What Exactly Are Build Agents?
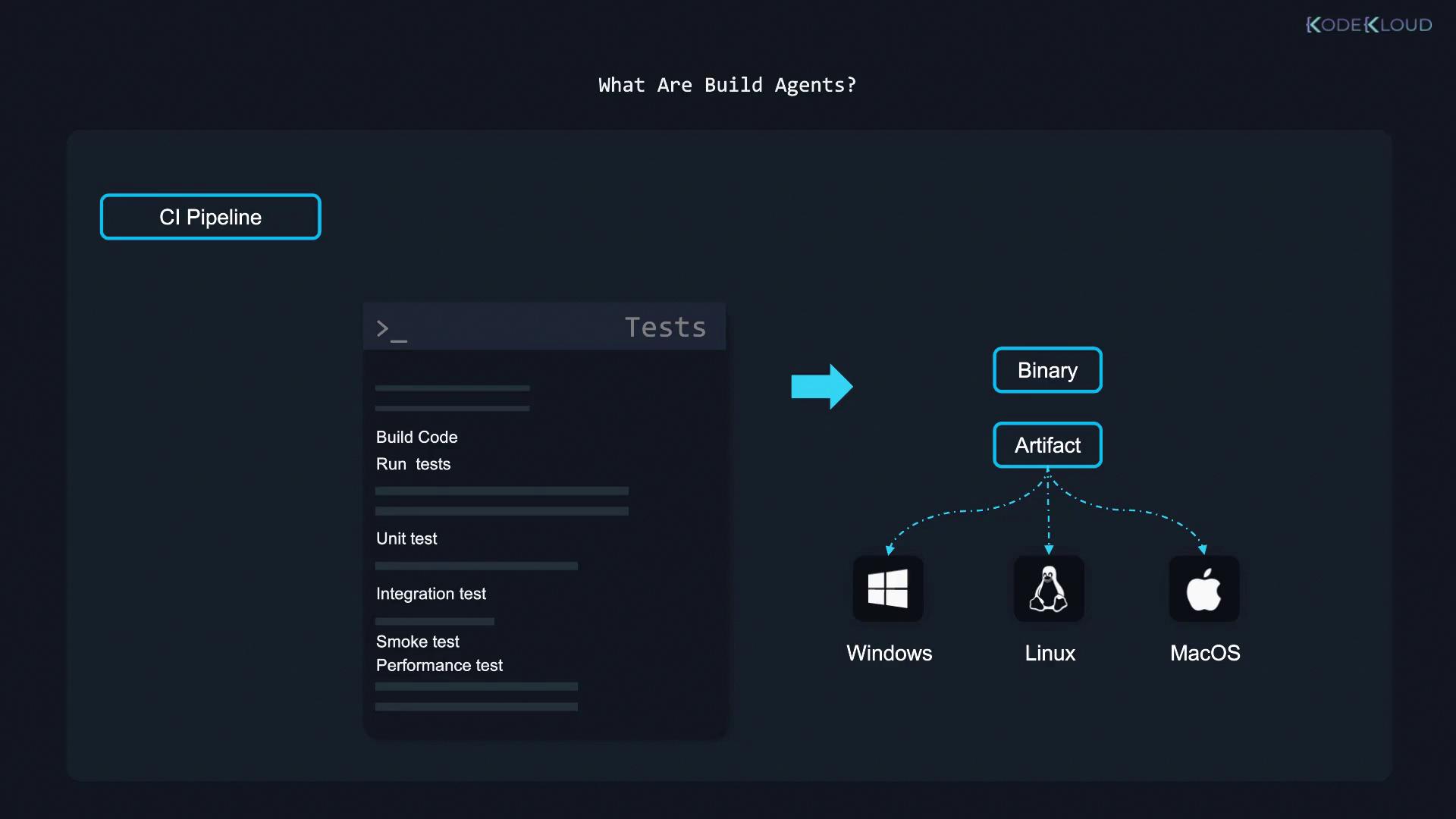
Build agents function as the executors in your CI/CD workflow. When a task is queued in the pipeline, a build agent picks it up and performs the required steps. The beauty of build agents is their versatility; any machine that can run Java can serve as a build agent. This includes:- A physical server (bare metal)
- A virtual machine or desktop
- A Docker container, which can even be managed through Kubernetes for scalability
- An ARM-based device like a Raspberry Pi
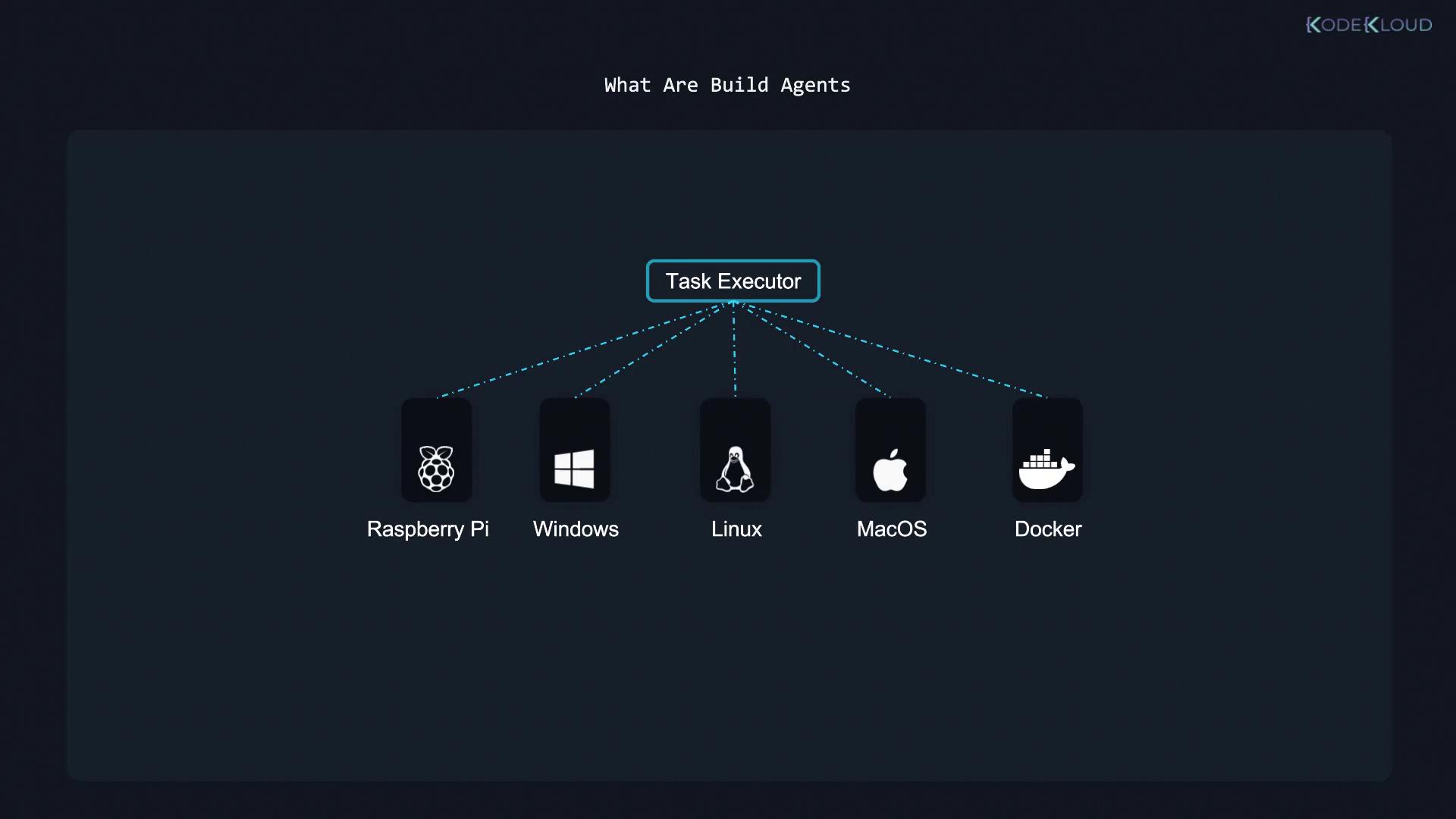
In production environments, it is advisable to deploy build agents on secure and resilient infrastructure, such as data centers or dedicated server racks, as opposed to personal machines.
Supported Operating Systems
Build agents can operate on various platforms, including:- Windows (e.g., Windows Server, Windows 10)
- Linux (distributions like Ubuntu, Red Hat, Debian, etc.)
- macOS (commonly used for building macOS applications)
Why You Need Build Agents
Although it is possible to run builds directly on the Jenkins server, this approach is generally discouraged for two main reasons:- Performance:
Running builds on the Jenkins server can overload it with heavy tasks. When multiple builds execute simultaneously, the server might struggle with CPU and memory constraints, leading to delays and reduced overall efficiency.
- Security:
Isolating build executions by offloading them to dedicated build agents improves security. Separating these tasks minimizes the risk of exposing the main Jenkins server to vulnerabilities that might occur during build or script execution.
Avoid running builds on your main Jenkins server to maintain stability and safeguard your system from potential security threats.