Creating the Virtual Machine
- Log in to the Azure Portal and navigate to Virtual Machines. Click on Create Virtual Machine to begin. Tip: Consider available resources (RAM, CPU) during selection to match your Jenkins workload.
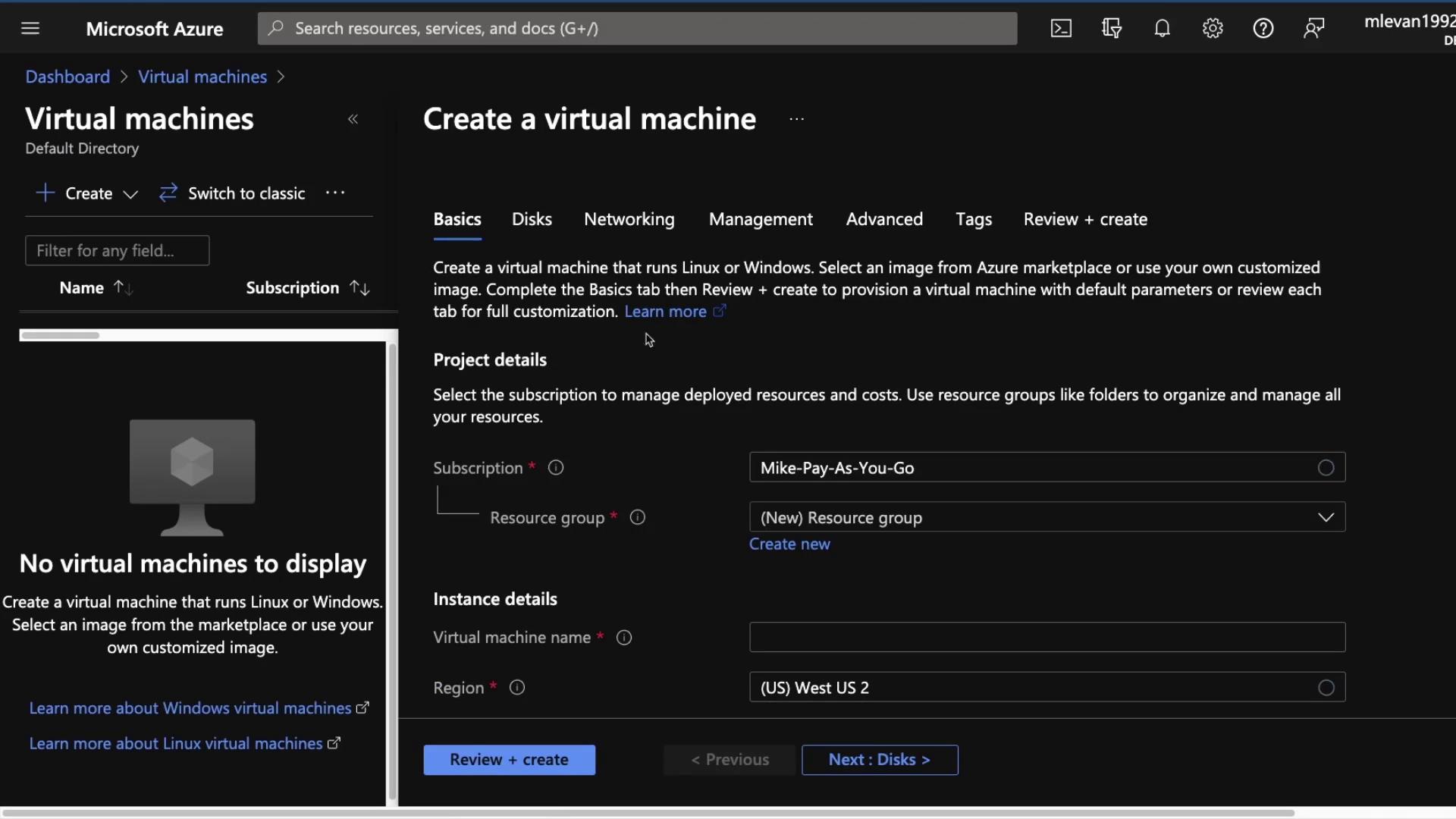
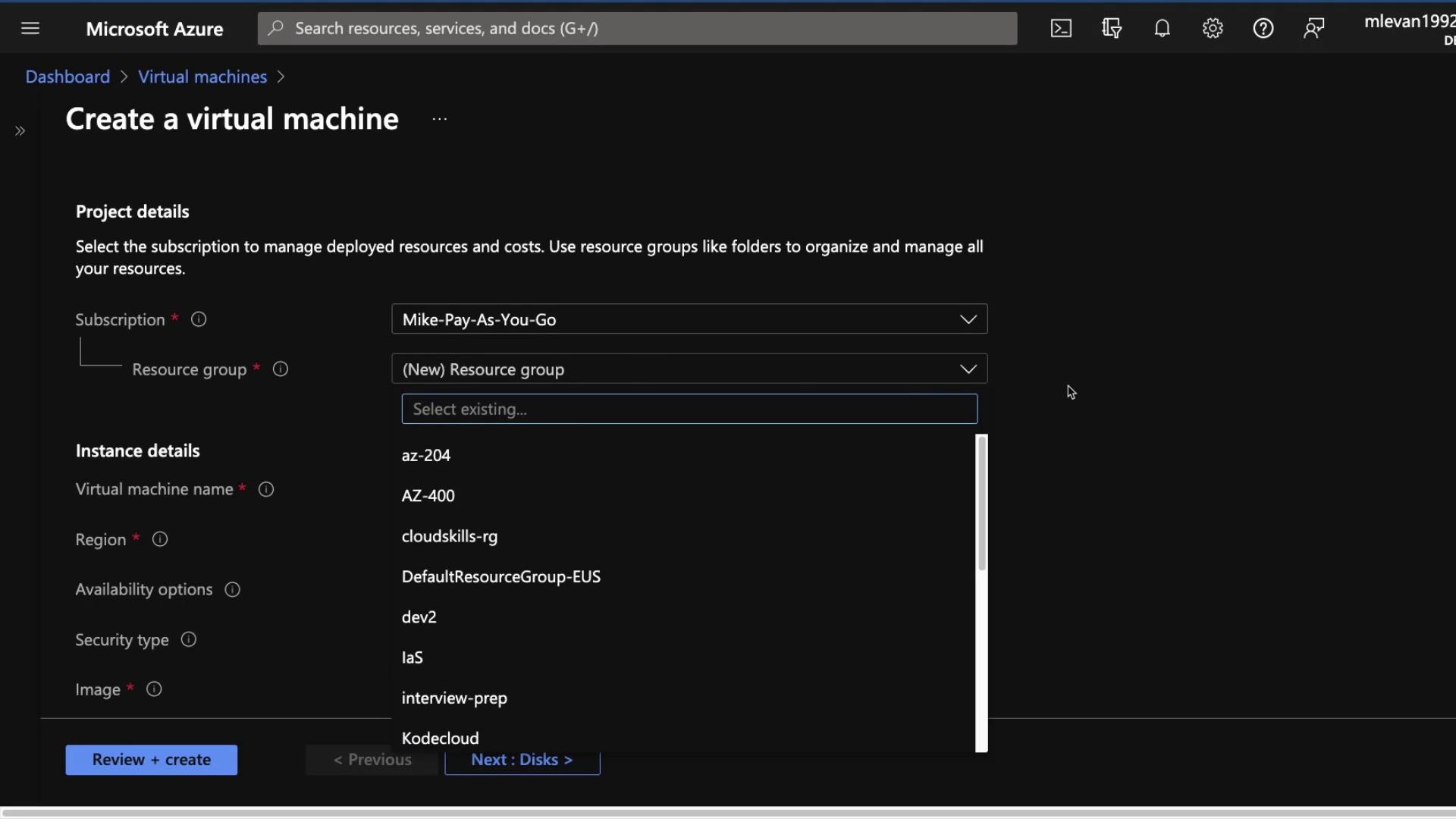
- Choose your resource group (e.g., “KodeKloud”) and enter a name for the VM. Select the Ubuntu 20.04 OS image. For a cost-effective option, opt for a VM size with 1 vCPU and 2 GB RAM.
- Continue by configuring the instance details:
- Set a username and password for SSH access. For demonstration purposes, open port 22.
Opening port 22 for SSH access is not recommended in production environments. Ensure network security groups or firewalls are correctly configured.
- For storage, choose a premium SSD, add the VM to your “KodeKloud VNet”, then click Next to review and confirm your settings. Enter your password again when prompted, then create the VM.
- Once the VM is created, open a terminal to connect via SSH.
Connecting to Your VM
-
Open your terminal and connect to the VM using its public IP address. For example:
-
When you see the authenticity warning, type “yes” and then provide your password:
-
Once connected, clear the terminal and update the package lists:
Installing Prerequisites
Jenkins requires Java to run. Update your package lists and install Java with the following command:Installing Jenkins
With Java installed, proceed to install Jenkins by following these steps:-
Add the Jenkins Repository Key:
You should see an “OK” response.
-
Append the Jenkins Repository:
-
Update the Package List:
The output confirms that the Jenkins repository is being fetched:
-
Install Jenkins:
During installation, you might see logs similar to:
Starting and Verifying Jenkins
-
Start the Jenkins Service:
-
Verify the Service Status:
Expected output indicates that the Jenkins service is active:
-
Open Firewall Port 8080:
To access the Jenkins UI, allow traffic on port 8080:
-
Confirm Firewall Status:
If the firewall is inactive, that is acceptable for a demo environment. In a production environment, ensure the firewall settings limit access to only trusted IP addresses.
-
Exit SSH Session:
Your terminal will indicate that the connection has been closed.
-
Access Jenkins:
Open your web browser and navigate to:
http://<Your_VM_Public_IP>:8080
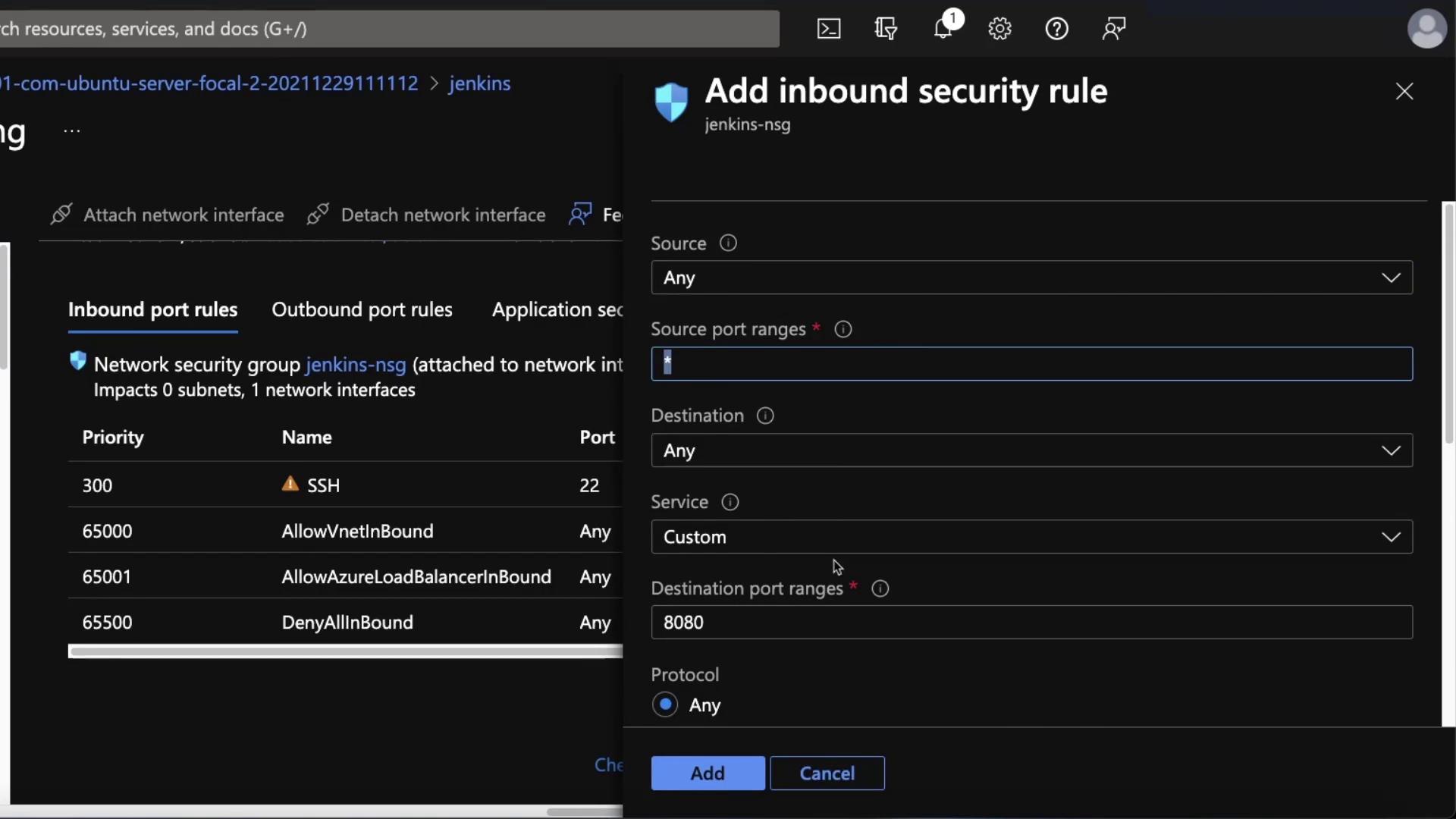
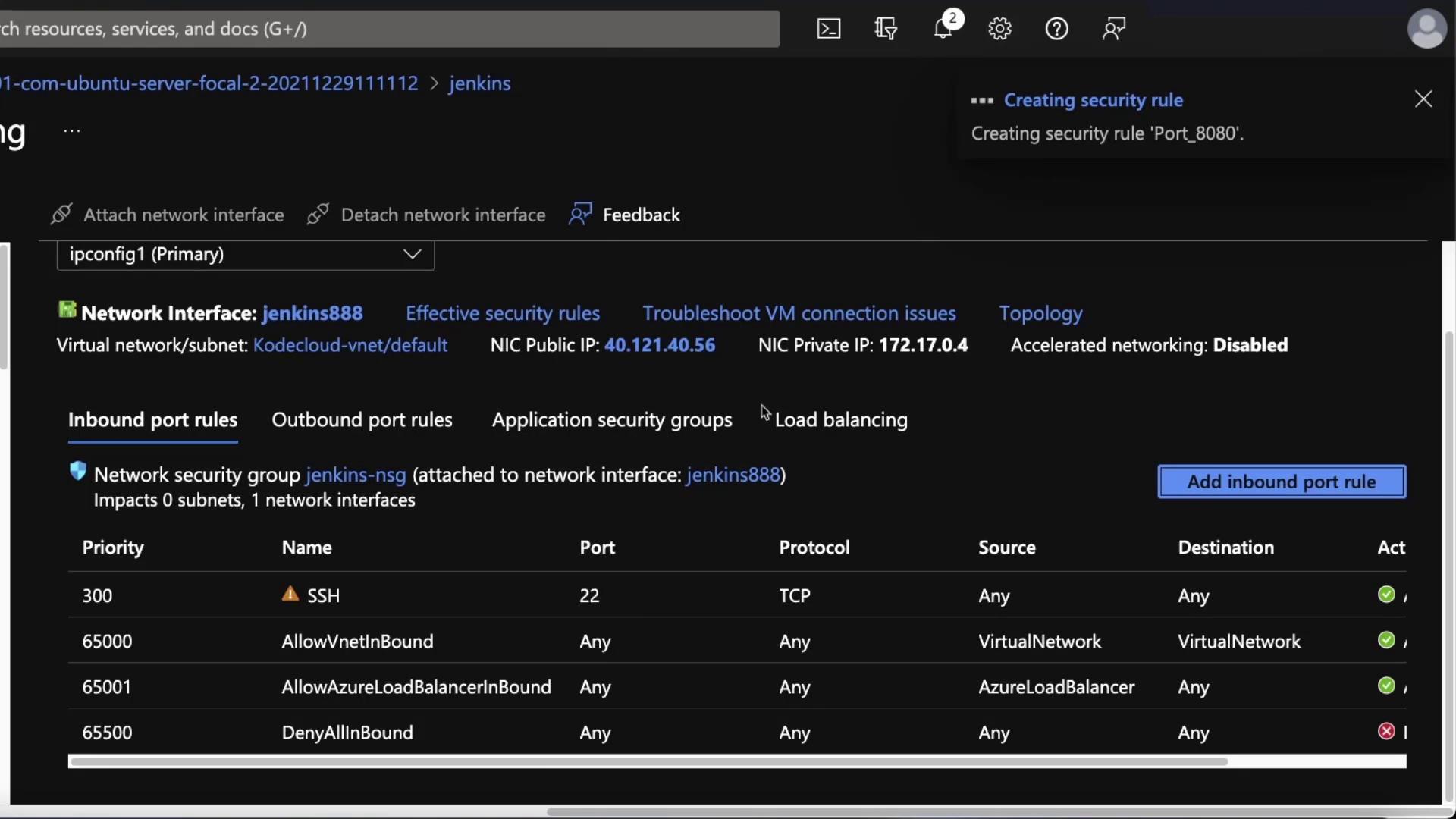
If Jenkins is not accessible, verify your network settings in the Azure portal under Networking. Confirm that port 8080 is open. If not, add an inbound security rule.
Unlocking and Setting Up Jenkins
-
Unlock Jenkins:
When you first access the Jenkins UI, you’ll be prompted to unlock Jenkins using the initial admin password. Retrieve the password from your server with:
Example output:
-
Complete the Setup:
- Copy the password from the terminal and paste it into the Jenkins setup screen.
- Choose to install the suggested plugins.
- When installation is complete, create your first admin user (e.g., Michael). Provide a username, password, full name, and optionally an email address.

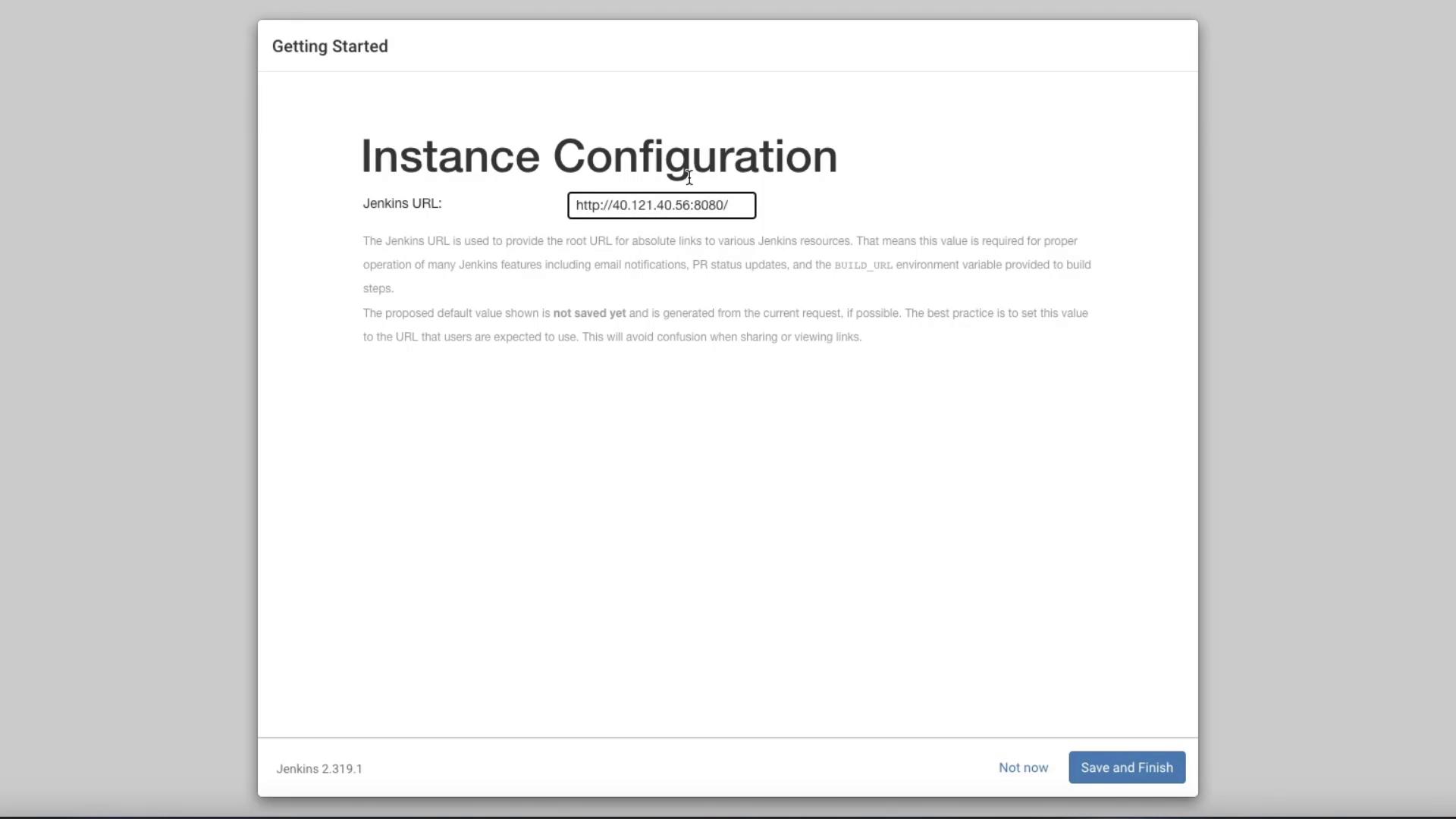
- Configure the Jenkins Instance: If you do not have a DNS record, simply use your VM’s IP address in the instance configuration screen.
- Finalize the Setup: After saving your configuration, you will see the Jenkins dashboard.