- Data Collection:
Gather data relevant to the problem (e.g., fraud detection). - Data Ingestion:
Collect data from diverse sources. - Data Transformation and Cleaning:
Process the gathered data to ensure it is structured and clean. - Data Analysis and Visualization:
Analyze and visualize the processed data to fully understand the problem. - Decision Point:
Determine whether a machine learning model is required.- If not, re-assess and redefine the problem statement.
- If yes, continue with:
- Feature Engineering
- Model Exploration, Building, and Training
- Model Evaluation
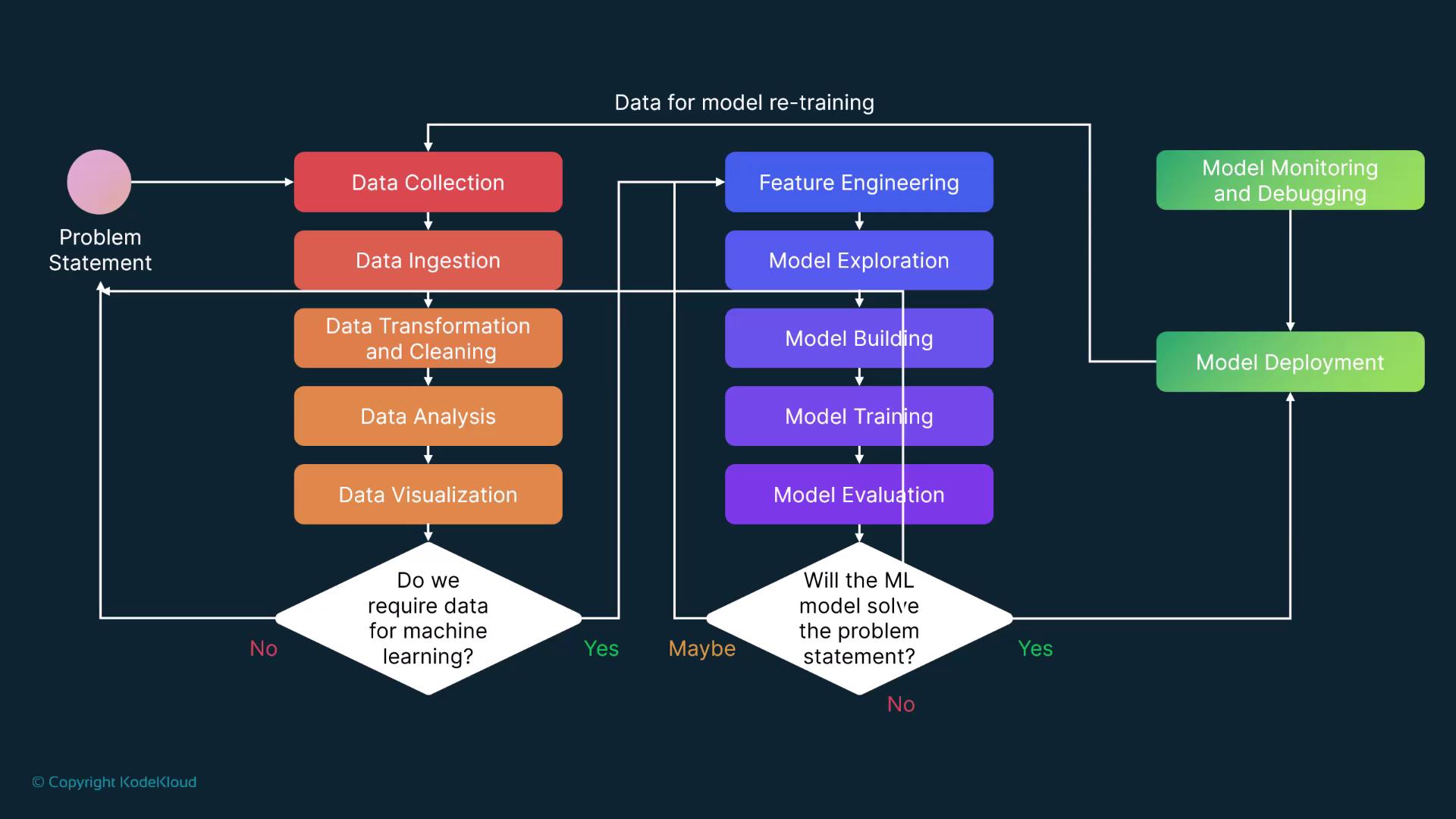
At every stage of this lifecycle, the MLOps engineer plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless integration and execution.
Common Challenges in the ML Development Lifecycle
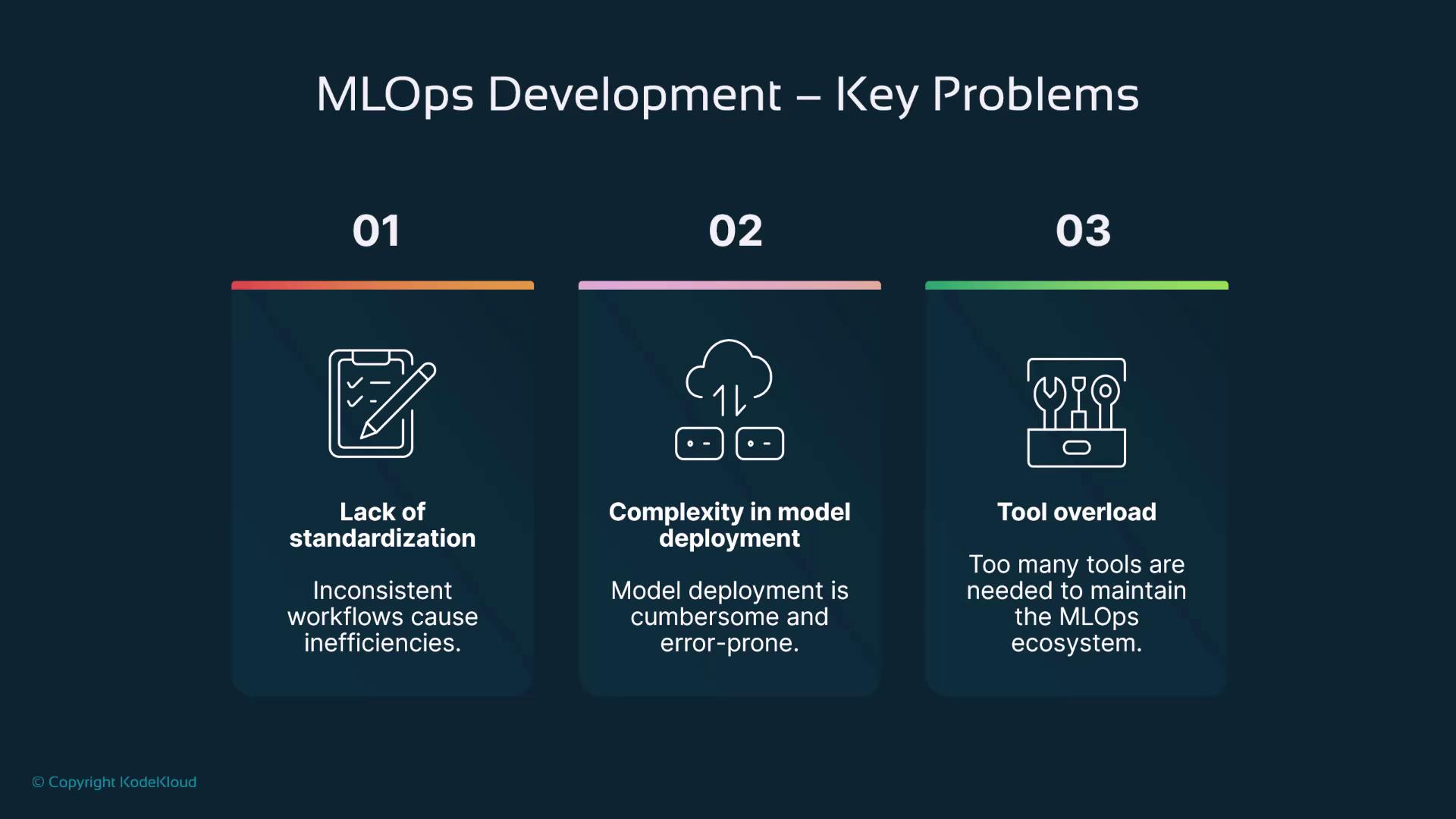
The ML development lifecycle is not without its challenges:-
Lack of Standardization:
Inconsistent workflows across teams can result in varied data preprocessing methods, leading to differences in data quality and model performance. -
Complexity of ML Models:
Manual deployment of ML models—including managing dependencies and environment configurations—can be error-prone and inefficient. -
Tool Overload:
The necessity to integrate and coordinate numerous open-source tools across multiple ML models (often 20–30) increases operational overhead significantly.
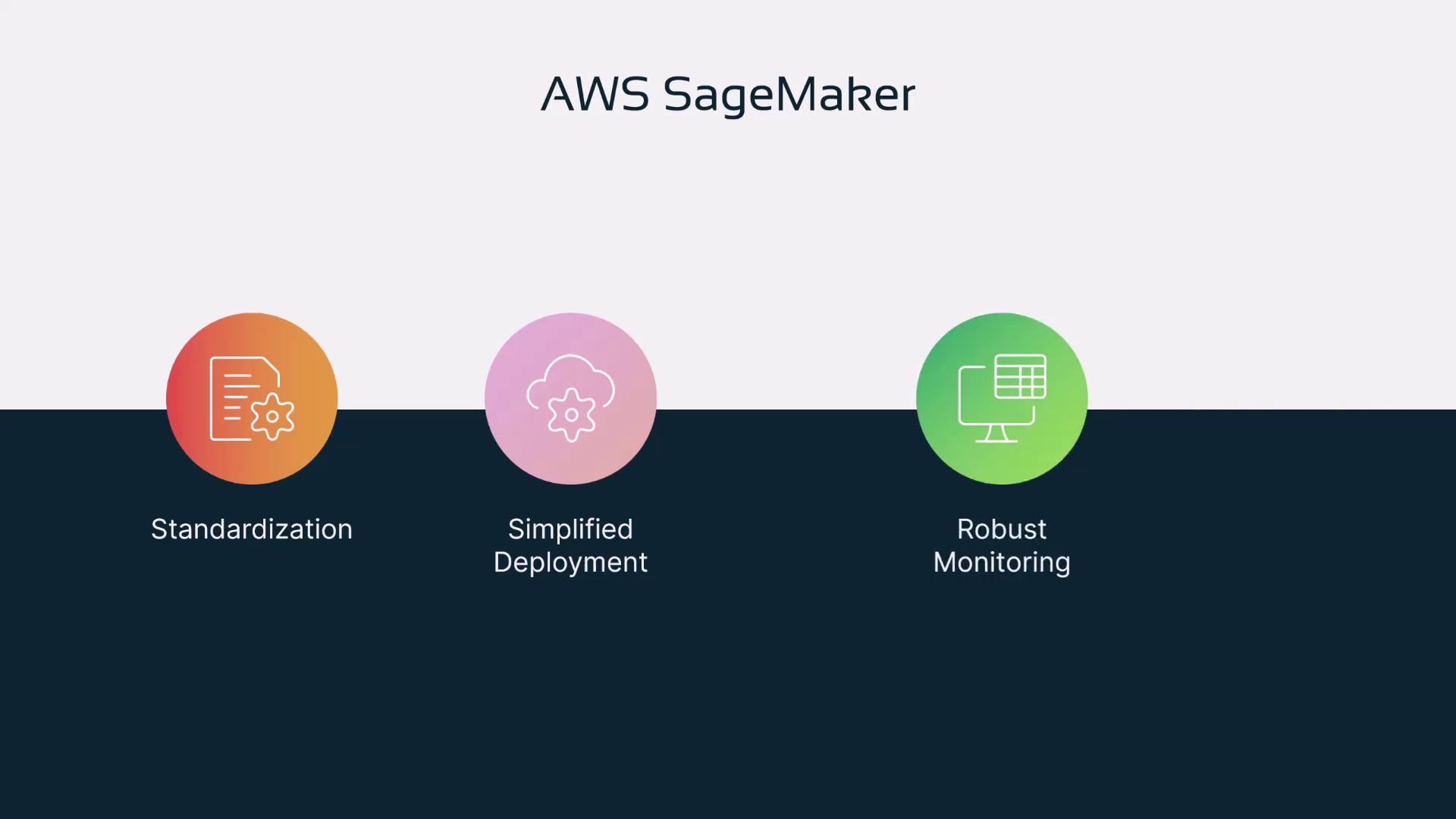
How AWS SageMaker Addresses These Challenges
AWS SageMaker is a fully managed service designed to simplify the machine learning lifecycle—from model building to deployment. It supports end-to-end ML workflows with a wide array of infrastructure options and tools tailored to address common MLOps challenges.Key Features of AWS SageMaker
-
Standardization:
SageMaker harmonizes workflows across teams by offering pre-built algorithms and support for custom model deployment through standardized pipelines. -
Simplified Deployment:
With one-click deployment, SageMaker removes infrastructural complexities. Its real-time monitoring and debugging features quickly address issues such as data drift or performance degradation.
-
Scalable Infrastructure:
Automatically scaling resources based on demand, SageMaker is ideal for compute-intensive tasks like training computer vision models. This scalability lets you focus on developing high-quality models without worrying about resource allocation. -
Reproducibility and Versioning:
Easily track changes in data, code, and configurations. This versioning capability is essential for managing multiple iterations of a model, such as those used in fraud detection. -
CI/CD Integration:
Operating seamlessly within the AWS cloud ecosystem, SageMaker supports integration with services like EKS, EC2, and S3. The platform also enables robust CI/CD pipelines for streamlined deployments, both within and outside AWS.