- The fundamentals and applications of Supervised Learning.
- How Unsupervised Learning uncovers hidden patterns without prior labels.
- The dynamic trial-and-error approach of Reinforcement Learning.
Supervised Learning
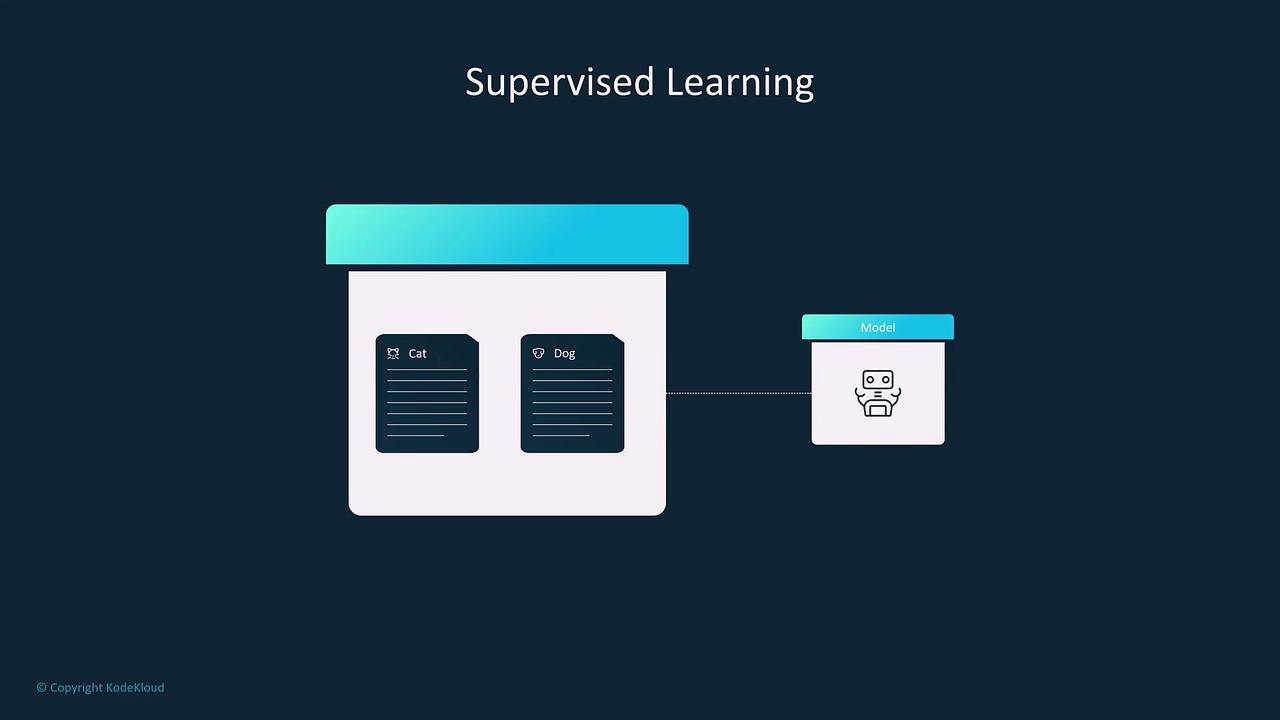
Supervised learning involves training a model on a dataset that includes both inputs and associated labeled outputs. The model learns the mapping between features and targets, enabling it to predict outcomes based on new input data. Common applications include:- Housing Price Prediction: Estimating property values using features like square footage, location, and number of bedrooms.
- Stock Market Forecasting: Analyzing historical trends to predict market movements.
- Image Classification: Differentiating between objects, like distinguishing between cats and dogs from labeled images.
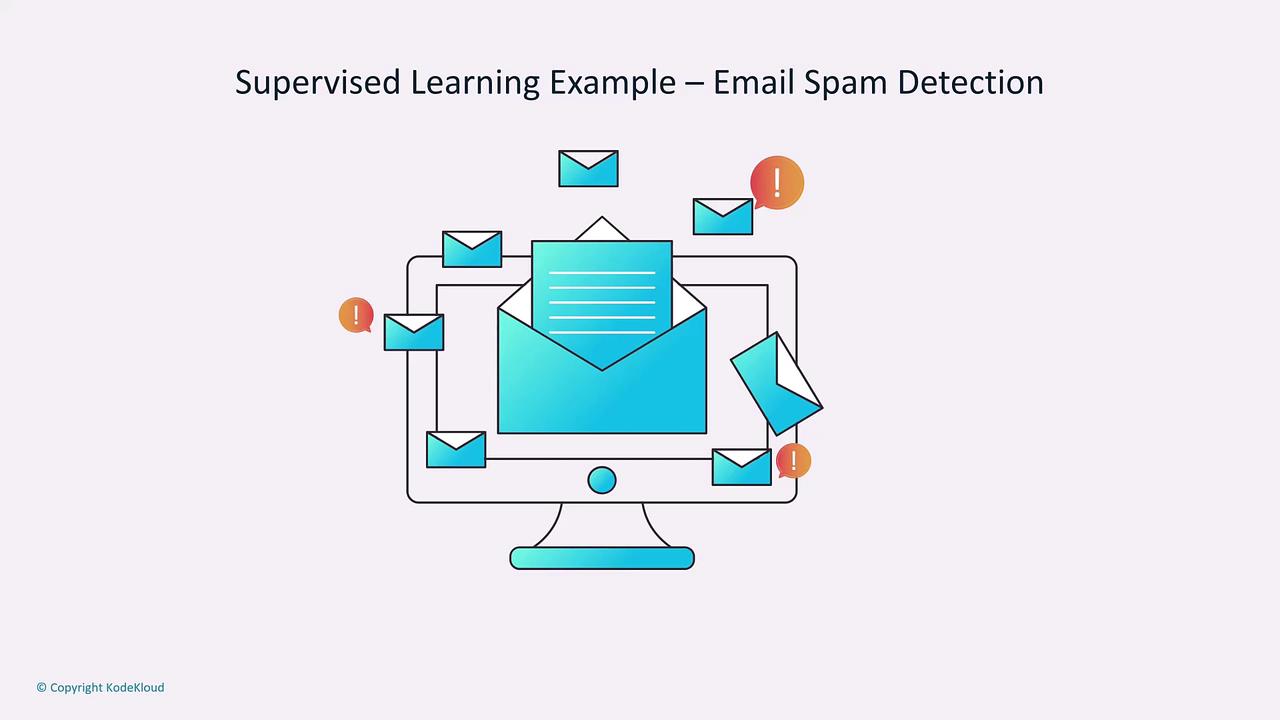
- Spam Detection: Identifying spam emails by learning from previously labeled instances.
- Credit Scoring: Predicting financial reliability based on historical credit data.
Supervised learning relies heavily on high-quality labeled data. More examples typically improve accuracy, especially in complex tasks such as spam detection.

Unsupervised Learning
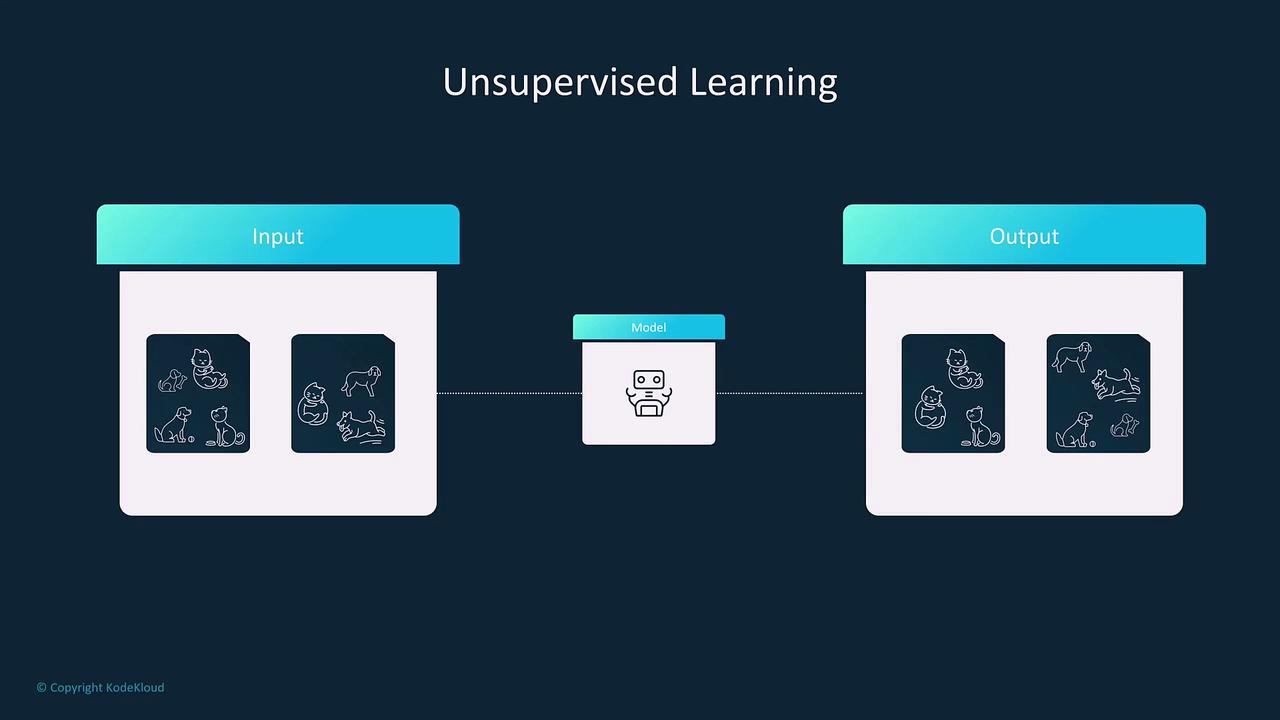
Unsupervised learning focuses on extracting hidden patterns from data that has not been labeled. The primary goal is to identify intrinsic structures such as clusters or anomalies. This technique is invaluable when pre-defined labels are not available. Key use cases include:- Image Grouping: Automatically organizing images by similar features (e.g., grouping together images of cats and dogs without prior labeling).
- Customer Segmentation: Dividing consumers into distinct groups like “Budget-Conscious” and “Premium Buyers” based on purchasing behavior.
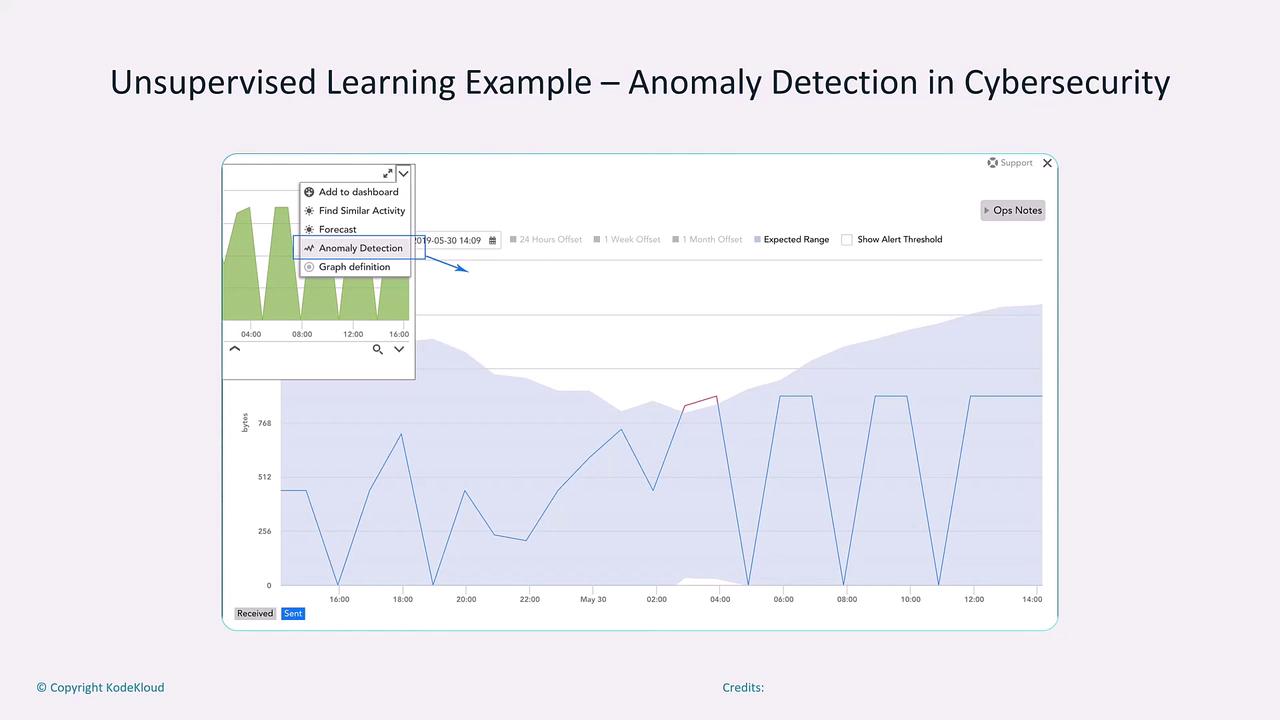
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual patterns in network traffic or system operations which may indicate security breaches or faults.

Reinforcement Learning
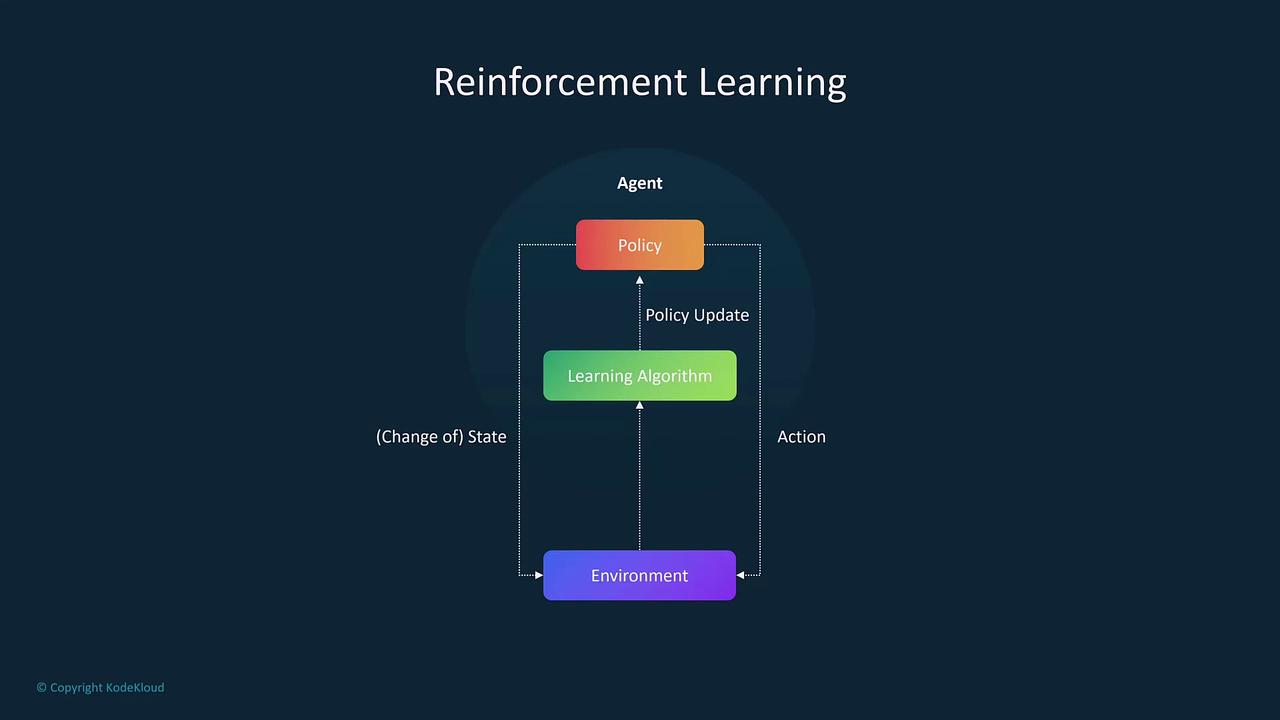
Reinforcement learning differs notably from the other types by emphasizing the role of an agent that learns through interaction with its environment. The agent receives rewards or penalties based on its actions, allowing it to iteratively improve its strategy. Practical applications include:- Game Playing: Training an AI to excel in chess or other board games by learning from successes and failures.
- Autonomous Driving: Allowing in-car systems to optimize driving strategies using live feedback from the surrounding environment.
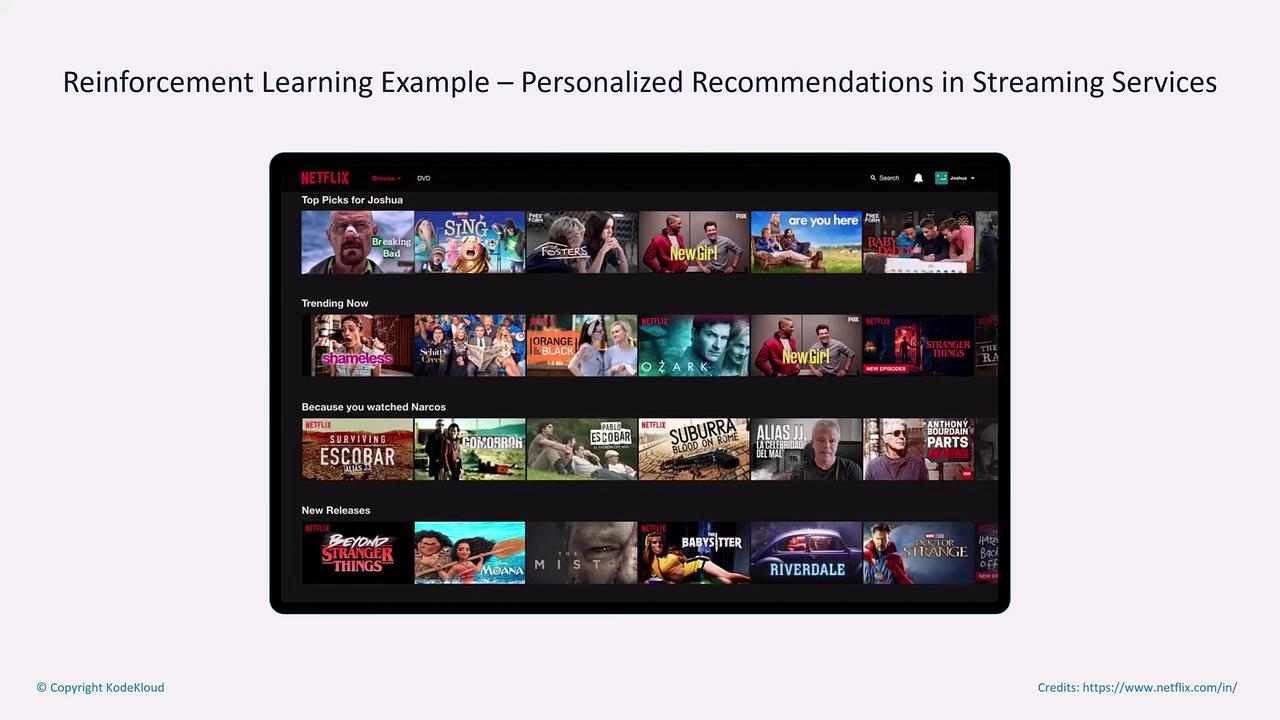
- Recommendation Engines: Adapting content suggestions based on viewer interactions to enhance user experience.
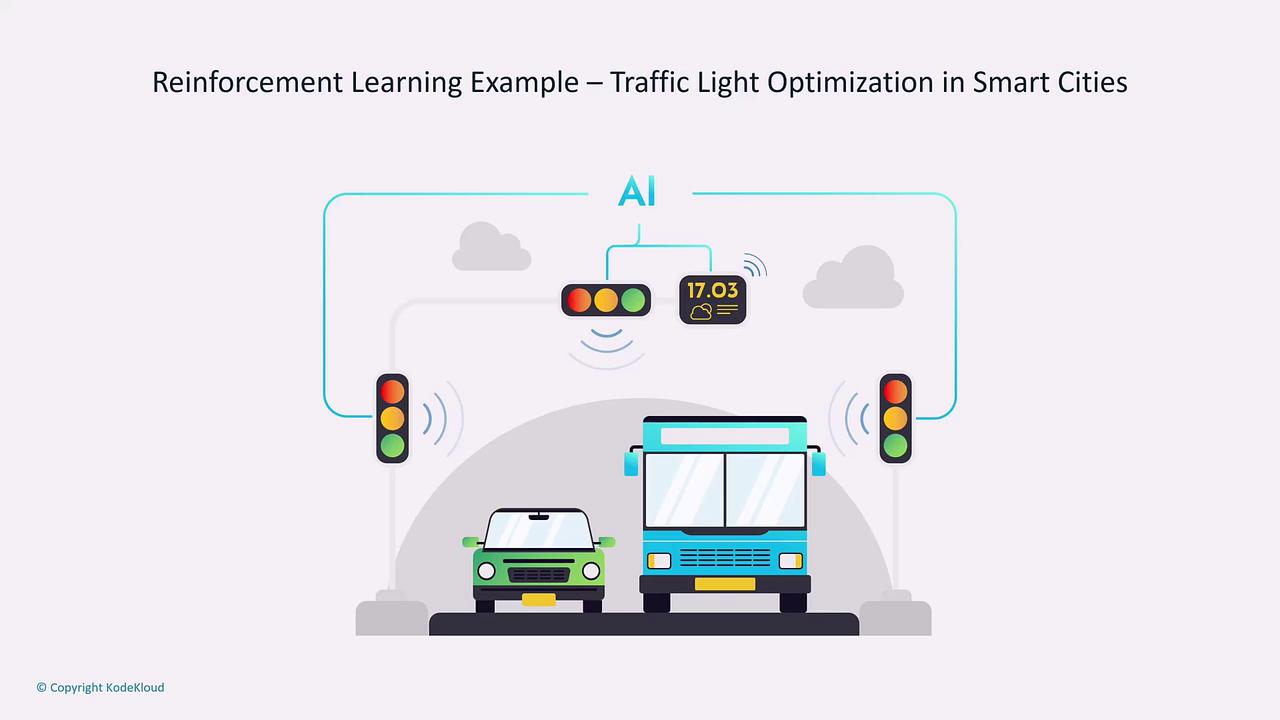
- Smart City Traffic Management: Dynamically managing traffic lights to improve flow and reduce congestion based on real-time sensor data.
When deploying reinforcement learning, carefully monitor the feedback loop to balance exploration and exploitation, ensuring that the agent does not adopt suboptimal strategies.

Summary
In this lesson, we covered:- Supervised Learning: Using labeled data to train models for predictions and decision-making.
- Unsupervised Learning: Discovering patterns and clusters in unlabeled data to inform strategic decisions.
- Reinforcement Learning: Training an agent through feedback within a defined environment to learn optimal actions.