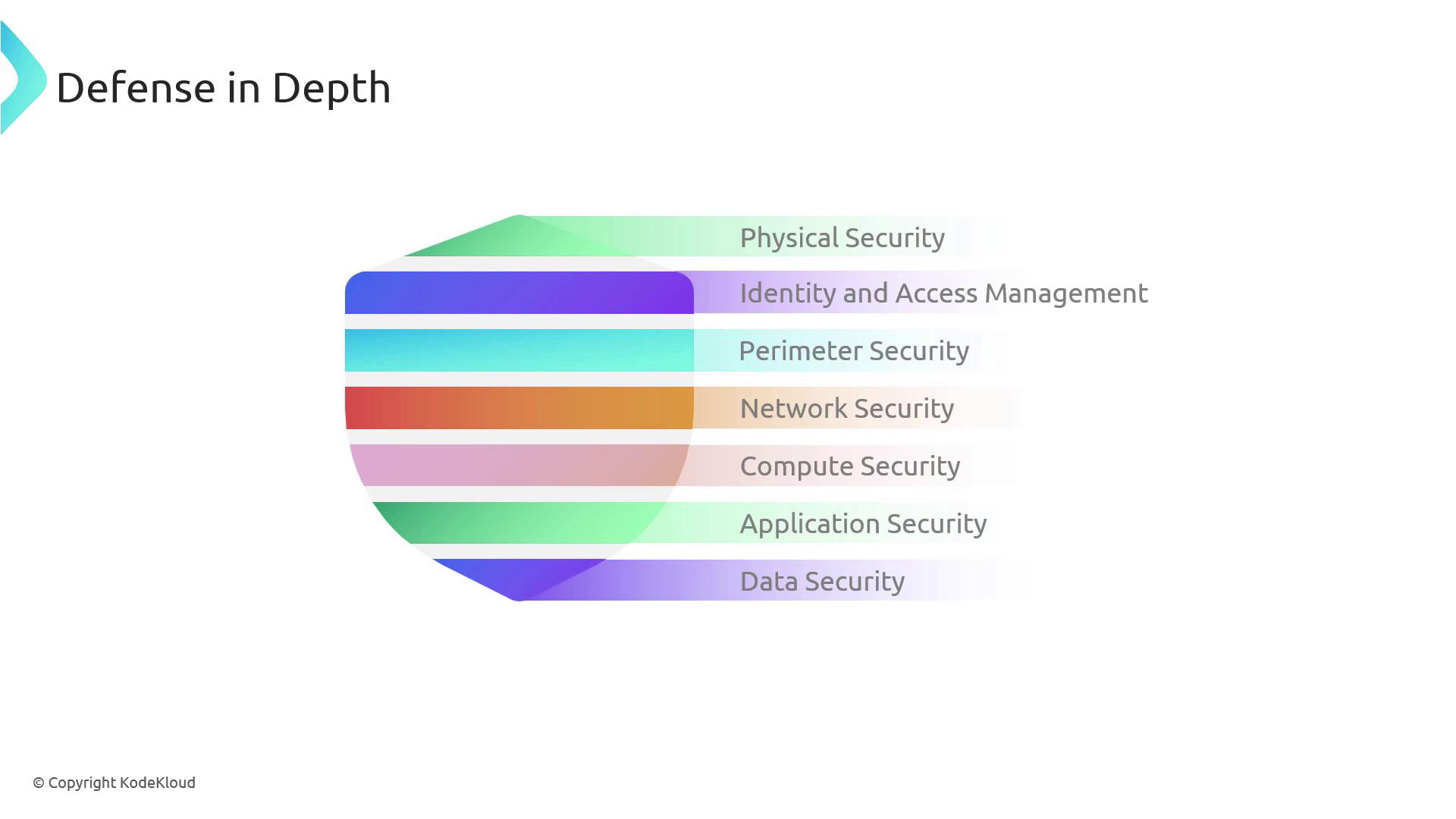
Physical Security
The first line of defense is Physical Security. This is akin to the sturdy castle walls that protect valuable assets from unauthorized access. Physical security covers the protection of hardware, data centers, and other tangible assets. For example, Microsoft’s data centers deploy stringent measures to prevent unauthorized entry, ensuring that no one can easily access or steal hardware containing sensitive data.Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) acts as the castle’s gatekeeper, controlling entry and ensuring that only authorized users gain access. This layer is vital for managing user credentials and permissions, often implemented with tools like Azure Active Directory and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
Implementing strong IAM practices is essential for meeting compliance requirements and reducing the risk of insider threats.
Perimeter Security
Perimeter Security serves as the lookout towers of a castle. This layer is designed to monitor and manage incoming traffic using firewalls and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection. It acts as the first barrier to filter out external threats.Network Security
After breaching the perimeter, attackers encounter Network Security, which functions like inner guards maintaining order. This layer focuses on controlling and segmenting internal network traffic, preventing unauthorized lateral movements within the infrastructure. Network segmentation is a key tactic to limit the spread of breaches.
Network segmentation not only improves security but also enhances network performance by containing traffic within defined segments.
Compute Security
Compute Security protects virtualized environments including Virtual Machines, containers, and serverless platforms. This layer ensures that every computing resource is safeguarded, much like securing individual rooms within a castle. Robust compute security helps prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in virtual environments.
Application Security
Application Security focuses on defending the digital armory. This layer involves implementing secure coding practices, regular vulnerability assessments, and using application firewalls to protect against external threats. Securing applications is critical as they are often the primary interface between users and the system.Data Security
Data Security is dedicated to protecting the crown jewels—your most valuable information. This layer ensures that data remains protected whether at rest or in transit. Techniques like encryption play a pivotal role in preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Data breaches can have severe implications, including financial loss and reputational damage. Always enforce strong encryption and access controls.
Benefits of Defense in Depth
Employing a Defense in Depth strategy offers numerous advantages:- Robust Protection: Multiple security layers ensure that if one measure fails, others continue to block or delay the attack.
- Risk Mitigation: By forcing attackers to bypass several defenses, the likelihood of a successful breach is significantly lowered.
- Holistic Security Approach: Integrating diverse security controls across all layers of your IT infrastructure minimizes vulnerabilities and strengthens overall protection.