SQL Databases
Relational (SQL) databases store data in a tabular format and adhere strictly to the ACID properties: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. These properties ensure robust transaction management and data integrity—an essential requirement in online transaction processing (OLTP) systems. Common examples include ticketing, order processing, and authentication systems where transactional integrity is critical.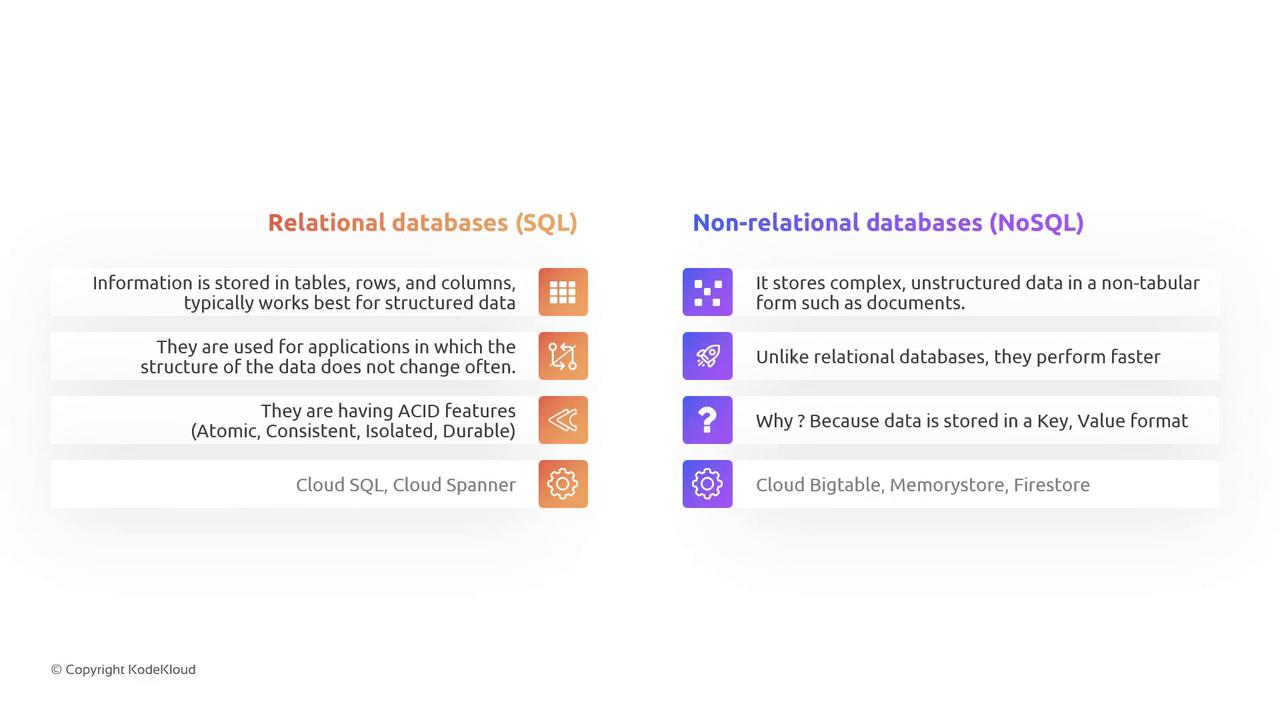
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Spanner
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases diverge from the traditional tabular structure by using storage models such as document-based or key-value pair systems. Each data entry is stored as a key and its corresponding value, which allows for a more flexible schema design. This flexibility makes NoSQL databases ideal for applications requiring rapid scalability and adaptable data structures. For instance, if you are analyzing which restaurants a customer ordered from in 2022, you might store the customer ID as the key and the associated restaurant IDs as values. This method is particularly effective for data science applications—such as tailoring personalized recommendations based on ordering patterns and taste preferences. In GCP, the key NoSQL databases include:- Cloud Bigtable
- Memory Store
- Firestore
When deciding on a database, it is crucial to evaluate your application needs. For data integrity and complex transactions, lean towards SQL databases. If your primary focus is on scalability and flexible data models, a NoSQL solution might be more appropriate.
Categorizing Database Models
A practical way to differentiate between SQL and NoSQL databases is by grouping them according to their design models—relational, non-relational, and in-memory databases. Each group is tailored to specific use cases:| Database Type | Use Case Description | GCP Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Relational (SQL) | High data integrity and transaction management | Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner |
| Non-relational (NoSQL) | Flexible schema designs, scalable for analytics and recommendations | Cloud Bigtable, Firestore, Memory Store |
| In-memory | Fast data retrieval, often combined with other models for enhanced performance | (Various caching services) |