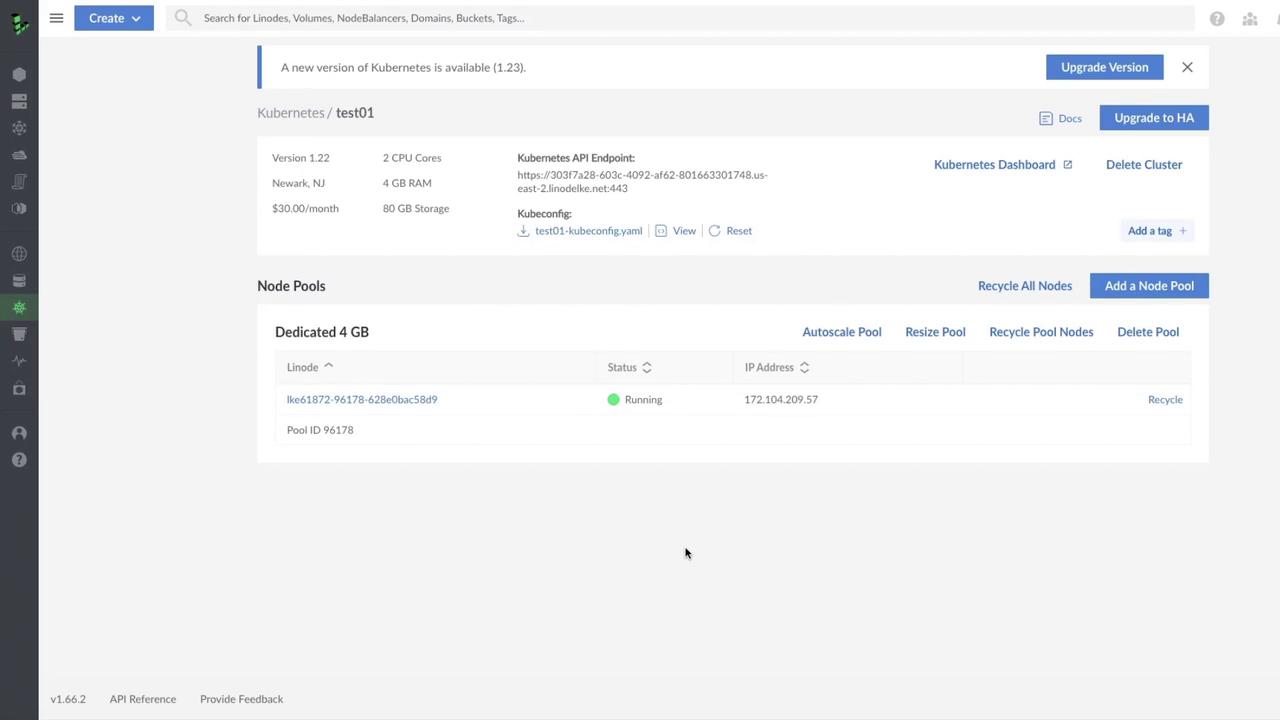
1. Check for Available Upgrades
On the LKE Dashboard, any available Kubernetes version upgrades appear as a notification banner. In our example, the cluster test01 is on v1.22 and ready to upgrade to v1.23.Why upgrade?
- Access new Kubernetes features and improvements
- Receive critical bug fixes and security patches
- Maintain compatibility with cloud-native tools
You can also review the official Kubernetes upgrade documentation for details on control plane components such as the API server, scheduler, and etcd.
2. Initiate the Upgrade
Click Upgrade Version to begin. A confirmation dialog shows your current and target versions: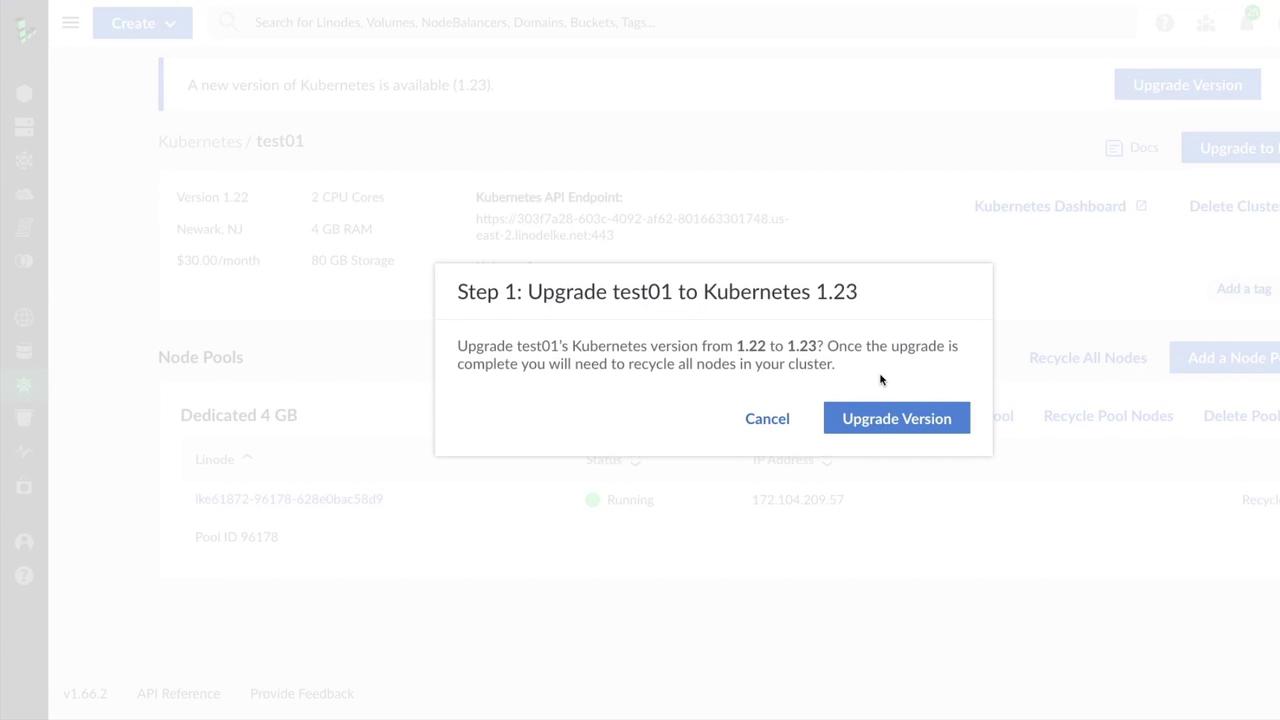
3. Recycle Worker Nodes
After version confirmation, LKE recommends recycling all worker nodes. Recycling terminates existing nodes and recreates them under the new control plane version.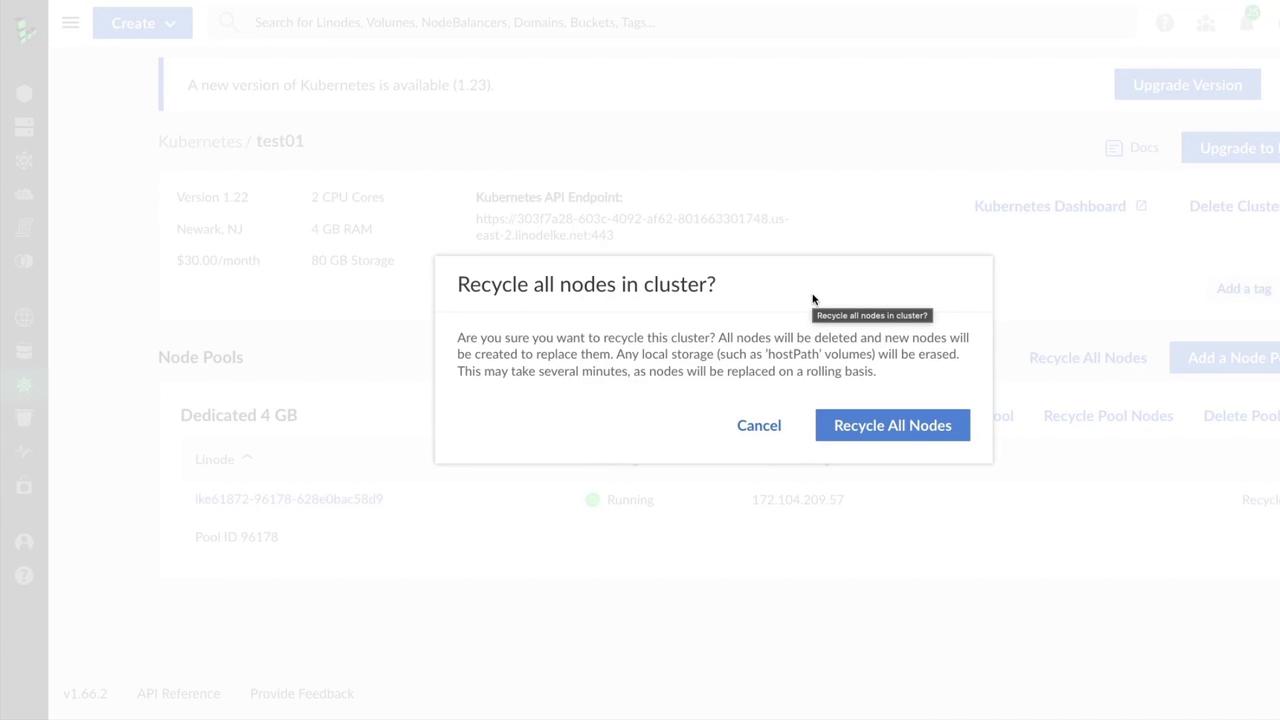
Recycling deletes any local storage, including
hostPath volumes. Ensure you back up persistent data or migrate workloads to avoid data loss.4. Monitor Upgrade Progress
Once confirmed, LKE handles the control plane update followed by node pool recreation. You can track real-time progress through the cluster details page: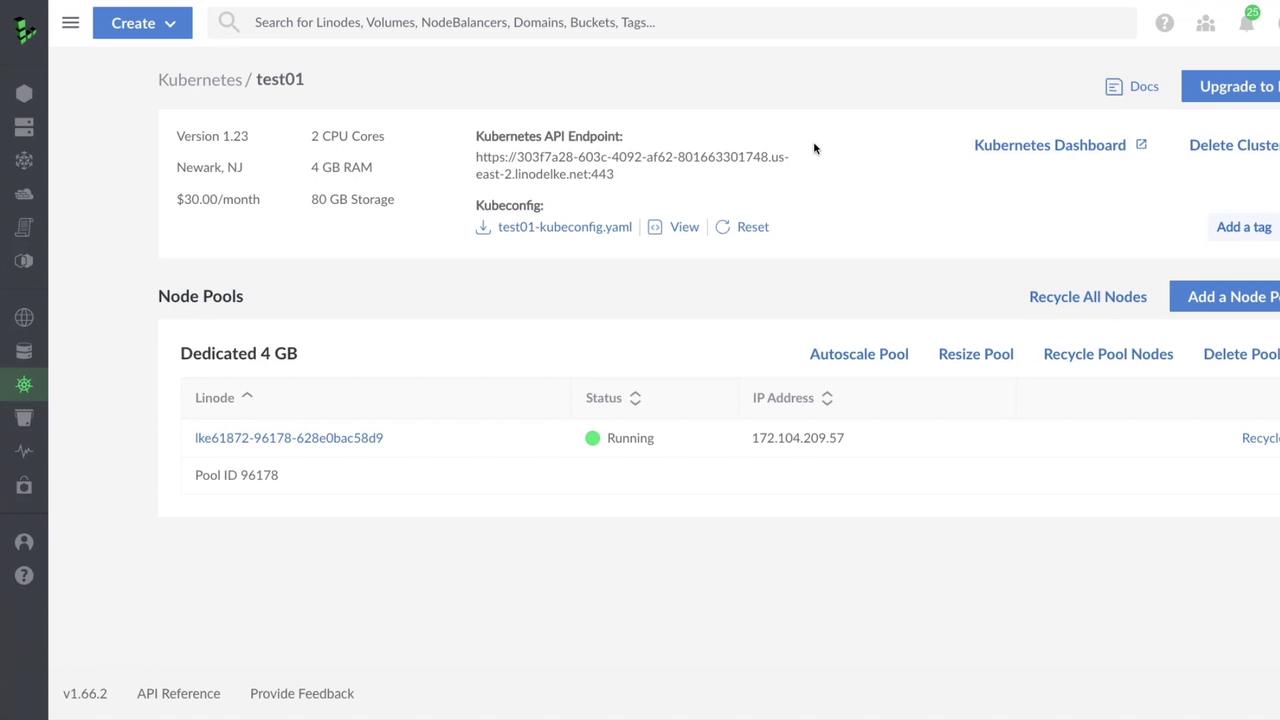
5. Post-Upgrade Checklist
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup Verification | Confirm backups for persistent volumes and cluster state |
| Workload Validation | Test application functionality and performance |
| Capacity Review | Ensure node pool sizing meets production demands |
| Rollback Plan | Have a strategy to revert to the previous version if issues arise |
Best Practices
- Schedule upgrades during low-traffic periods
- Use staging clusters to validate new Kubernetes versions
- Automate backups with Linode Block Storage or external snapshot tools
- Review Linode LKE documentation