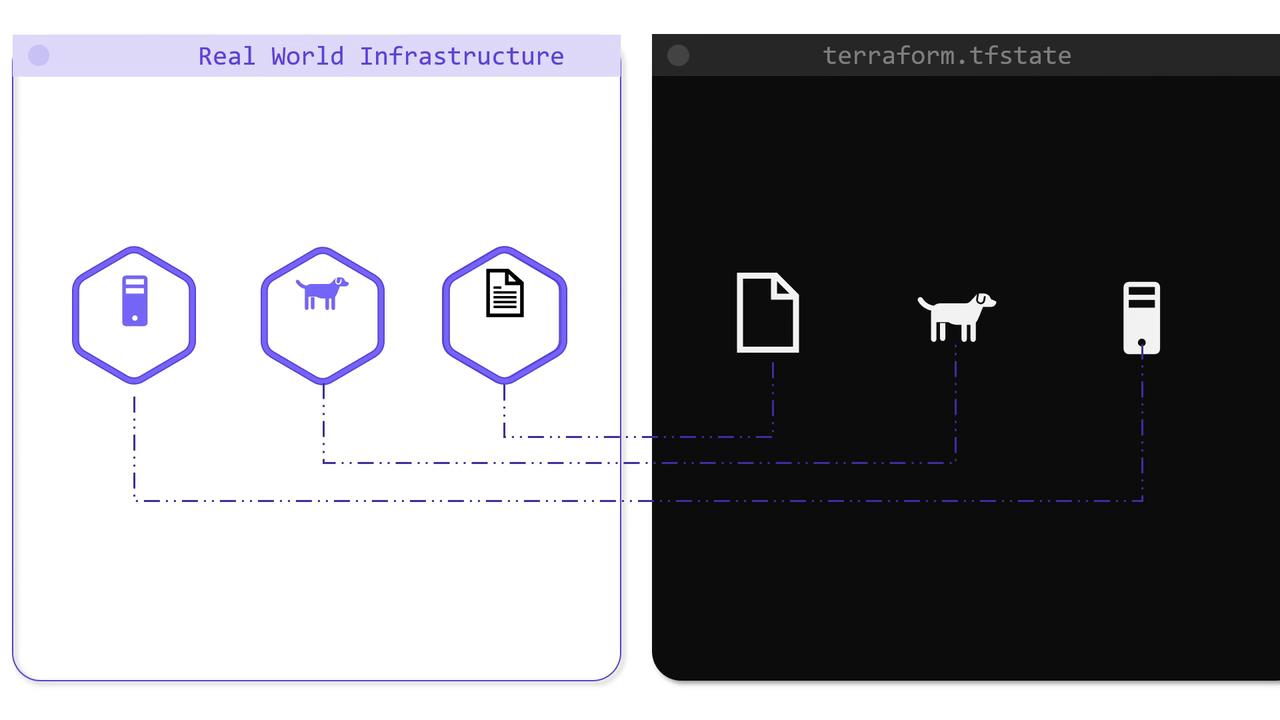
terraform apply, a file named terraform.tfstate is created in your configuration directory.
Benefits of the Terraform State
Storing state locally provides several benefits:- Mapping Terraform configurations to real infrastructure.
- Tracking metadata and resource dependencies, enabling Terraform to create and delete resources in the correct order.
- Enhancing performance when managing large configurations across multiple cloud providers.
- Facilitating team collaboration by offering a single view of the infrastructure state.
For individual projects, a local state file might suffice. However, as your team grows and your infrastructure becomes more complex, managing state locally can lead to significant challenges.
Challenges with Local State Files
In early configurations, the state file was created and maintained on a developer’s machine. Although this approach works for smaller projects, it poses several risks:- Sensitive data (e.g., IP addresses, initial database passwords, key names) remains on a local machine.
- Concurrent modifications become difficult to manage, leading to potential state corruption.
- Storing the state file in version control is not recommended because it may expose sensitive information.
terraform plan and applying the configuration, Terraform generates a local state file (terraform.tfstate). Abdul then commits all configuration files, including the state file, into a Git repository. Later, when another developer, Lee, pulls the repository, he makes his modifications, reviews the plan, applies the changes, and pushes the updated configuration and state file back to the Git repository.
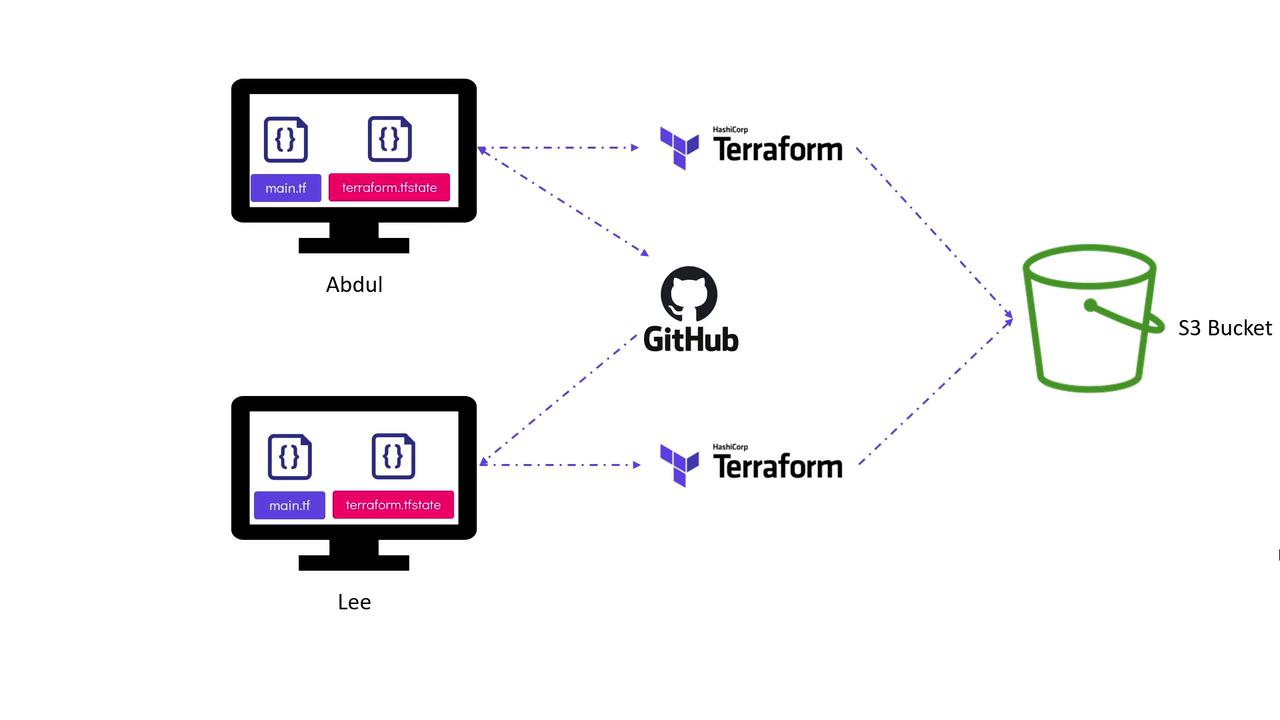
- Sensitive infrastructure details (such as IP addresses and key names) are stored within a Git repository.
- Concurrent updates using local state files can lead to conflicts or even state corruption.
How Terraform State Locking Works
Terraform incorporates a mechanism called state locking to prevent simultaneous modifications. When you run commands liketerraform apply, Terraform locks the state file to avoid interference from another operation. Consider the following execution process:
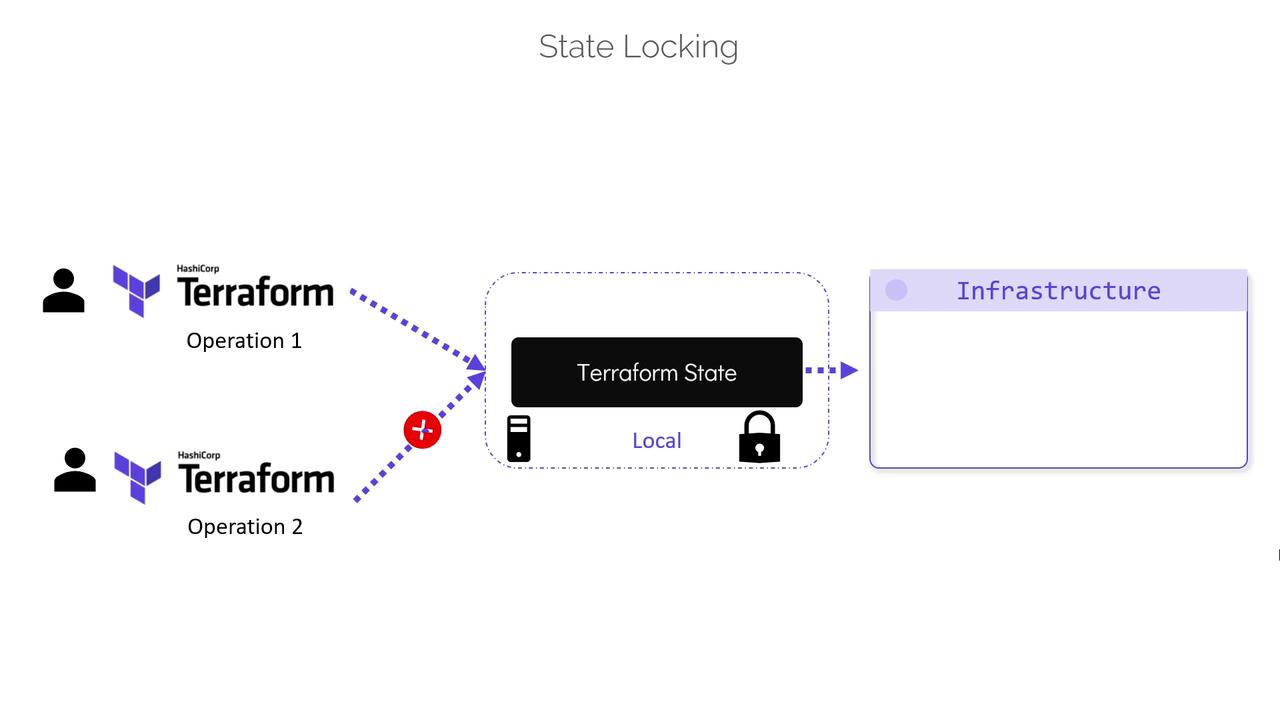
Avoid disabling state locking with the “-lock=false” flag in a team environment, as doing so can lead to concurrent modifications and potential data loss.
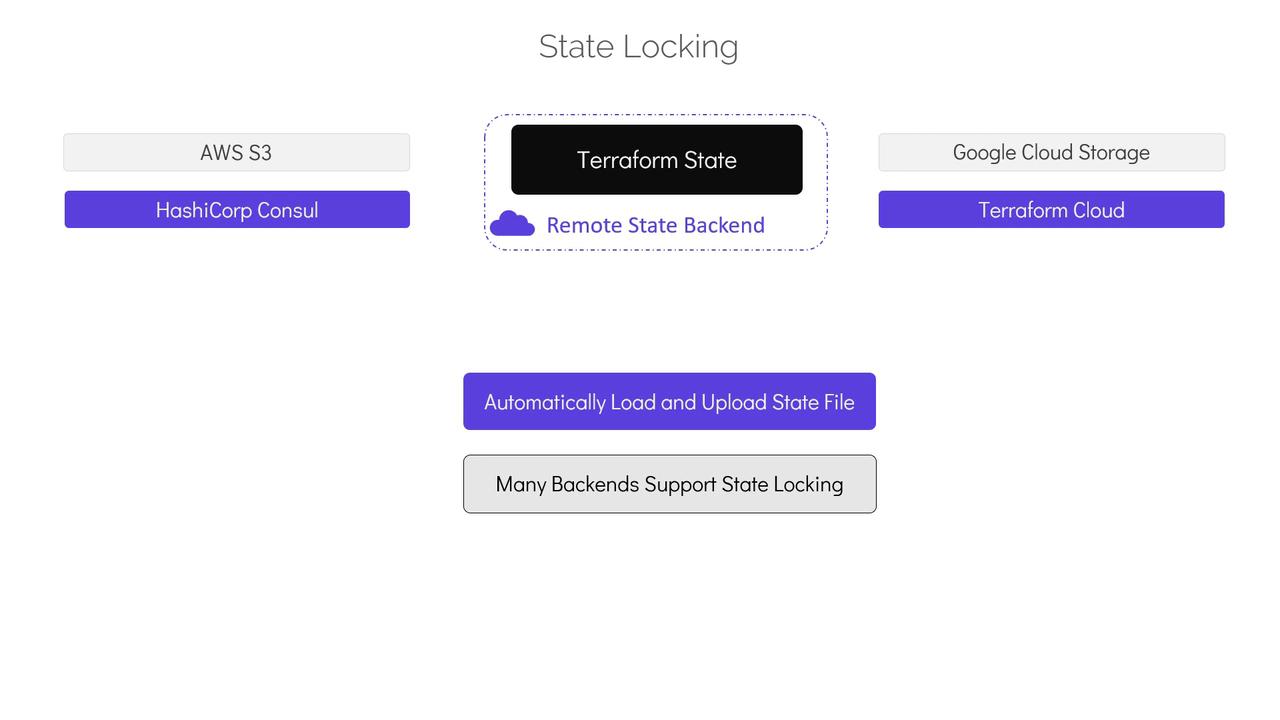
Remote Backends: A Secure Alternative
Version control systems like GitHub do not support state locking. If multiple users access and modify a state file stored in version control simultaneously, it can result in conflicts and even data loss. Additionally, working with outdated state files (by not pulling the latest changes) can lead to accidental destructive actions, such as unintended resource rollbacks or deletions. A far better approach is to store the Terraform state in a secured, shared storage solution using remote backends. Remote backends store the state file outside the configuration directory and version control system using services such as AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, HashiCorp Consul, or Terraform Cloud. With a remote backend, Terraform automatically:- Loads the state from shared storage for every operation.
- Uploads state updates after each
terraform apply. - Provides state locking to maintain state integrity.
- Enhances security by offering features like encryption at rest and in transit.