How Jenkins Works
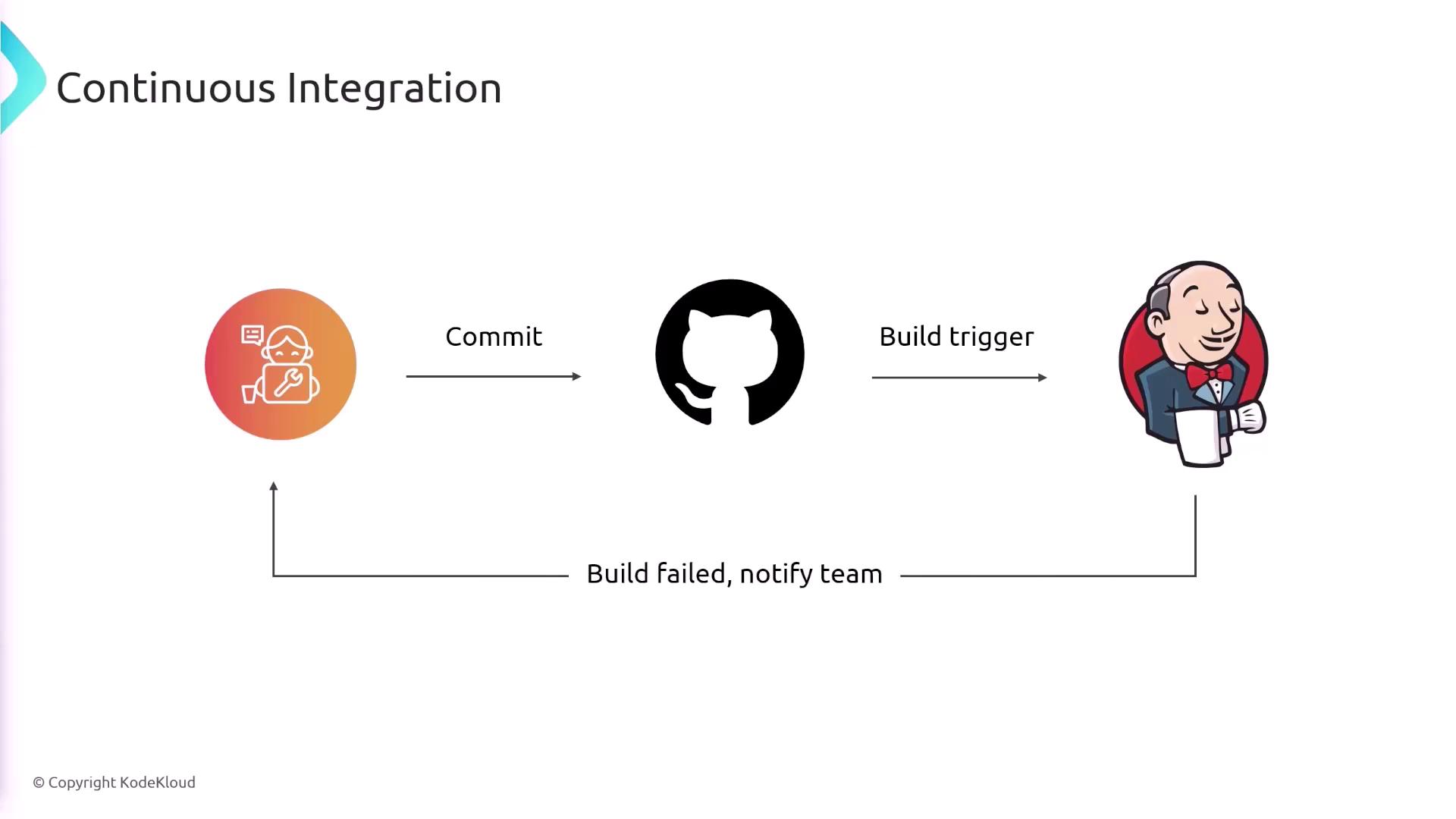
The Jenkins workflow typically begins when a developer commits code to a Git repository. This commit triggers a build in Jenkins, which then follows a series of preset steps, including:- Linting and formatting the code
- Running unit and integration tests
- Building and packaging the application
Advantages of Using Jenkins
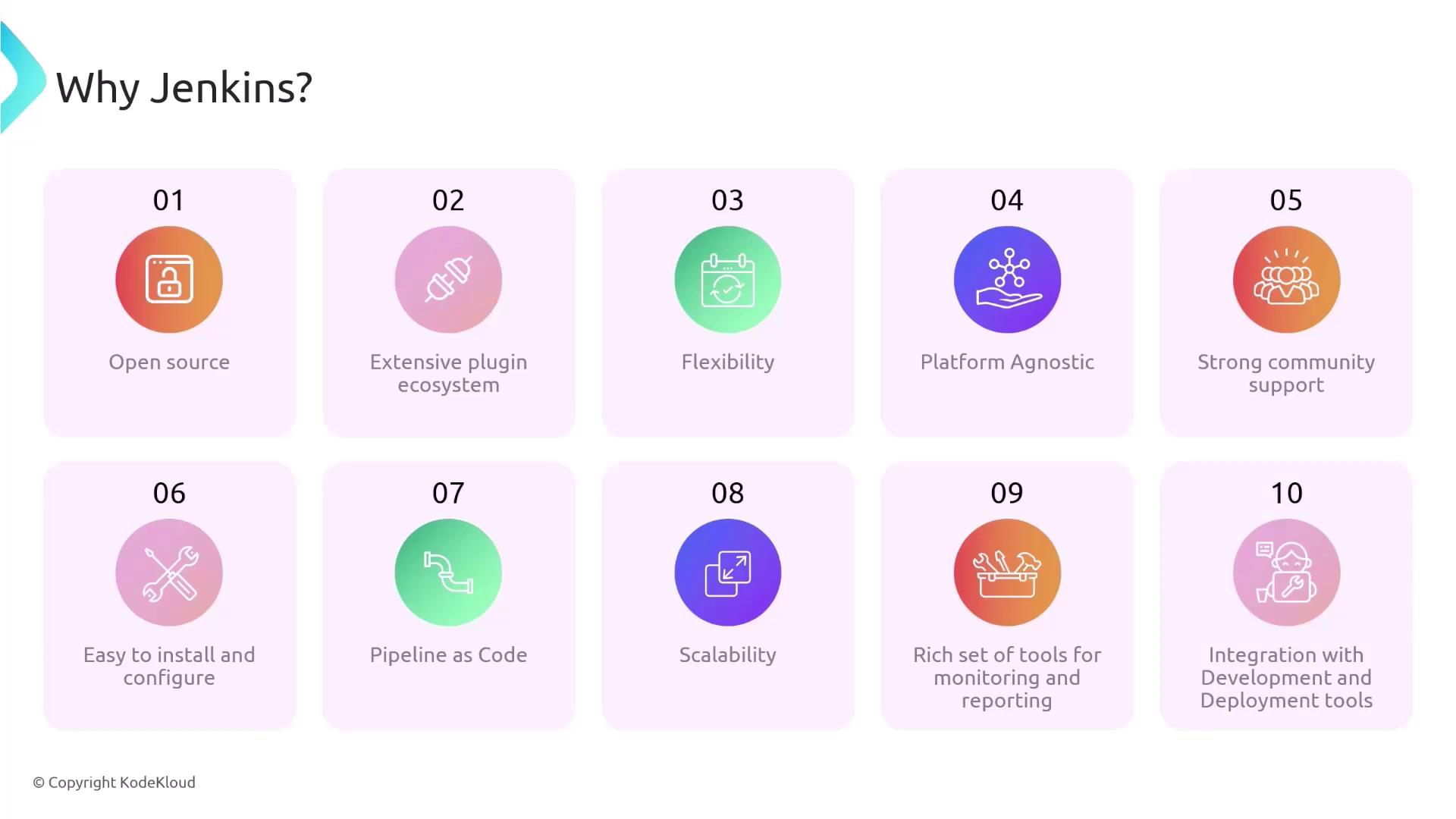
Jenkins has become a popular CI/CD solution not only because it is open source and free, but also because of its numerous advantages:- Extensive Plugin Ecosystem: Enhance functionality by integrating with various source control systems, deployment platforms, and testing tools.
- Flexibility and Customization: Configure Jenkins to support nearly any CI/CD workflow, making it adaptable to projects of various sizes and complexities.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Work effortlessly across different operating systems—Windows, macOS, and Linux—and deploy it on-premises or in the cloud.
- Community Support: Benefit from a large, active community that frequently updates Jenkins with security patches and improvements.
- Pipeline as Code: Maintain your CI/CD pipeline in code (via a Jenkinsfile) to ensure consistency and enable version control tracking.
- Scalability: Distribute builds across multiple machines to reduce build and test times significantly.
- Detailed Reporting and Logging: Monitor build statuses, test outcomes, and deployment logs, enhancing visibility and simplifying troubleshooting.
By automating repetitive tasks, Jenkins not only boosts productivity but also minimizes errors that often arise in manual build and deployment processes.
Addressing Development Challenges with Jenkins
Manual build and deployment processes can be tedious, inconsistent, and error-prone. Without automation, teams face challenges such as:- Tedious manual steps that risk human error
- Environment inconsistencies between development and production
- Delayed detection of integration issues
- Limited visibility into build statuses and test results
- Fragmented collaboration across distributed teams
- Resource-intensive processes that strain time and computing power
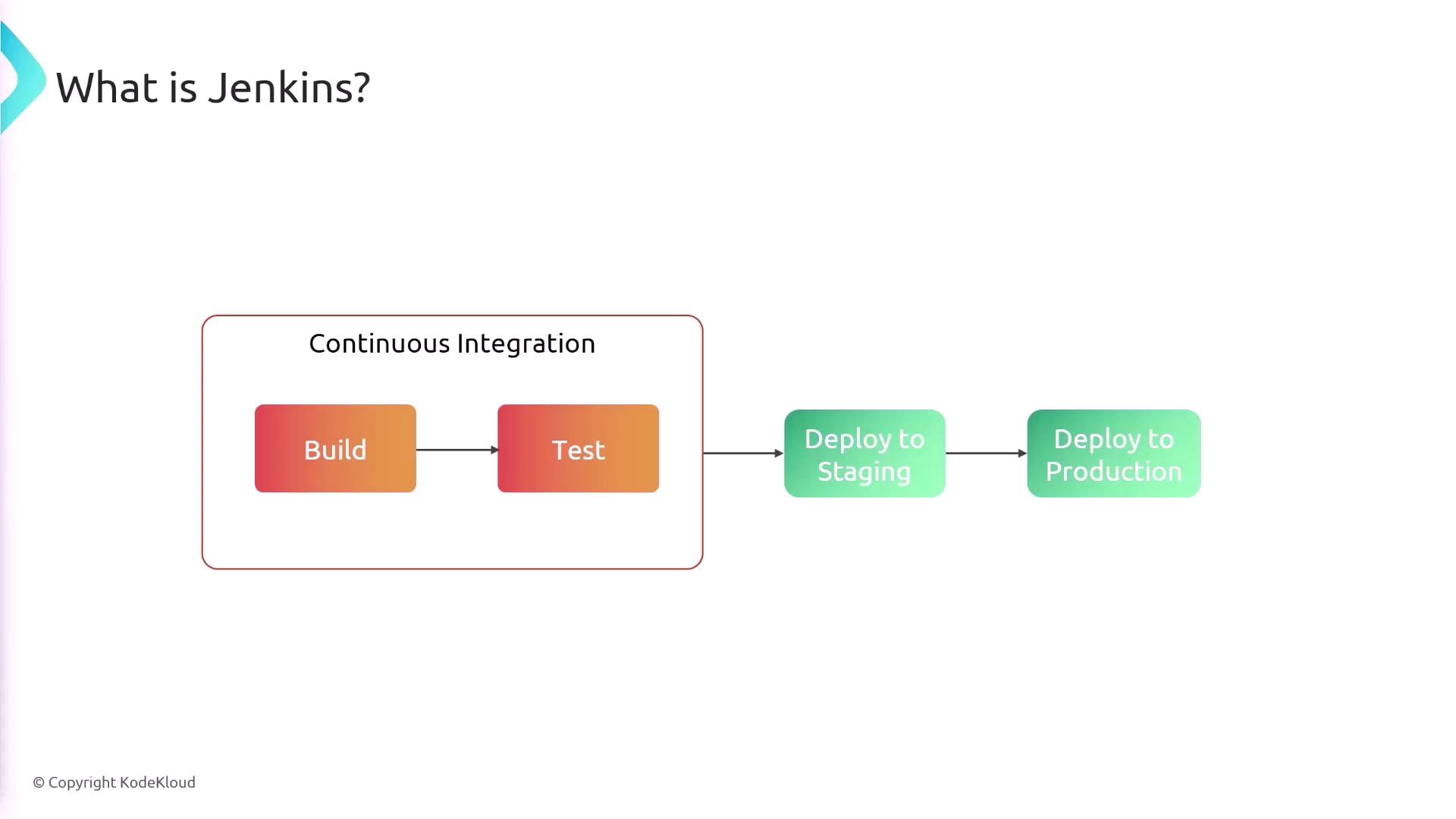
Manual development processes can lead to delayed feedback and integration errors, making continuous integration with Jenkins essential for modern software development.
Overcoming Manual Process Pitfalls
Without Jenkins automation, teams would struggle with the following issues:- Error-prone manual build and deployment procedures
- Inconsistent environments causing integration challenges
- Slow detection of issues due to infrequent code merges
- Poor visibility into the status of builds and deployments
- Challenges in collaborative teamwork and communication
- Increased risk of human-induced errors