1. Creating the Task Definition
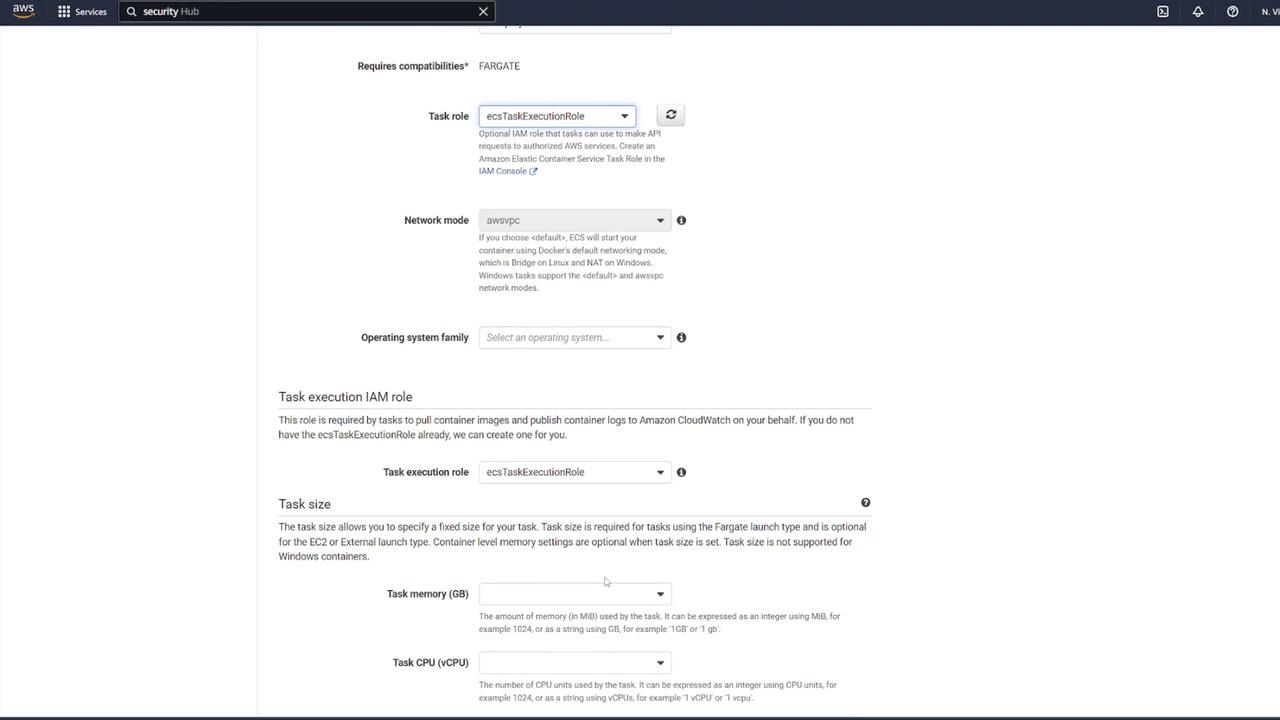
Begin by navigating to your ECS dashboard and selecting Task Definitions. Create a new task definition by choosing Fargate as the launch type. Give it a meaningful name (for example, “ECS-Project1”), assign the ECS task execution role, and select the smallest available memory option. After these steps, proceed to add your containers.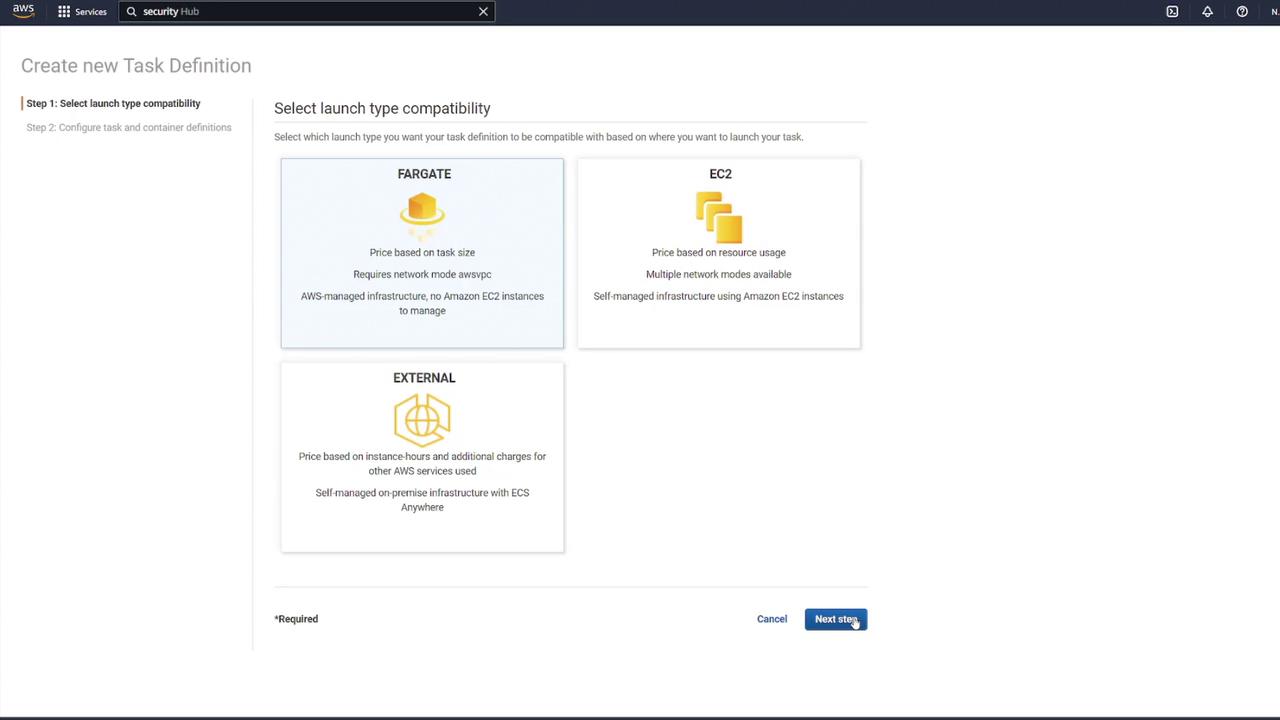
2. Configuring the MongoDB Container
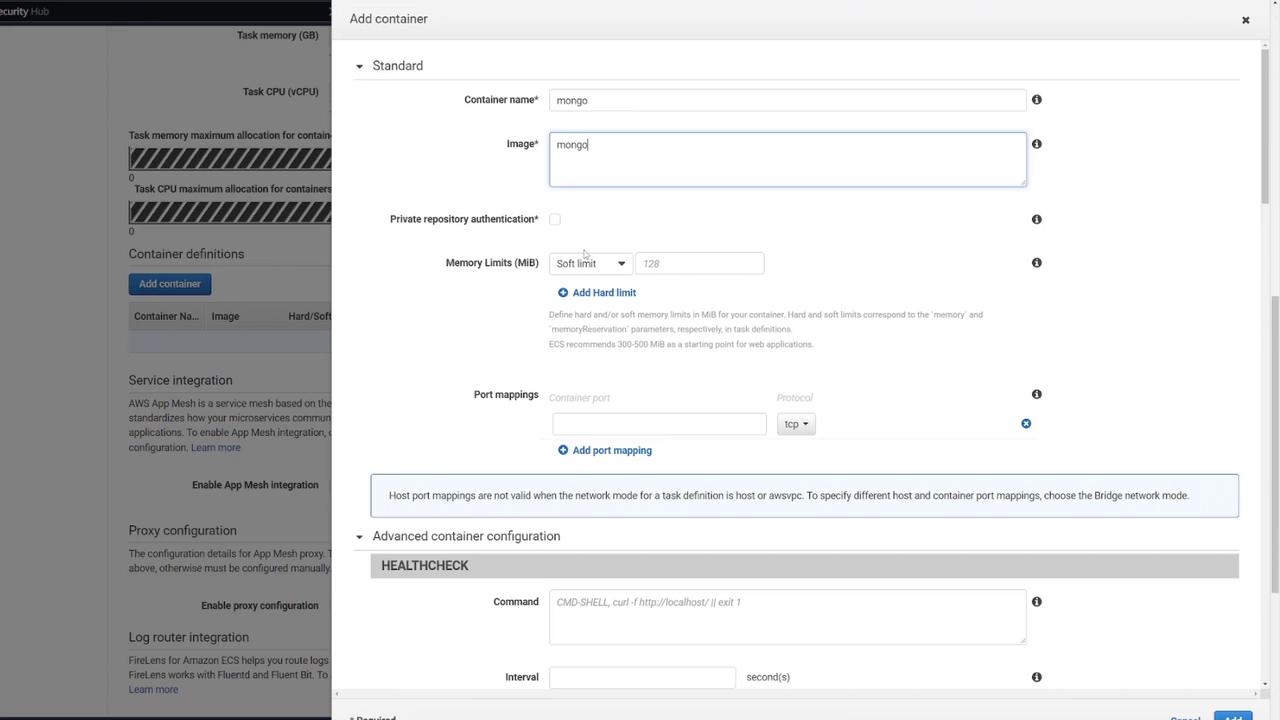
The first container will run the MongoDB database. Configure it with the following steps:- Name the container “Mongo” and select the default Mongo image from Docker Hub.
- Set the port mapping to 27017 (MongoDB’s default port).
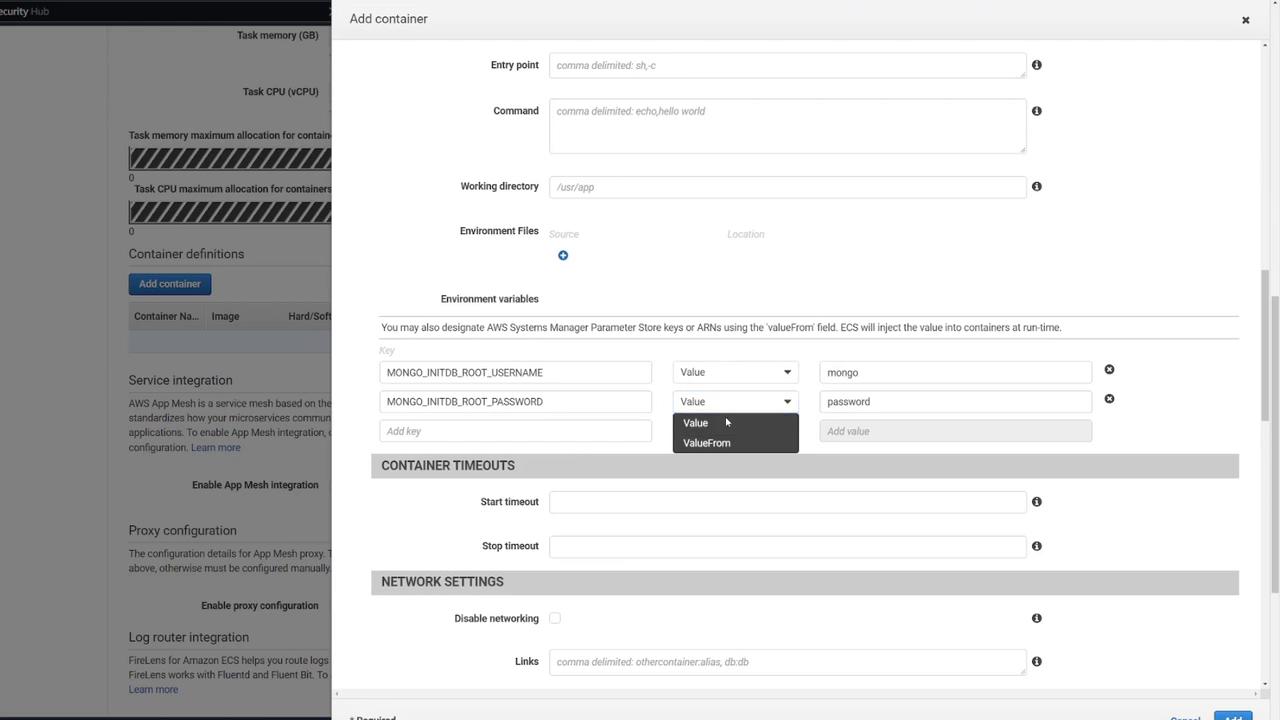
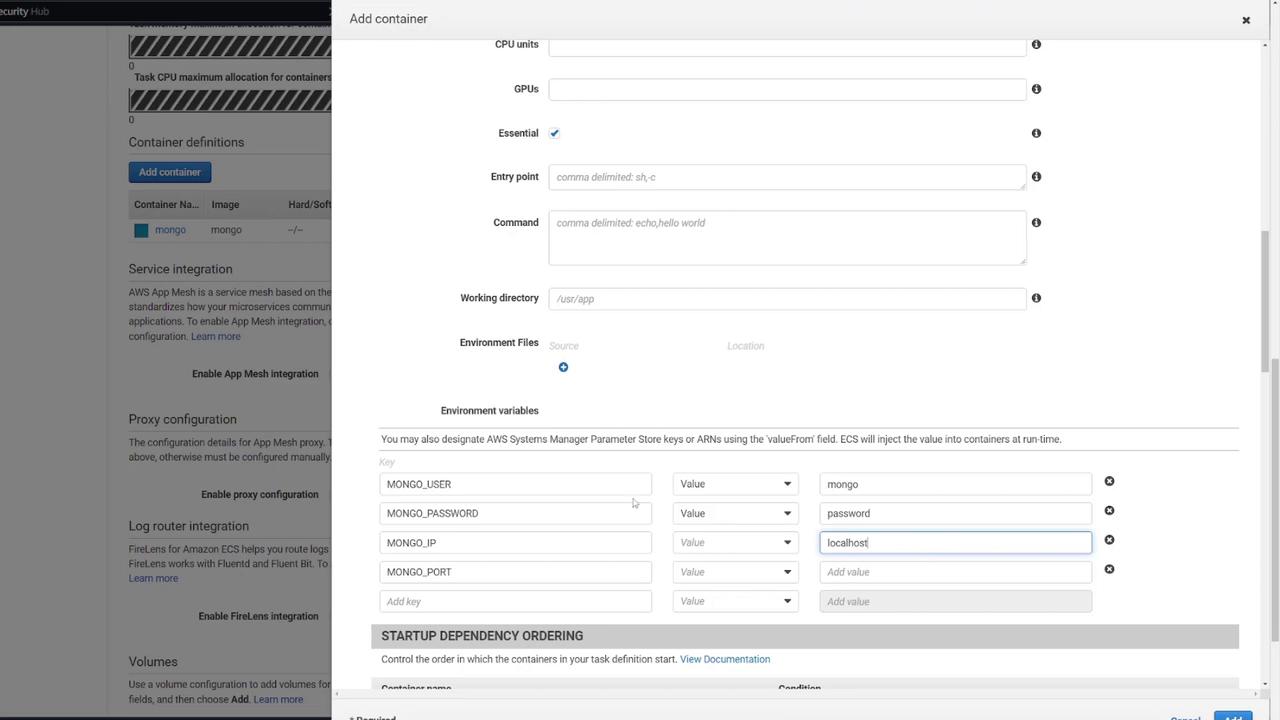
- Define the necessary environment variables for MongoDB initialization.
You can add an optional health check for MongoDB. For example:CMD-SHELL, curl -f http://localhost/ || exit 1
Using “password” for MongoDB credentials is not secure and is used here solely for demonstration purposes.
3. Configuring the Web API Container
Next, configure the second container to host your Express-based web API:- Add a new container (for example, named “web API”).
- Use the image “ECS-Project2” from Docker Hub.
- Set the container to listen on port 3000.
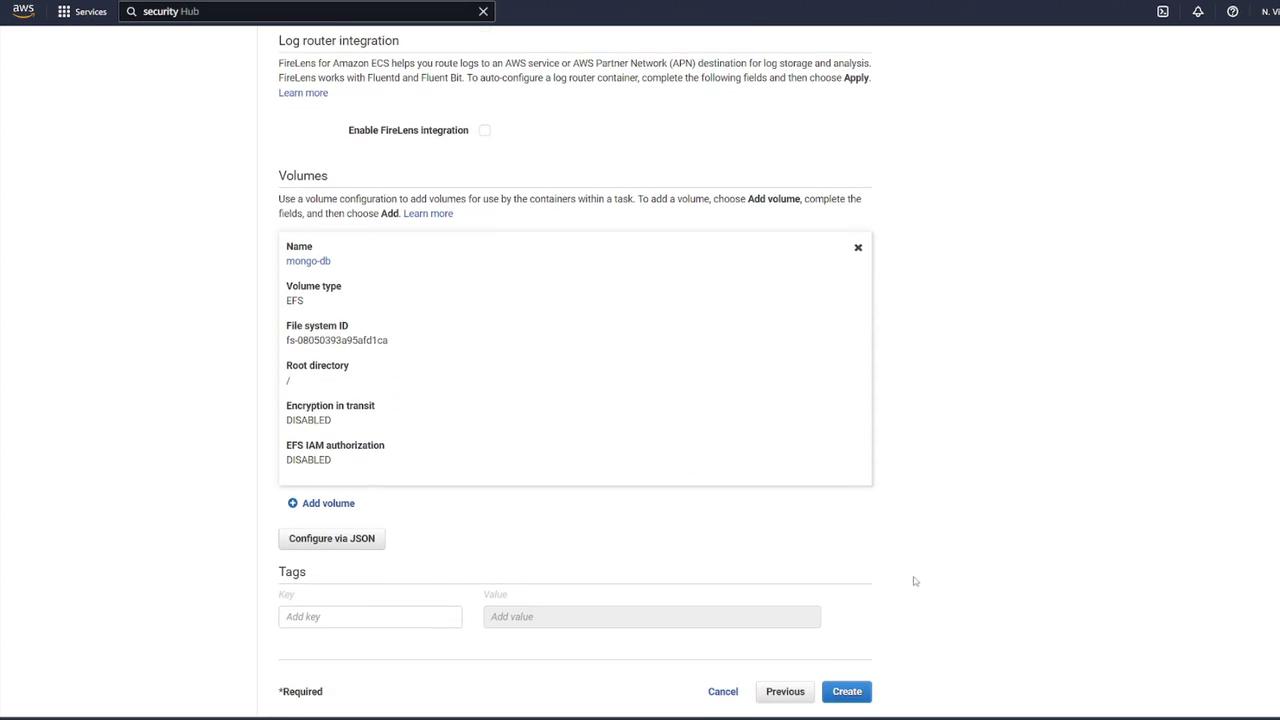
4. Defining a Volume for MongoDB
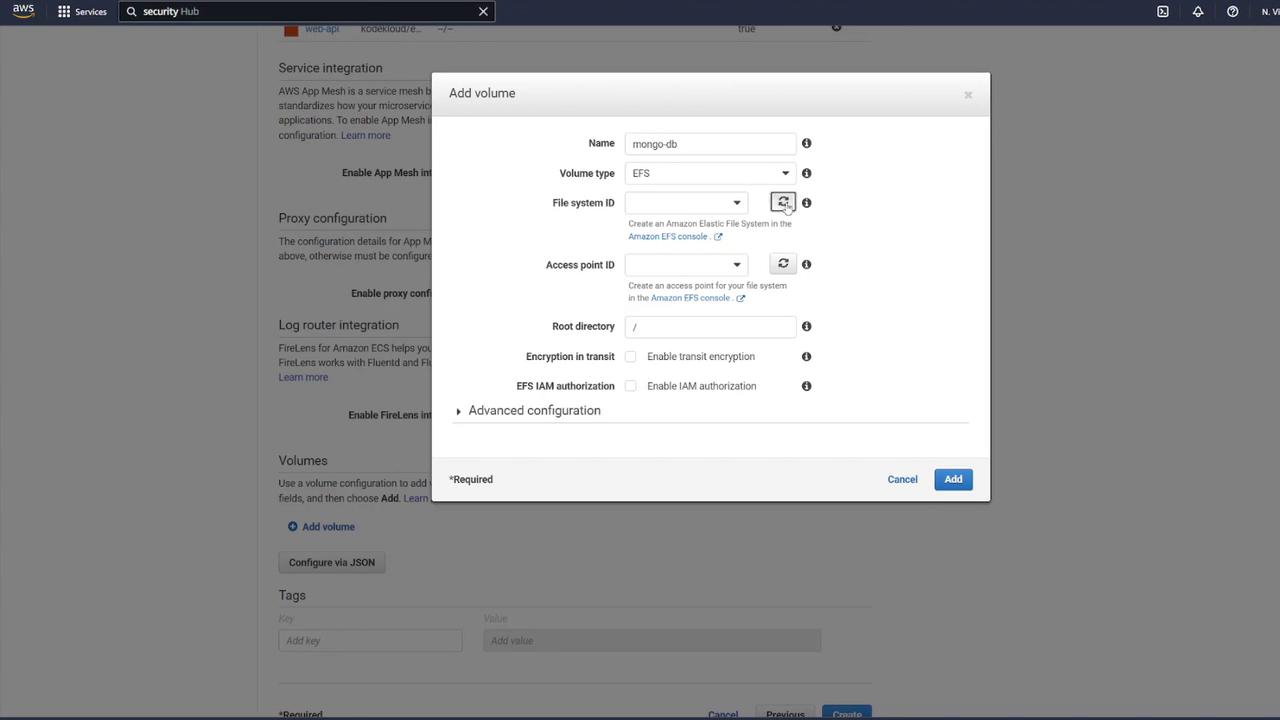
To ensure data persistence for MongoDB, attach an EFS volume to the MongoDB container:- In the ECS task definition, locate the volume section and add a new volume.
- Name the volume “mongo-db” and choose AWS Elastic File System (EFS) as the volume type.
- If no EFS is available, click the link to create a new one.
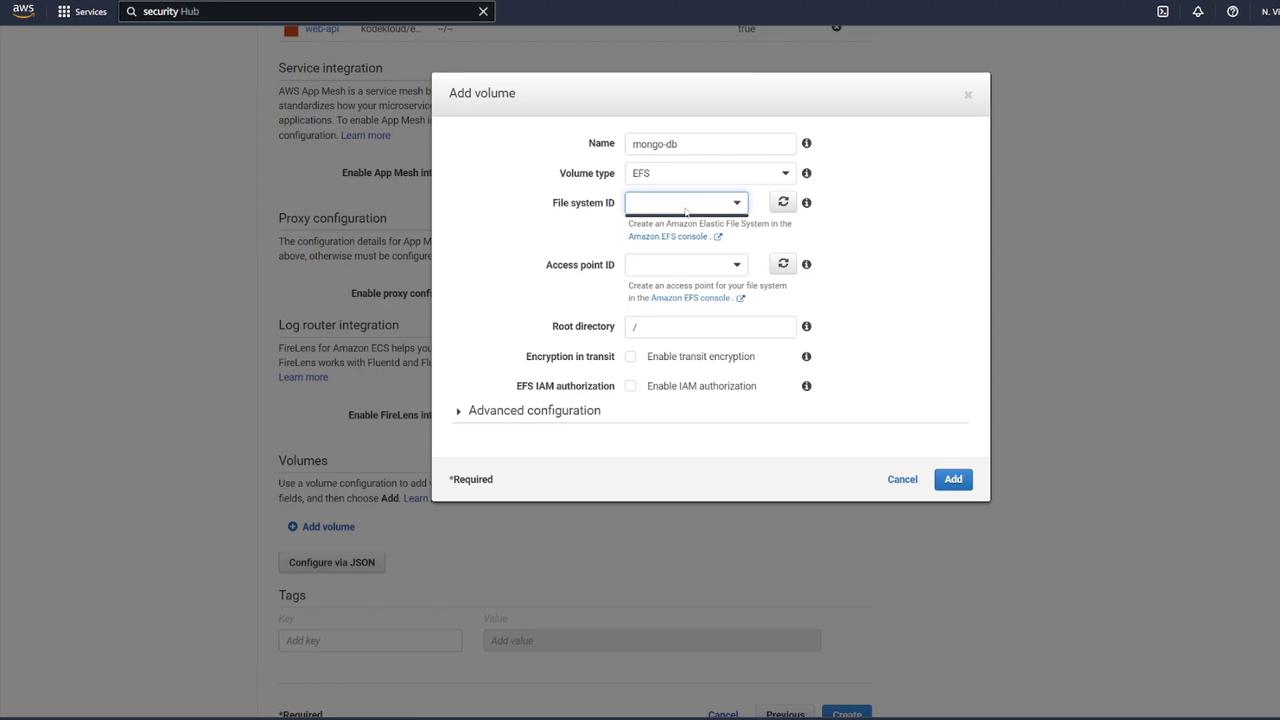
- Name it “mongo-db”.
- Use the same VPC as your ECS cluster.
- Select the proper subnets and update the security group to permit ECS container communication.
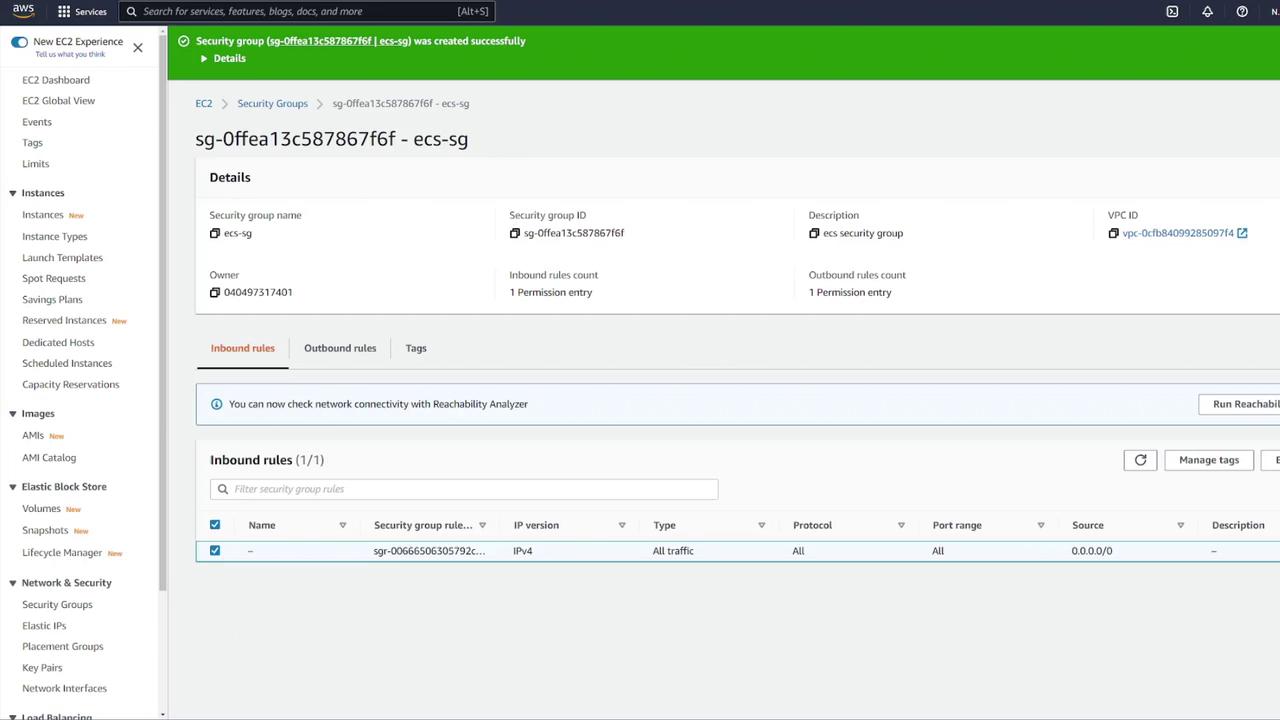
5. Mounting the EFS Volume in the MongoDB Container
Associate the EFS volume with your MongoDB container by performing the following:- Edit the MongoDB container’s settings.
- In the “Storage and Logging” section, select Mount Points.
- Choose the “mongo-db” volume and set the container path to
/data/dbas recommended by MongoDB.
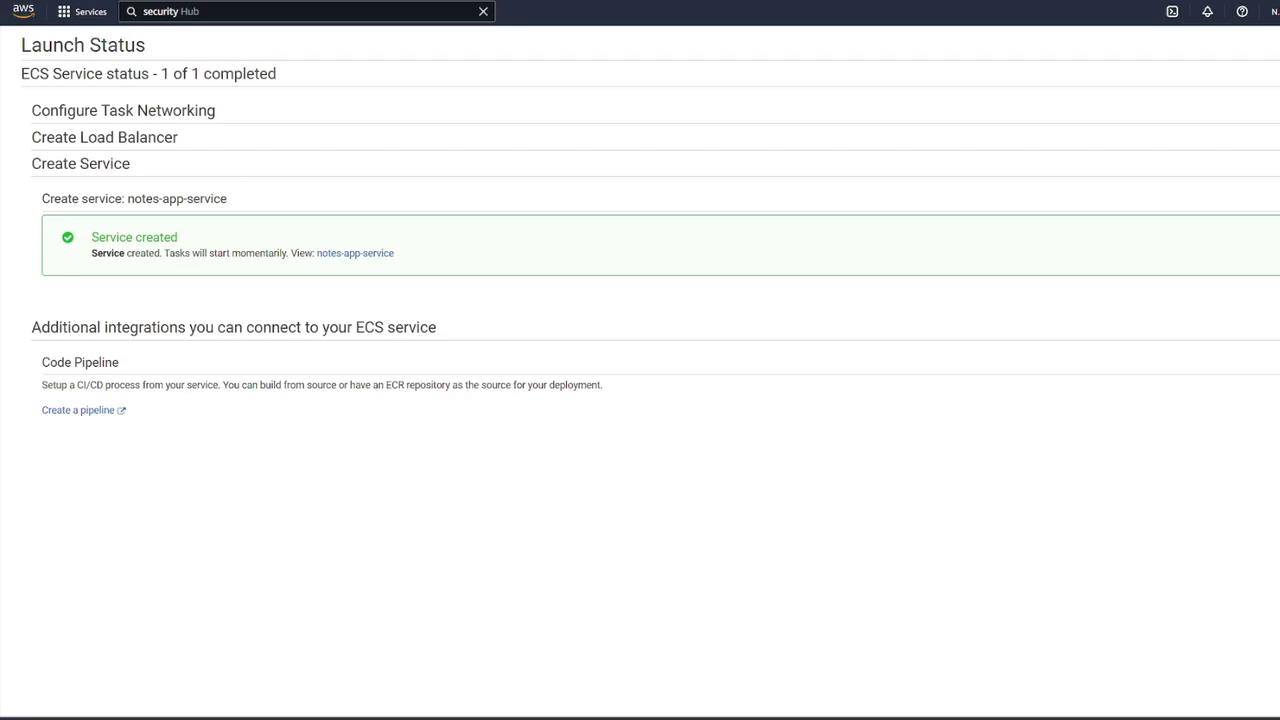
6. Creating the ECS Service and Configuring the Load Balancer
Now that the task definition is complete, create a new ECS service:- Navigate to your ECS cluster (e.g., “cluster one”) and create a service.
- Select Fargate as the launch type and Linux as the operating system.
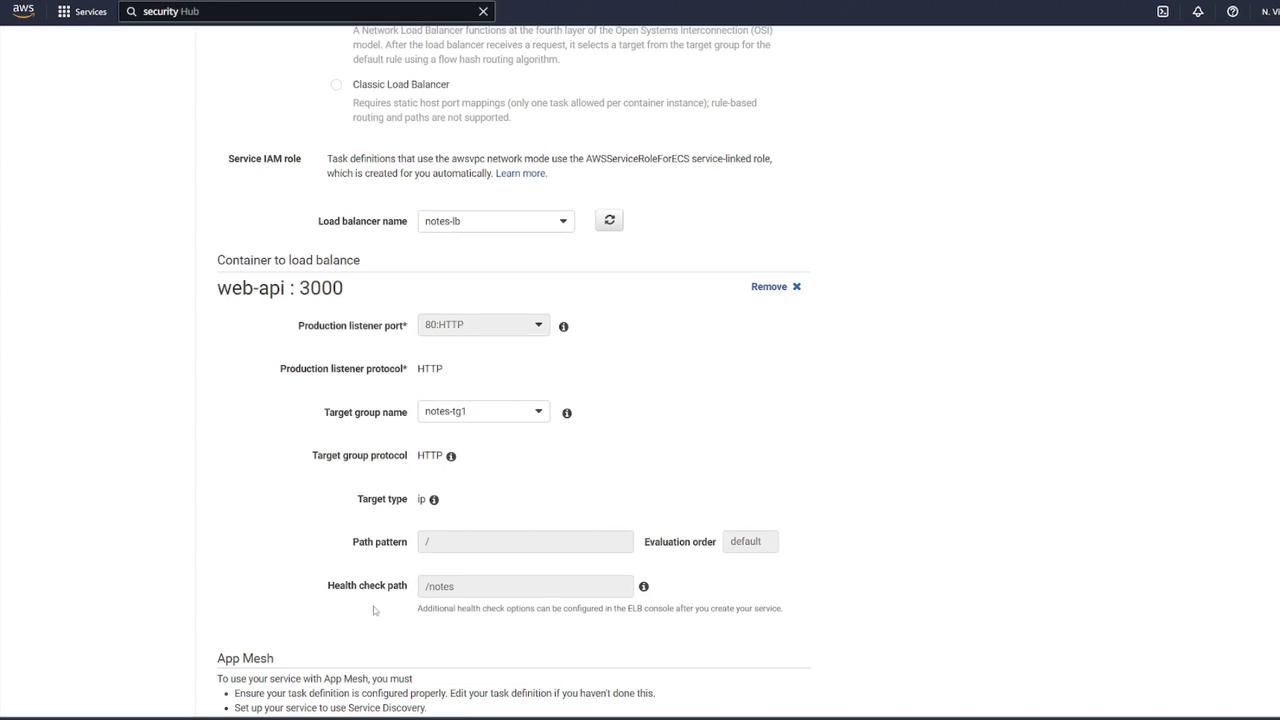
- Choose the newly created task definition (e.g., “ECS-Project2”) and assign a service name (for instance, “notes app service”).
- Set the number of tasks to 1.
- Select the appropriate VPC, subnets, and ECS security group (e.g., “ECS-SG”).
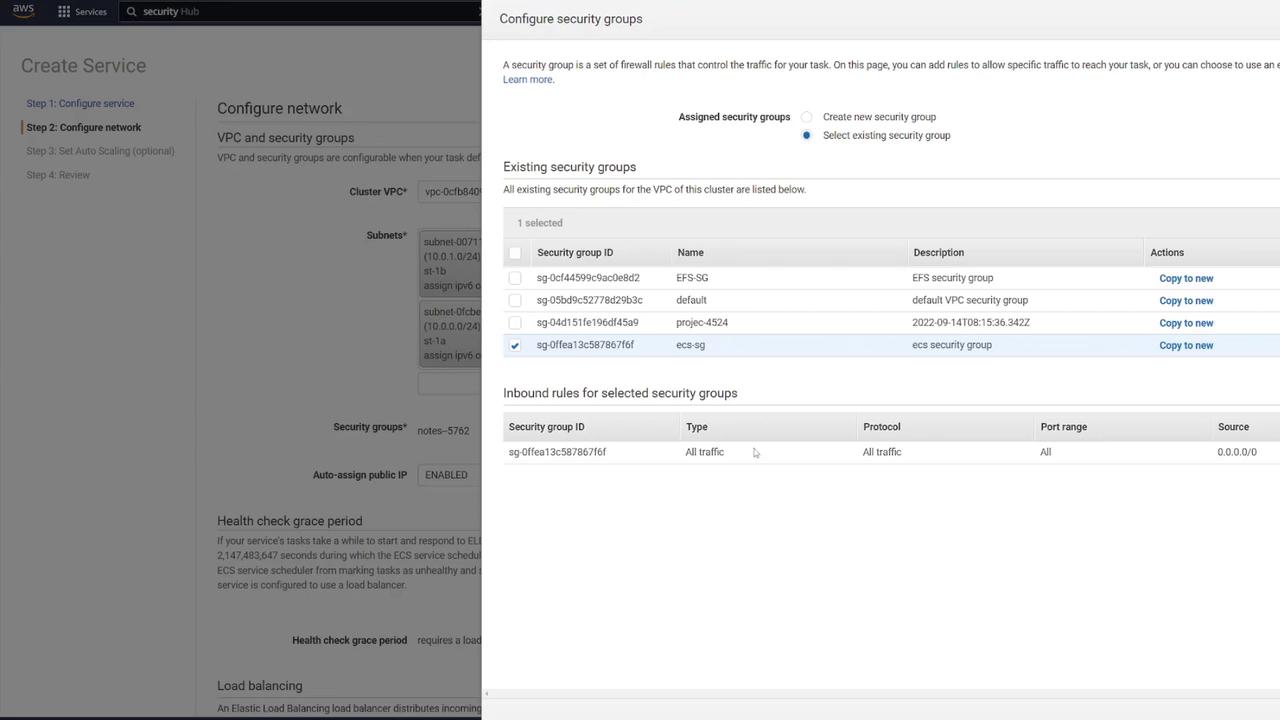
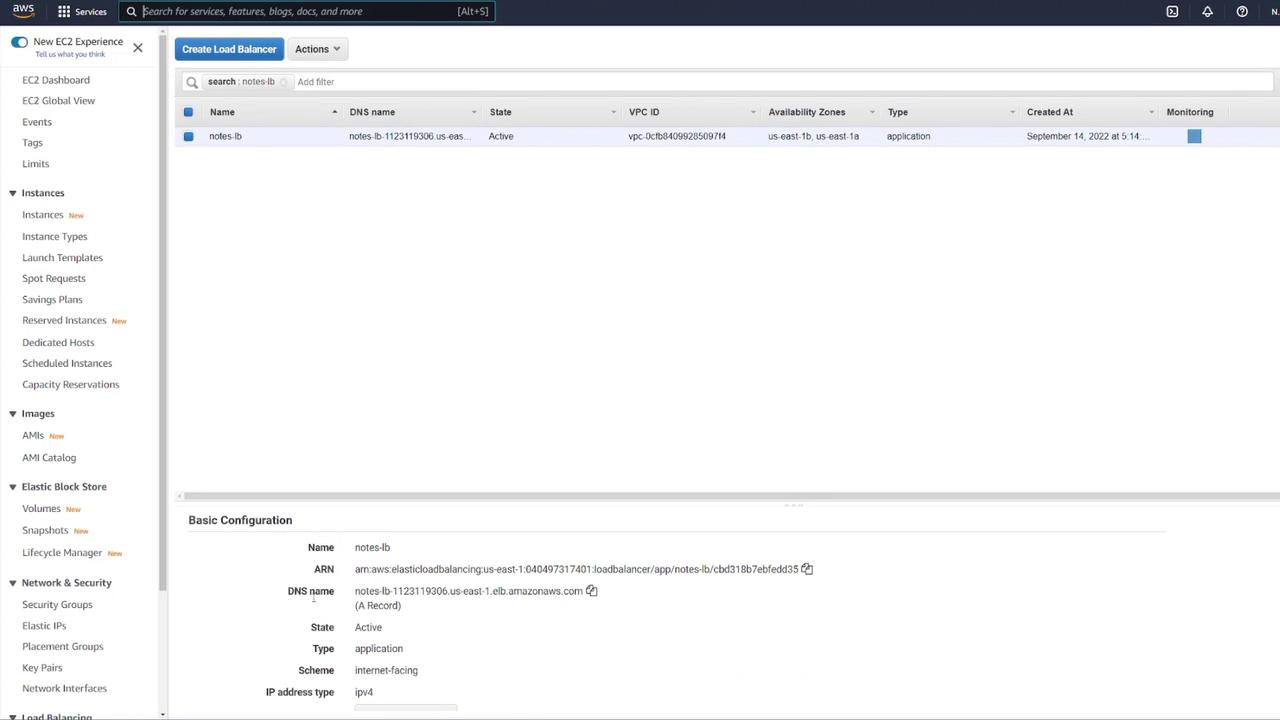
Configuring the Application Load Balancer
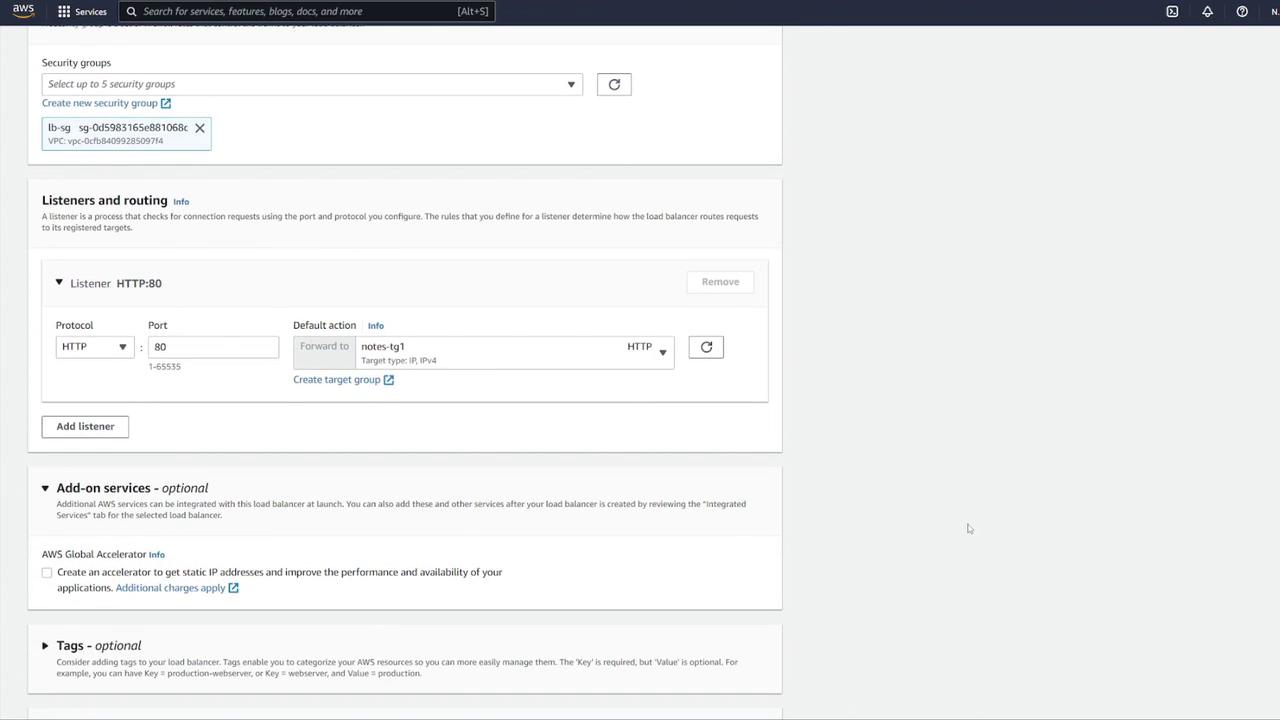
To distribute traffic and enhance scalability, set up an ALB:- Click the link to open the ALB configuration in a new tab.
- Choose the Application Load Balancer type, set it as internet-facing, and select IPv4.
- Map the ALB to the appropriate VPC.
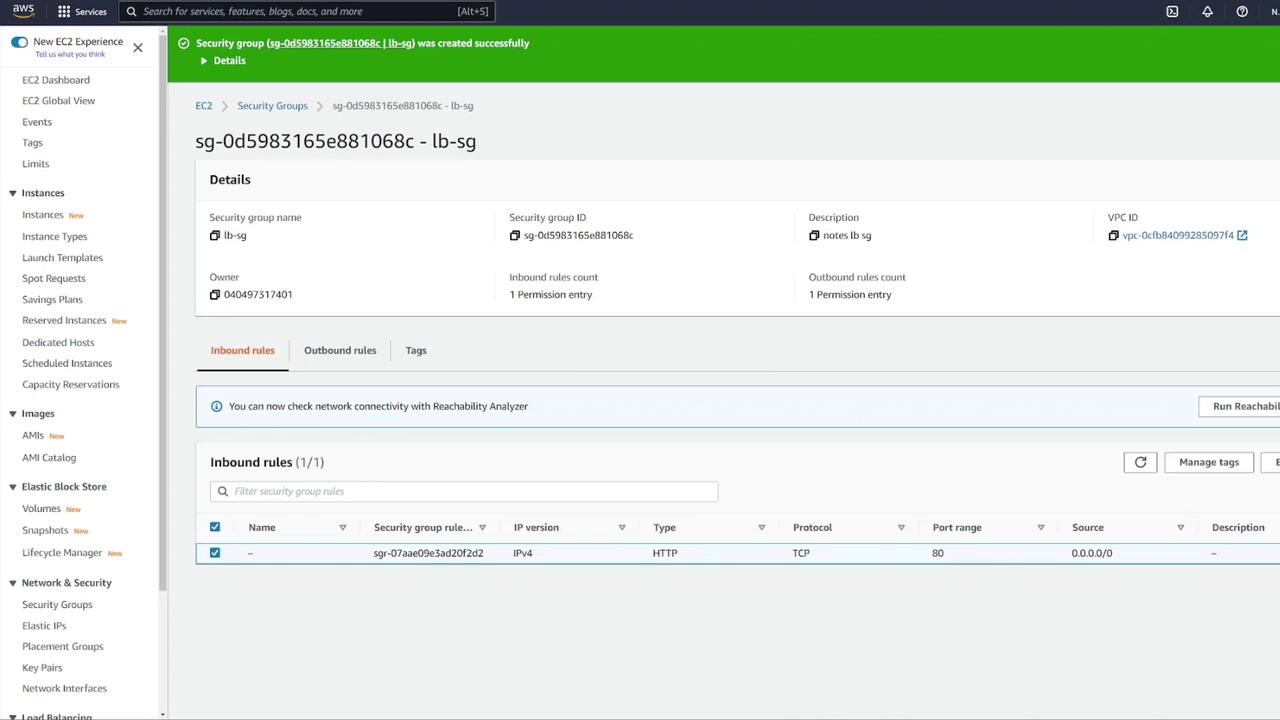
- Create a new security group for the ALB (e.g., “LB-SG”).
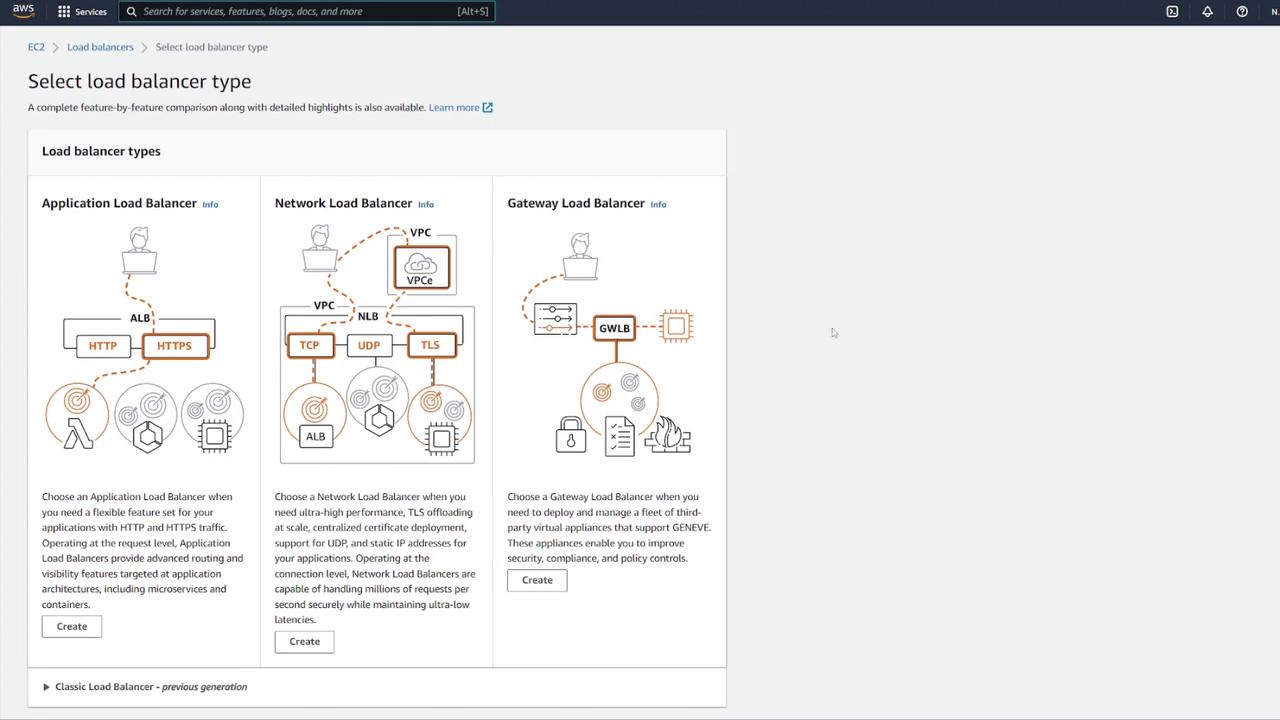
- Name it appropriately (e.g., “notes LB”).
- Set it as internet facing with IPv4.
- Configure inbound rules to allow HTTP traffic on port 80. Although the container listens on port 3000, the ALB will forward requests to port 3000 using listener rules.
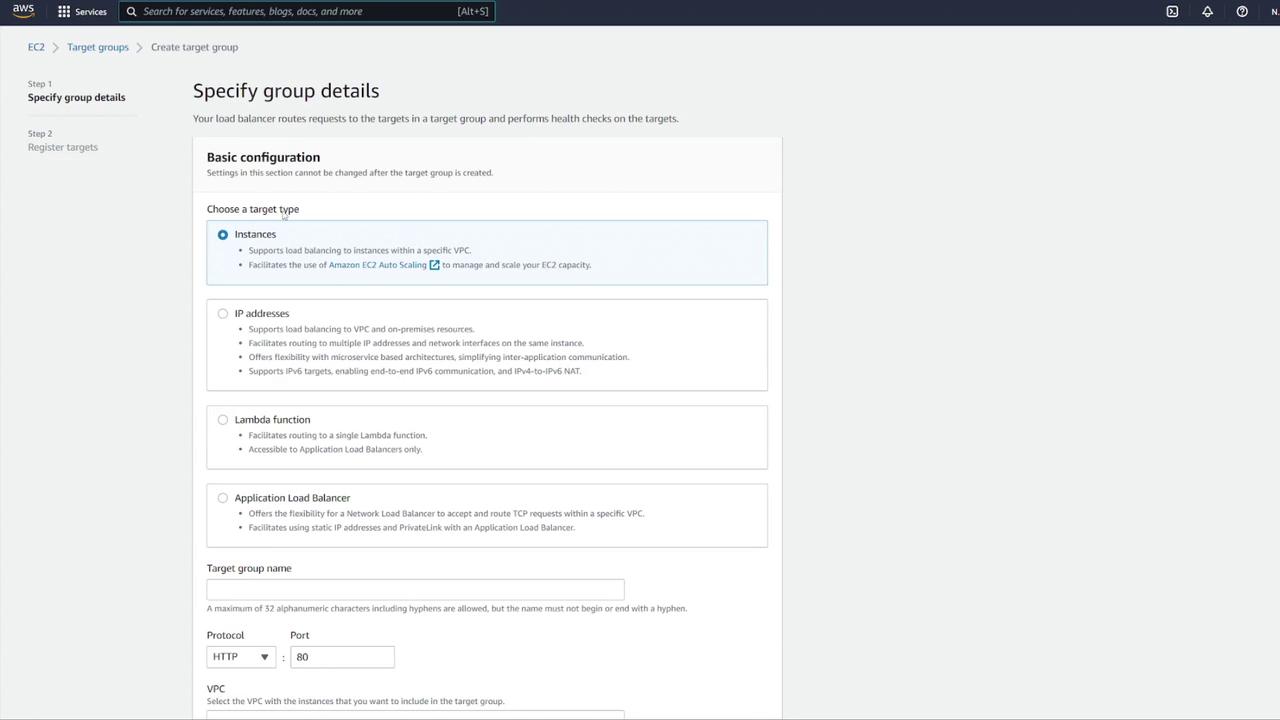
- Select IP addresses as the target type.
- Name the target group (e.g., “notes-tg1”) and choose the correct VPC.
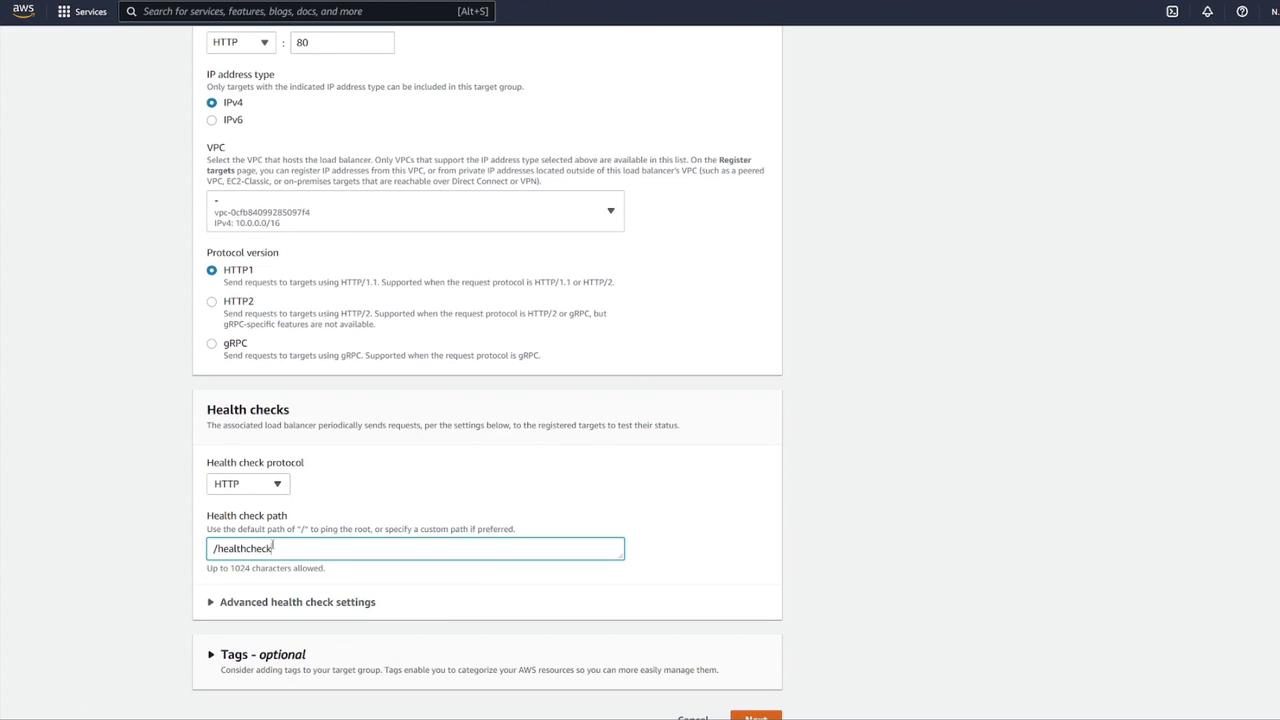
- Modify the health check configuration: update the health check path to
/notesand override the health check port to 3000 if required.
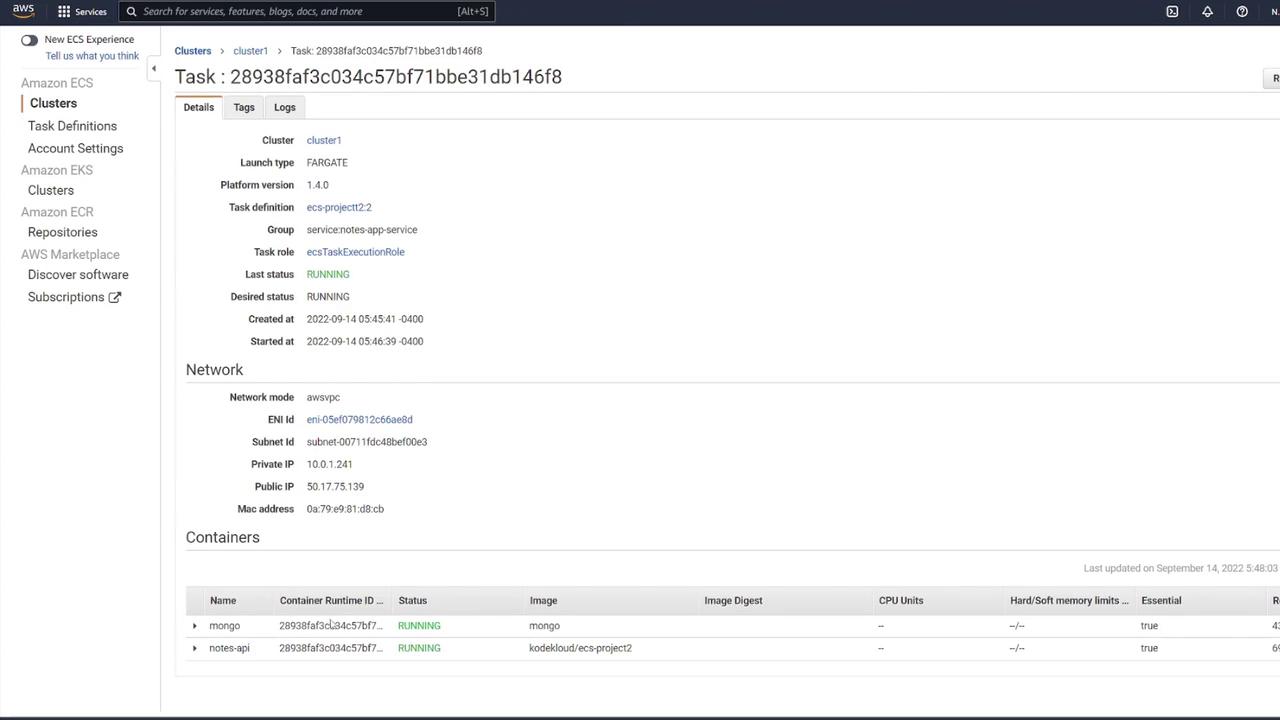
7. Testing the Application
Once your service is running, test your application using tools like Postman:-
Send a GET request to the container’s IP on port 3000 at the
/notesendpoint. The initial response should be: -
Send a POST request with JSON data, such as:
-
A subsequent GET request to
/notesshould display the newly created note:
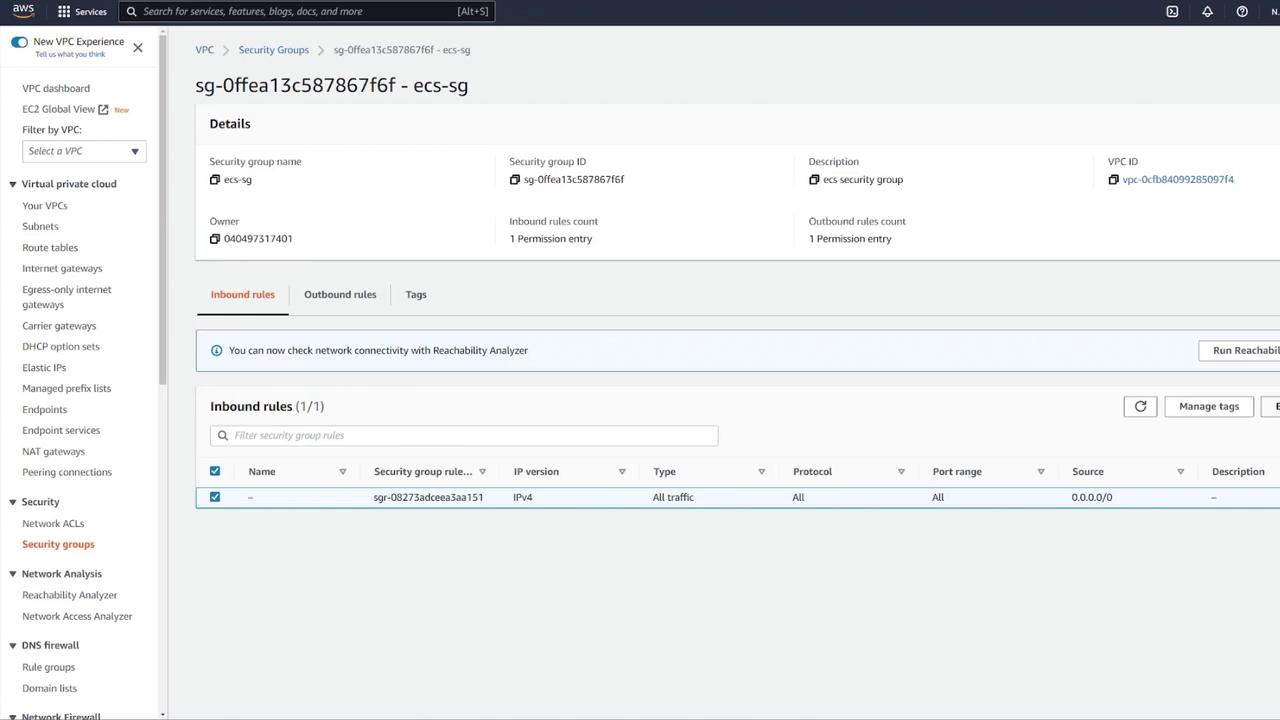
8. Enhancing Security Group Rules
For improved security, update your ECS security group rules:- Instead of allowing all IP addresses on any port, remove the overly permissive rule.
- Add a custom TCP rule on port 3000 with the source set to your load balancer’s security group. This ensures that only traffic routed through the ALB reaches your ECS containers.
In this article, we successfully deployed a multi-container application on Amazon ECS using Fargate. This deployment includes a MongoDB database with persistent EFS storage, an Express-based web API, an Application Load Balancer for efficient traffic distribution, and tightened security through proper security group configurations. For more detailed information on ECS and related services, please refer to the following resources: Happy deploying!