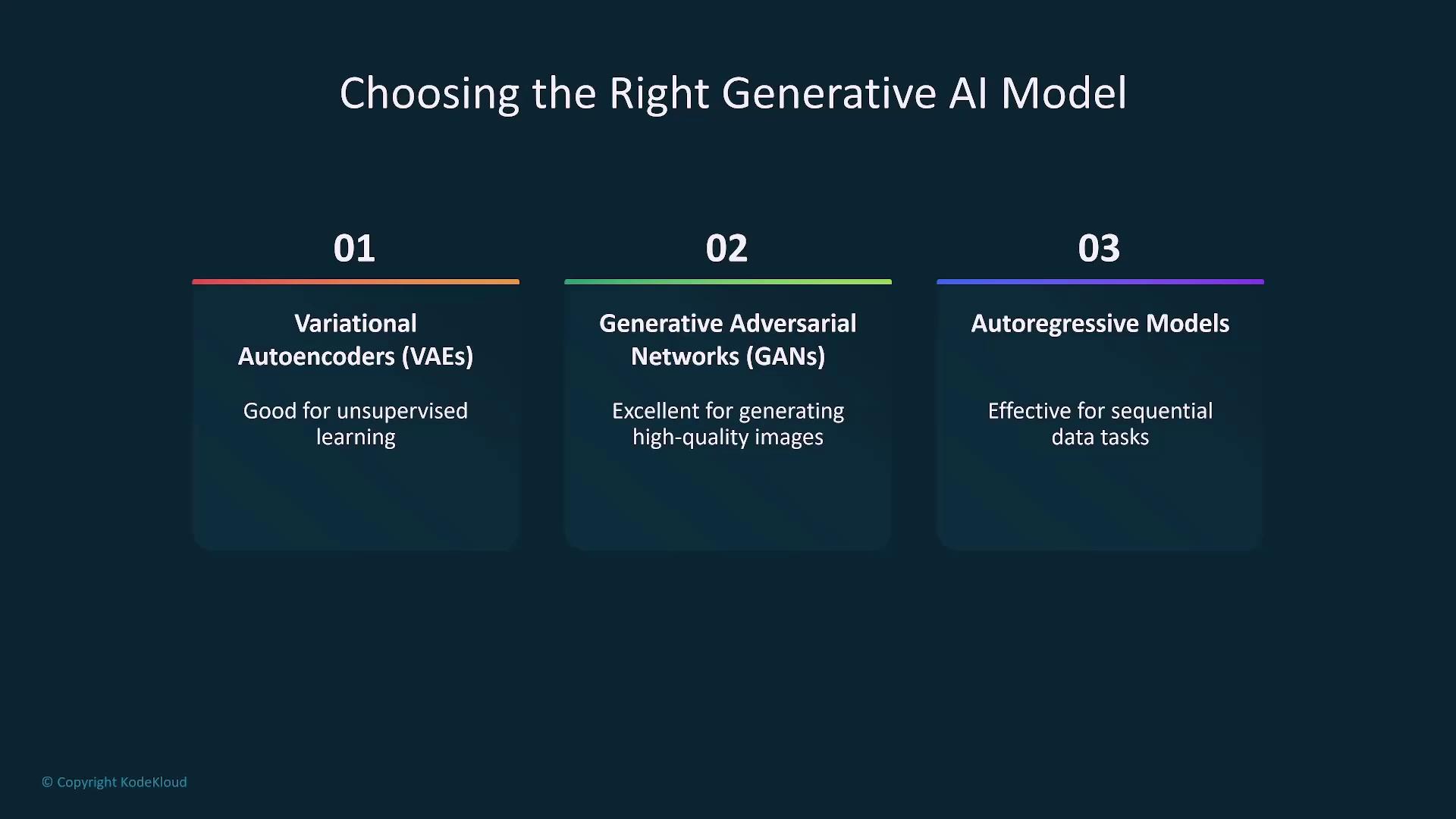
Choosing the Right Model
Selecting the most suitable model depends on project-specific data requirements and overall objectives. Common model options include:| Model Type | Use Case | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) | Unsupervised learning | Data clustering, dimensionality reduction |
| Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | Generating high-quality synthetic images | Image synthesis, data augmentation |
| Autoregressive models | Sequential prediction tasks | Text generation, time-series forecasting |
Foundation Models and Customization
Foundation models like GPT-4 provide a robust starting point that can be customized for specific tasks, such as customer support or product recommendations. Fine-tuning these models with detailed human feedback enhances their performance by addressing issues like toxic language and misalignment with desired outcomes.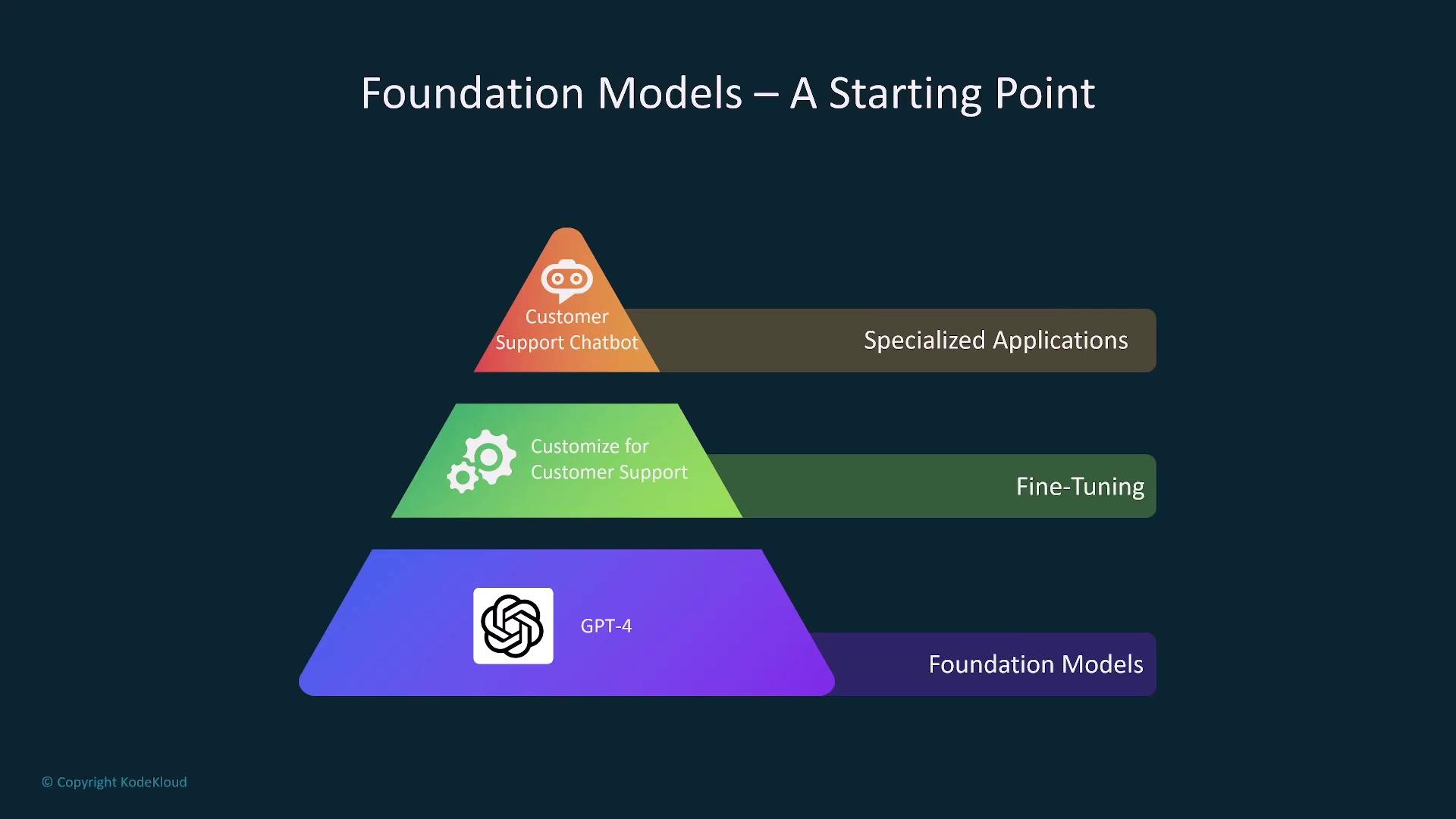
Business Metrics and Monitoring
Monitoring key business metrics—including accuracy, efficiency, and conversion rate—is essential to evaluate the success of generative AI applications. These metrics ensure that AI outputs consistently align with business objectives, delivering a measurable return on investment.

Scaling AI with Foundation Models
When scaling AI solutions, incorporating multiple agents that work in unison is crucial. Scalable foundation models enable organizations to reduce manual intervention, automate complex tasks, and efficiently serve various user segments through systems like automated customer service and tailored content recommendations.