Introducing Variables with a Real-World Example
Previously, we saw an arithmetic operation without context:amount_of_apples for the quantity of apples, and cost_of_apple for the price of one apple. Using these variables makes our code self-explanatory:
amount_of_apples and cost_of_apple store the values 2 and 5, respectively.

Python Variable Naming Conventions
When naming variables in Python, there are specific rules to follow:- A variable name can include uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and an underscore.
- It must begin with a letter or an underscore.
- Python is case-sensitive; for instance,
costOfAppleandCostOfApplerepresent two different variables.
Valid Variable Names:
- amount_of_apples
- cost_of_apple
- _total_cost
- COST_OF_APPLE
- am*unt_0%_ap|les
- c*st_0%_app|e
- 5apples_cost

Updating Variable Values
Variables are mutable, meaning their stored values can change over time. For example, if the price of an apple increases by $2, you can update thecost_of_apple variable accordingly:
Shortcut Operators for Efficient Coding
Shortcut operators are available for most arithmetic operations. They help keep your code clean and reduce redundancy. For example, here is a comparison:| Operation Type | Without Shortcut | With Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple + 2 | cost_of_apple += 2 |
| Subtraction | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple - 2 | cost_of_apple -= 2 |
| Multiplication | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple * 2 | cost_of_apple *= 2 |
| Exponentiation | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple ** 2 | cost_of_apple **= 2 |
| Division | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple / 2 | cost_of_apple /= 2 |
| Floor Division | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple // 2 | cost_of_apple //= 2 |
| Modulus | cost_of_apple = cost_of_apple % 2 | cost_of_apple %= 2 |
Summary of Key Points
- Variables store values under a specific name, making code more readable.
- Valid variable names must start with a letter or underscore and include only letters, digits, or underscores.
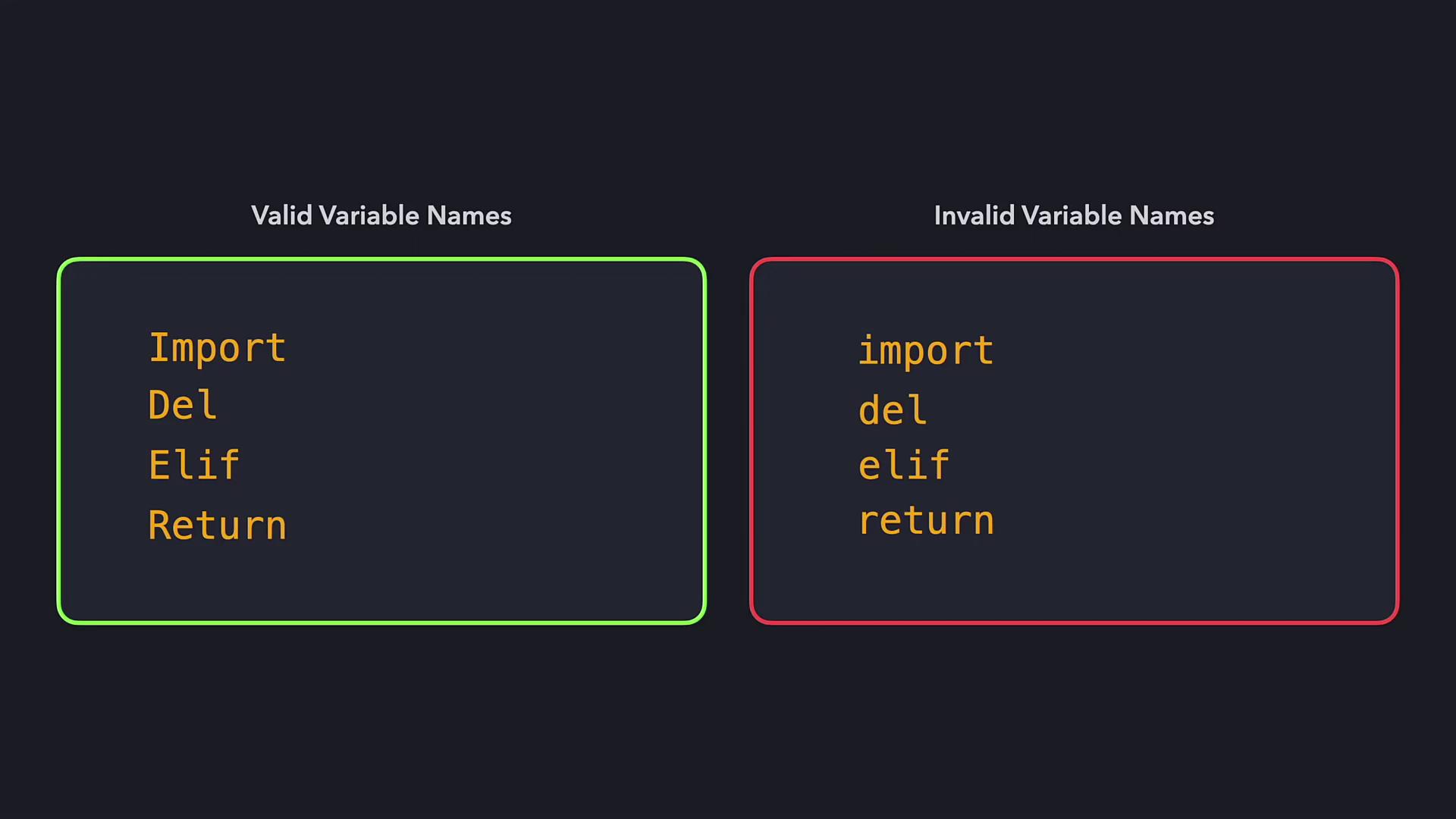
- Variable names should not overlap with Python’s reserved keywords.
- Variables can be reassigned, and shortcut operators simplify the code.
That’s it for this lesson on variables. Now, try the exercises to reinforce your understanding and elevate your Python programming skills.