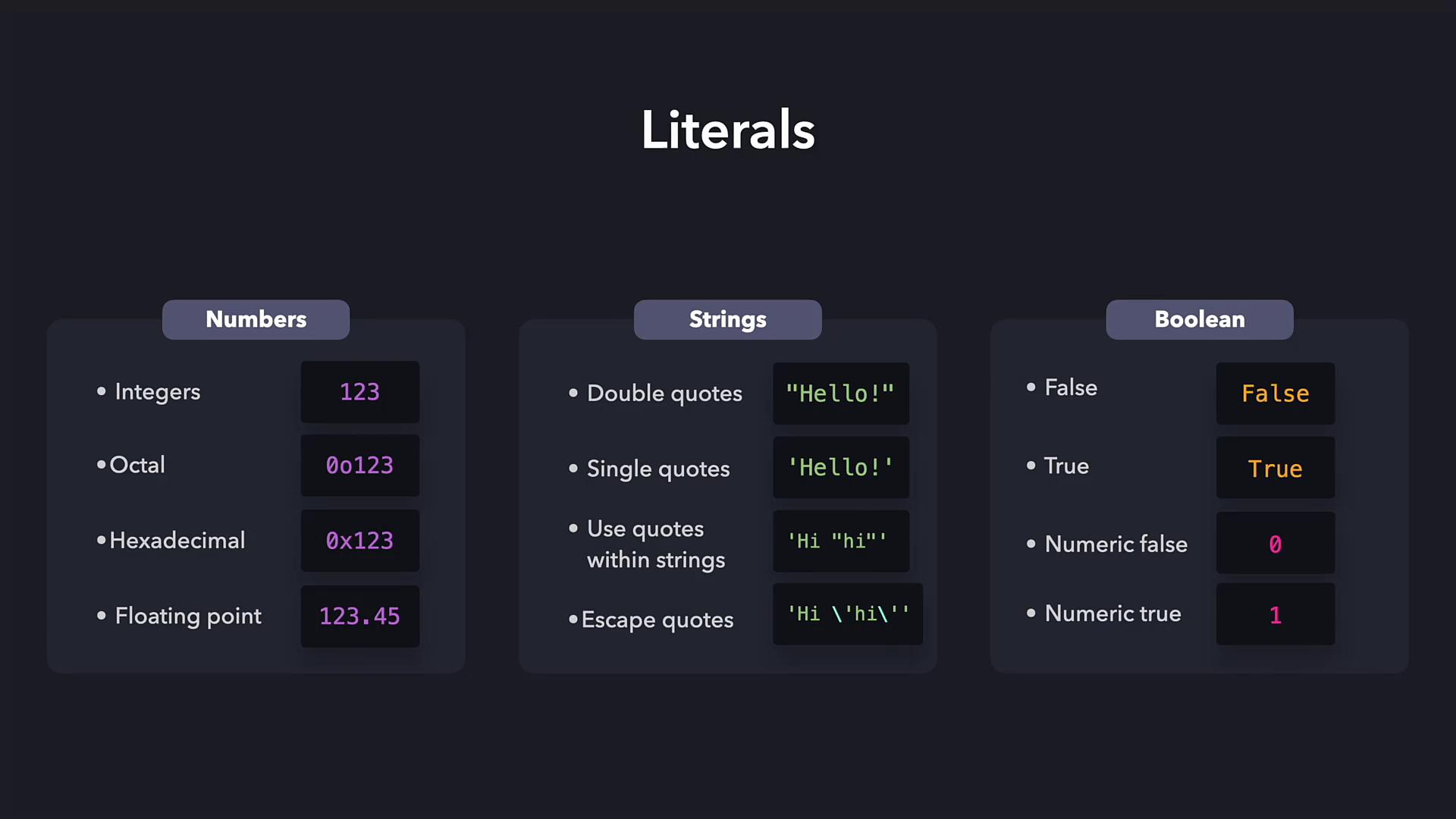
Integer Literals
An integer literal represents a whole number without a fractional part. Examples include 200, 1289901, -90, and 1_000_000. The underscore in numbers such as 1_000_000 improves readability; Python ignores these underscores when evaluating the value.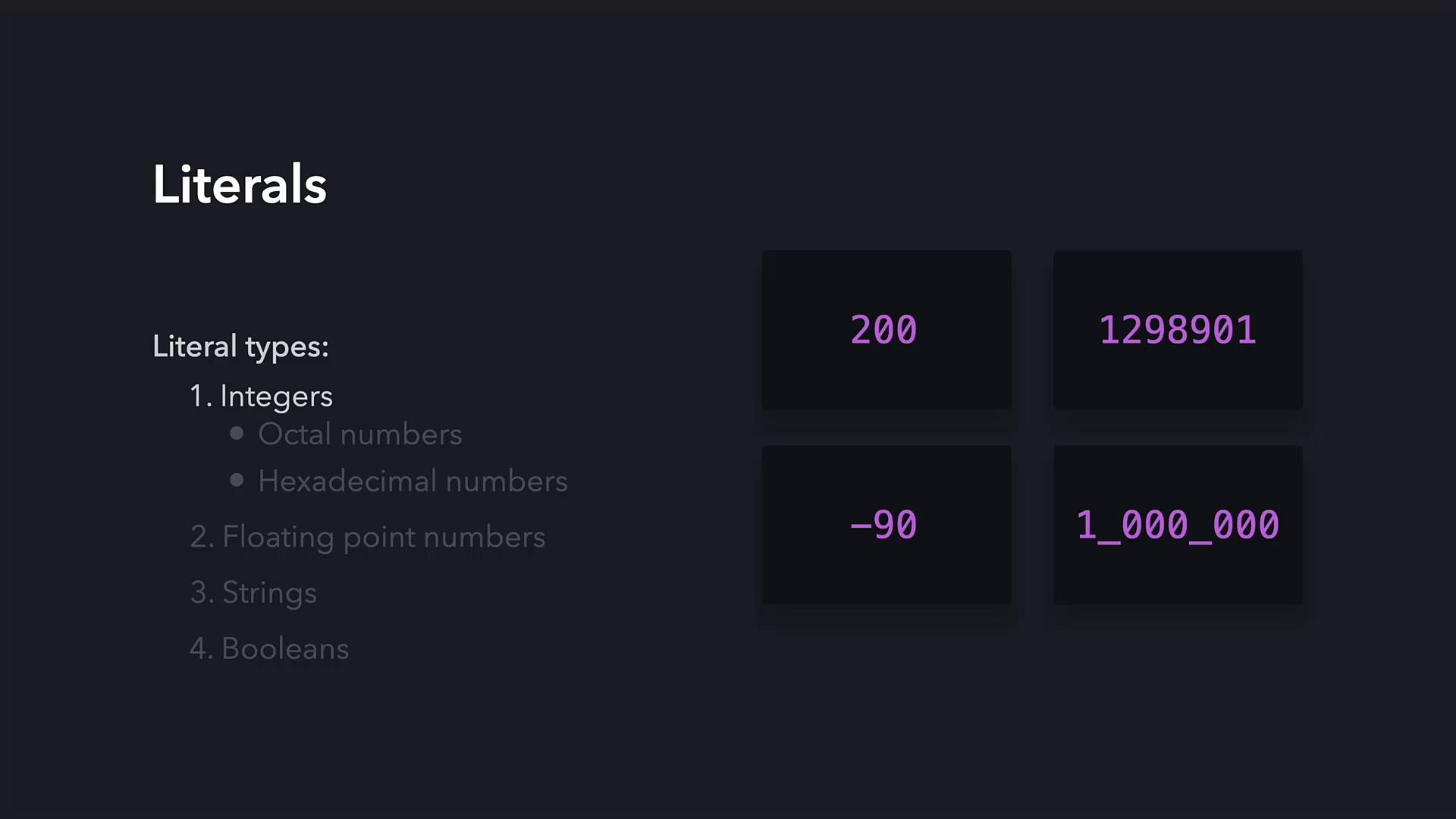
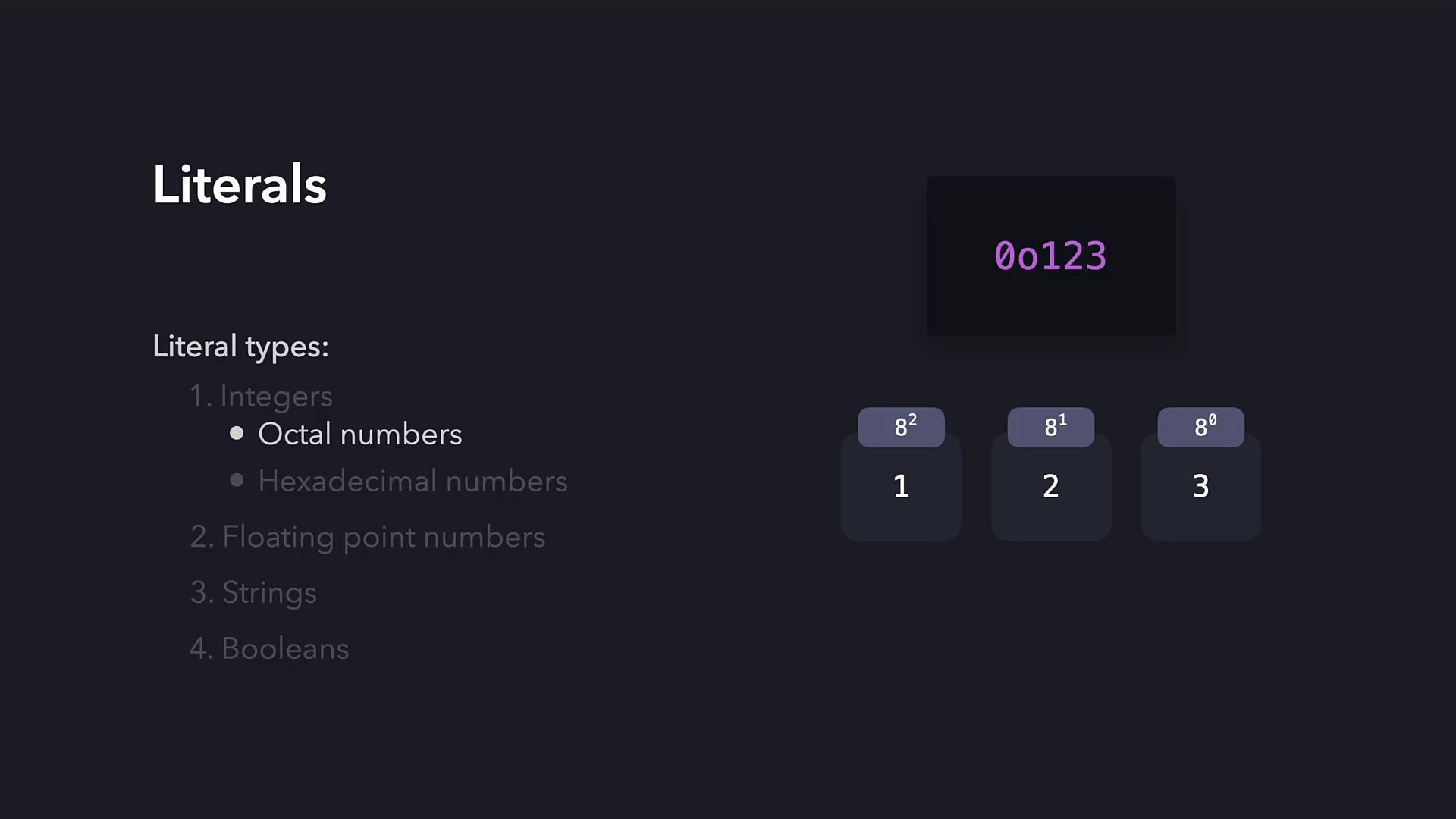
Octal Numbers
Octal numbers in Python are indicated by a leading0o (or simply 0 in older notations). To compute the value of an octal number, each digit is multiplied by 8 raised to the power corresponding to its position (with the rightmost digit at position 0). For instance, with an octal number:
- The weights are calculated as follows:
- 8² = 64
- 8¹ = 8
- 8⁰ = 1
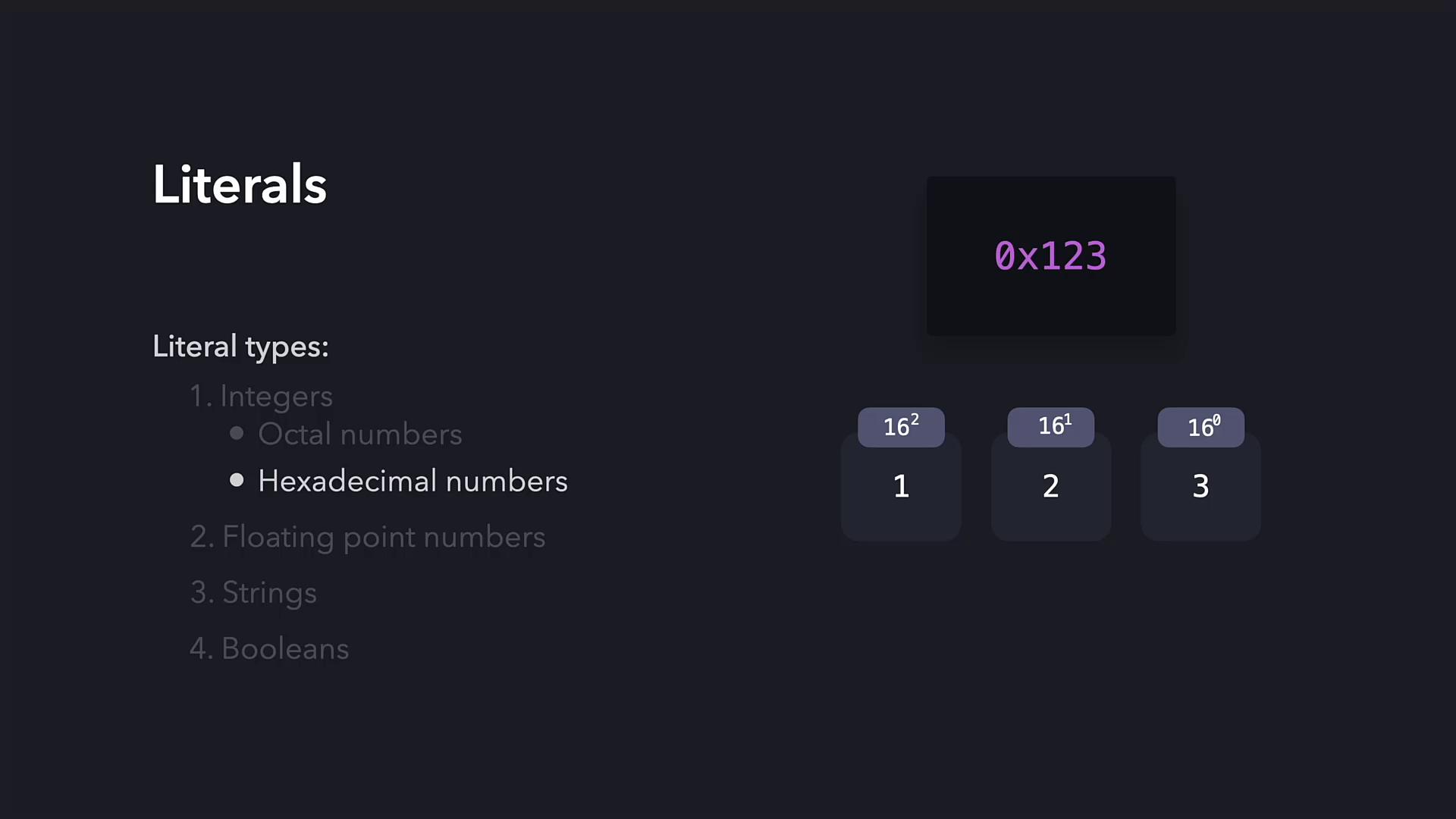
Hexadecimal Numbers
Hexadecimal numbers function similarly to octal numbers but use base 16. They always start with0x. The positional weights are based on powers of 16:
- 16² = 256
- 16¹ = 16
- 16⁰ = 1
0x123:
- Leftmost digit multiplied by 256,
- The next digit by 16, and
- The rightmost digit by 1,
resulting in the calculation:
Floating-Point Numbers
Floating-point literals represent real numbers that include a decimal point. They denote fractional values and can also be expressed using scientific notation (using the letter E) to represent very large or very small numbers efficiently.String Literals
String literals handle textual data in Python. To define a string, enclose the text in either single (') or double (") quotes. This differentiation allows Python to easily distinguish text from other data types.
For example, both of these string definitions are valid:
\):
When working with strings, always choose a quoting style that minimizes the need for escaping characters. This makes your code cleaner and more readable.
Boolean Literals
Boolean literals represent one of two truth values:True or False. In certain contexts, such as when interfacing with external data systems, booleans can also be represented numerically, where 1 indicates True and 0 indicates False.
Summary
Below is a quick summary of Python literals:-
Numbers:
- Integers: Whole numbers that can be expressed in decimal, octal (with a
0oprefix), or hexadecimal (with a0xprefix) formats. - Floating-point: Numbers that contain a decimal point and can also be represented using scientific notation.
- Integers: Whole numbers that can be expressed in decimal, octal (with a
-
Strings:
- Enclosed in single or double quotes.
- Use alternating quotes or escape characters to include quotes within strings.
-
Booleans:
- Represent truth values with
TrueorFalse. - Numerical representations of booleans can also be used in certain contexts.
- Represent truth values with