What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Why Use Kubernetes for Model Deployment?
Kubernetes offers several compelling benefits when deploying machine learning models:- High-Volume Request Handling: Designed to manage a high volume of simultaneous requests, making it ideal for production environments where model traffic can fluctuate.
- Seamless Scalability: Its inherent scalability allows your application to grow without requiring extensive modifications to your deployment configuration.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Kubernetes optimally allocates limited resources like GPUs, ensuring cost-effective operations for resource-heavy AI workloads.
- Versatile Deployment Scenarios: Whether deploying for real-time data inference or batch processing of historical data, Kubernetes adapts easily to various deployment scenarios.
- Automated Resource Management: It automates critical processes such as scaling during peak demand and adjusting resources during low-demand periods, while continuously monitoring system health for high availability and reliability.
Handling Specialized Workloads
ML and AI tasks often require specific hardware configurations. Kubernetes enables precise resource allocation and workload scheduling by using node affinity, node selectors, taints & tolerations, and resource requests and limits.Node Affinity
Node affinity allows you to define which nodes should execute particular workloads. For instance, if a node is labeled withgpu=true, you can ensure that your ML tasks run specifically on these GPU-enabled nodes.

gpu="true":
Node Selector
Alternatively, you can use a node selector to ensure pods are scheduled on nodes with a specific label. Consider the following example, where pods are assigned to nodes labeledcpu=high-performance:
Taints and Tolerations
Taints prevent pods from being scheduled on certain nodes unless they expressly tolerate them. This is useful for dedicating nodes exclusively to ML workloads.
Resource Requests and Limits
Defining resource requests and limits ensures that your ML models receive the necessary CPU, GPU, or memory while preventing competition between workloads.
Deploying an ML Model to Kubernetes
Deploying an ML model with Kubernetes involves a series of well-defined steps:- Containerization: Package your trained model into a container using a model serving framework. Test the container locally to ensure it functions as expected.
- Preparing Kubernetes Resources: Define your deployment, services, config maps, and secrets using YAML manifests. These configurations instruct Kubernetes on how to run and manage your model.
- Deployment: Apply the YAML files using
kubectlor integrate them into a GitOps pipeline. Verify the deployment using commands likekubectl get podsandkubectl logs. - Testing and Scaling: Use a REST client (such as Postman) to test the model endpoint. Configure an autoscaler (e.g., Horizontal Pod Autoscaler) to adjust pod counts dynamically based on traffic.
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)
The Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) is critical for managing workload fluctuations. It automatically adjusts the number of pods based on real-time metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, or custom metrics, ensuring your deployment remains responsive and resource-efficient.


Best Practices for Deploying ML Models on Kubernetes
Adopting best practices is crucial for robust and efficient ML model deployments:- Container Optimization:
Use lightweight, optimized containers such as slim Docker images that include only the necessary files and dependencies. This practice speeds up deployments and reduces resource overhead.

- Resource Monitoring:
Leverage monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana to track CPU, memory, and GPU usage. Always define resource limits to avoid contention, especially in shared cluster environments.

- Rolling Updates:
Employ rolling updates for model deployments to minimize downtime. This approach allows gradual updates and ensures a smooth user experience.

- Security Measures:
Implement strict security best practices by using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and network policies to restrict permissions for pods. This minimizes unauthorized access risks.

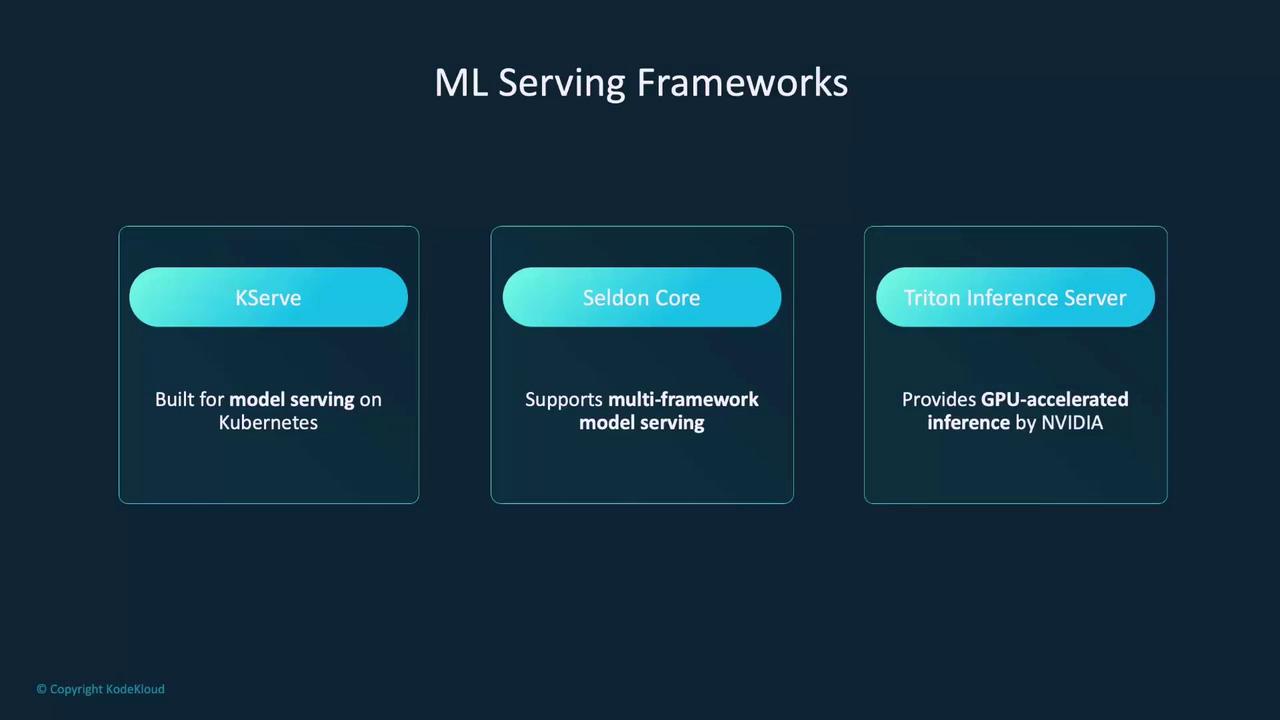
ML Serving Frameworks for Kubernetes
While Kubernetes’ native resources (Deployments, Services, etc.) suffice for many model deployments, specialized ML serving frameworks can streamline and enhance the process:-
KServe (formerly KFServing):
Specifically designed for serving ML models on Kubernetes, KServe supports advanced features such as explainability and model monitoring, making it perfect for production-grade deployments. -
Seldon Core:
Offers interoperability for models built on different frameworks. Seldon Core facilitates complex workflows like ensemble models and A/B testing while integrating natively with Kubernetes. -
Triton Inference Server:
Developed by NVIDIA, Triton provides GPU-accelerated inference and supports dynamic batching across multiple ML frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX).