Azure AD Identity Types
At a high level, Azure AD supports four identity types:-
User Identity
An individual AAD account used for interactive sign-ins and access control. -
Application Identity
A registered app in AAD that can authenticate and access resources on behalf of a user or itself. -
Service Principal
A non-interactive app identity for automation, CI/CD pipelines, or service-to-service scenarios. It authenticates with a client ID and secret (or certificate).
Service principals require regular secret or certificate rotations. If credentials expire, any AKS operations using that principal will fail.
- Managed Identity
A system-assigned or user-assigned identity created and managed by Azure. Eliminates manual secret management by obtaining tokens directly from AAD.
If you’re familiar with on-premises Active Directory, managed identities behave like built-in system accounts that Azure handles automatically.
Service Principal vs. Managed Identity
| Feature | Service Principal | Managed Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Credential Management | Secrets or certificates to rotate | No secrets; tokens issued transparently |
| Lifecycle | Provisioned manually | Auto-provisioned with Azure resources |
| Use Cases | Custom automation, CI/CD pipelines | AKS control plane, VM-to-Azure service access |
- A managed identity for the cluster control plane
- Two service principals in the same resource group
- The managed identity appears under Enterprise Applications in AAD
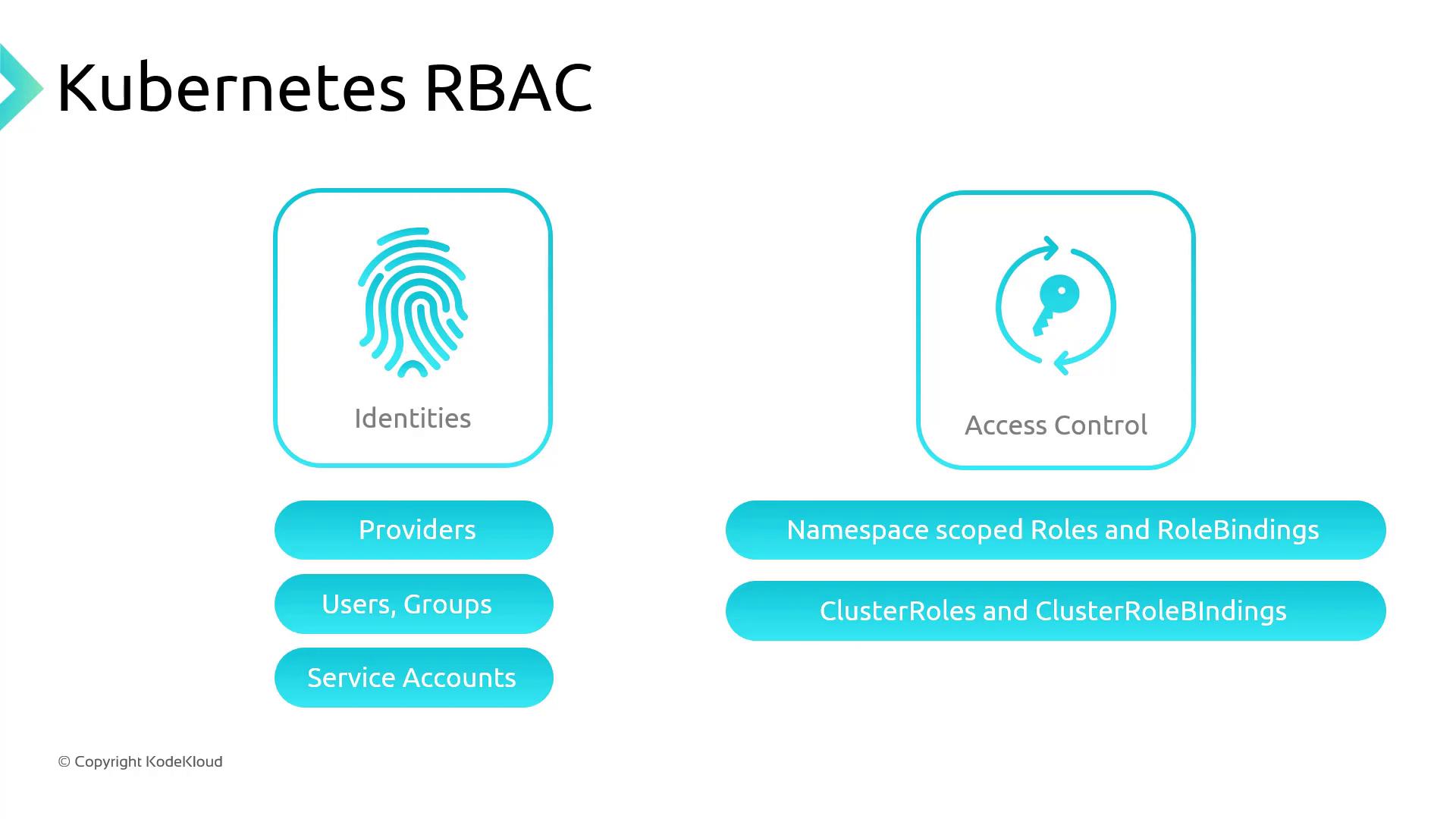
Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Kubernetes RBAC lets you define fine-grained permissions via Roles and RoleBindings:- Roles (namespace-scoped) or ClusterRoles (cluster-wide) specify allowed
verbson resources. - RoleBindings or ClusterRoleBindings assign these roles to subjects (users, groups, or service accounts).
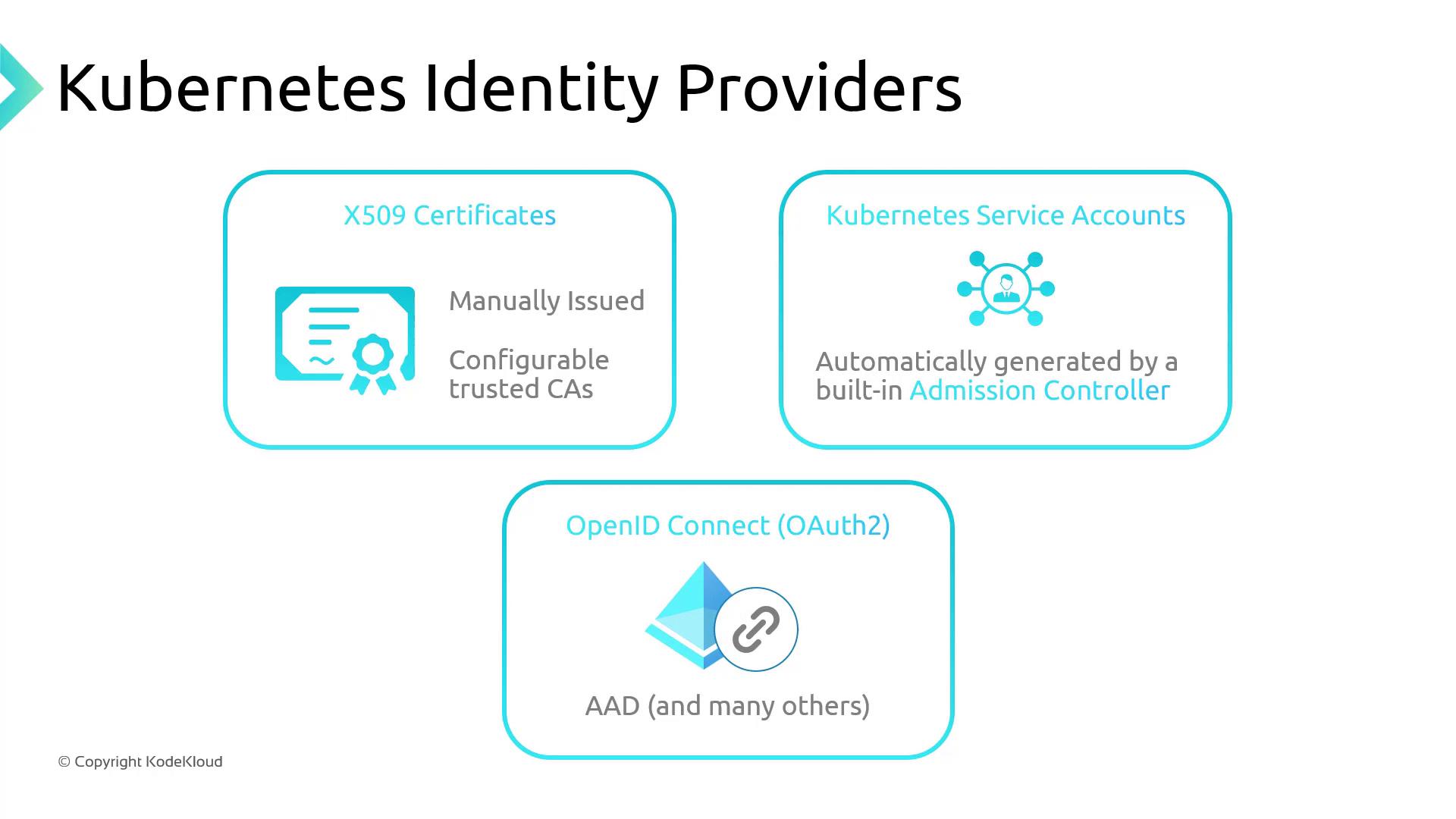
- X.509 Certificates
- Service Accounts (in-cluster)
- OpenID Connect (e.g., Azure AD)
Example ClusterRole
Grantsget and patch on daemonsets and deployments (in the apps API group), and get on configmaps (in the core API group):
Example ClusterRoleBinding
Binds the aboveClusterRole to an Azure AD group by its object ID:
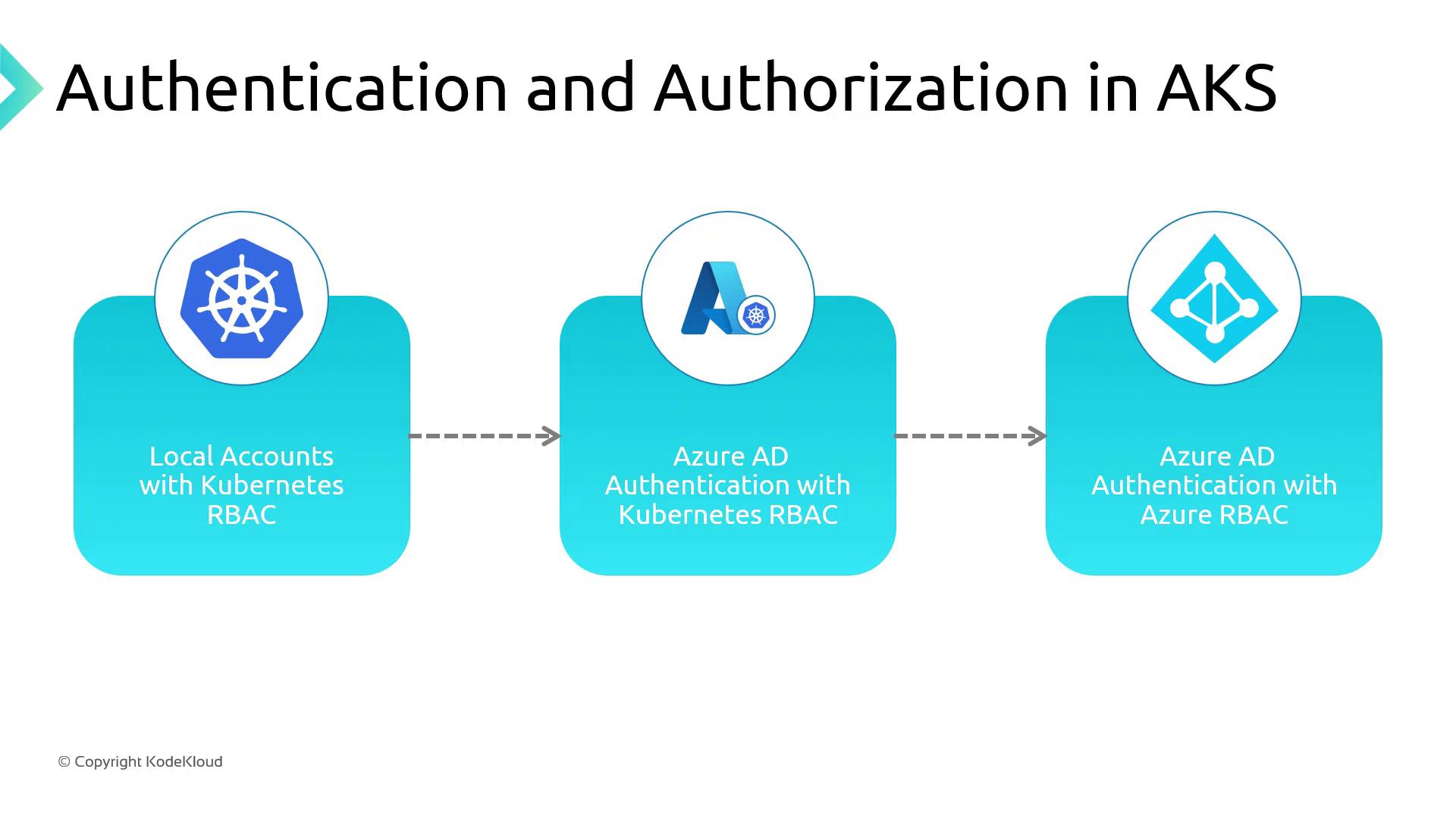
AKS Authentication and Authorization Options
| Method | Authentication | Authorization | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Accounts + Kubernetes RBAC (Default) | K8s service accounts, tokens | Kubernetes RBAC | Quick start with built-in K8s controls |
| Azure AD Auth + Kubernetes RBAC | Azure AD users/groups | Kubernetes RBAC | Leverage MFA, conditional access policies |
| Azure AD Auth + Azure RBAC | Azure AD users/groups | Azure role assignments | Centralized IAM across Azure resources |
-
Local Accounts with Kubernetes RBAC (Default)
- Native service accounts, roles, and bindings stored in the cluster
- Auth via certificates, tokens, or basic auth
-
Azure AD Authentication with Kubernetes RBAC
- Users sign in with Azure AD credentials
- K8s RBAC enforces permissions
- Supports Azure AD features like MFA
- Azure AD Authentication and Azure RBAC
- Azure AD handles both authentication and authorization
- Use Azure role assignments to grant AKS permissions
- Provides a seamless IAM experience across Azure